Process for preparing high purity strontium carbonate
A high-purity strontium carbonate and strontium sulfate technology, applied in the direction of calcium carbonate/strontium/barium, etc., can solve the problems of low production cost of high-purity strontium carbonate, consumption of hydrochloric acid chemical raw materials, and small dissolution of calcium sulfide, etc., to achieve low production cost, The effect of short process route and narrow particle size distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
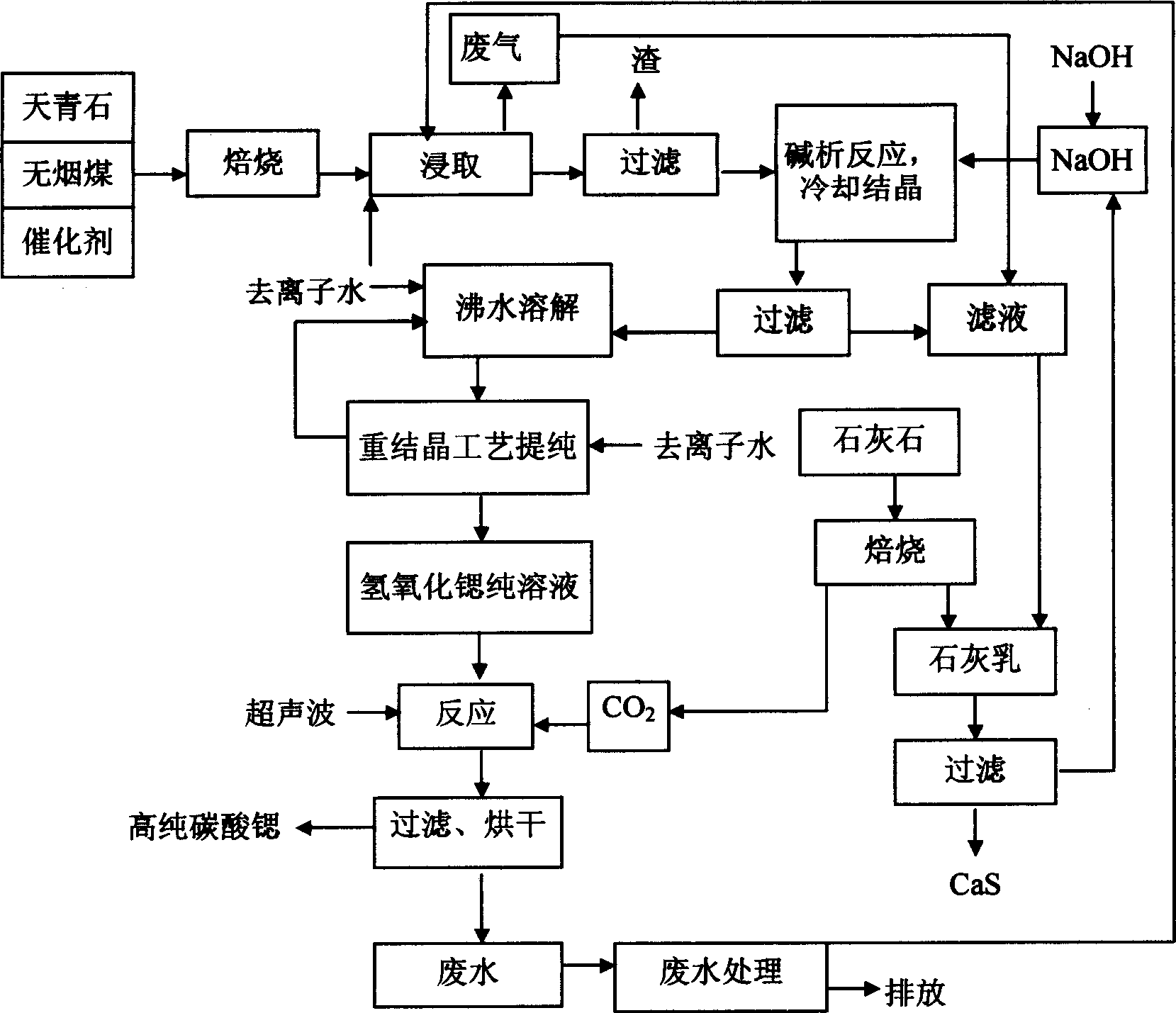
[0033] Embodiment 1: The content is 93.7% lapis lazuli, anthracite, calcium chloride are batched with the weight ratio of 100:60:0.6, and ground to 80~120 meshes, after mixing evenly, roasting at 1000~1200 ℃ for 1~2 Hour. The roasted powder is leached while it is hot, and the leaching temperature is 75-90°C; the dry weight of the filter residue accounts for about 4.5% of the weight of the roasted powder, indicating that 95.5% of the roasted powder is soluble, and the conversion rate of strontium sulfide is high; The strontium leaching solution was kept at constant temperature and analyzed for Sr 2+ concentration, add NaOH in proportion (5-10% in excess), cooling and crystallizing to precipitate strontium hydroxide octahydrate crystals. Strontium hydroxide octahydrate crystals are directly dissolved in hot water and reacted with carbon dioxide. The reaction temperature is 75-85°C, and strontium carbonate powder can be directly obtained with a purity of 97.48% (see Table 1), me...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Dissolve the strontium hydroxide octahydrate crystal obtained in Example 1 in boiling water (100°C) to obtain a saturated solution, cool to 20°C to obtain a recrystallized strontium hydroxide octahydrate crystal, according to the reaction conditions of Example 1 Strontium carbonate was prepared with a purity of 99.24% (see Table 1).
Embodiment 3
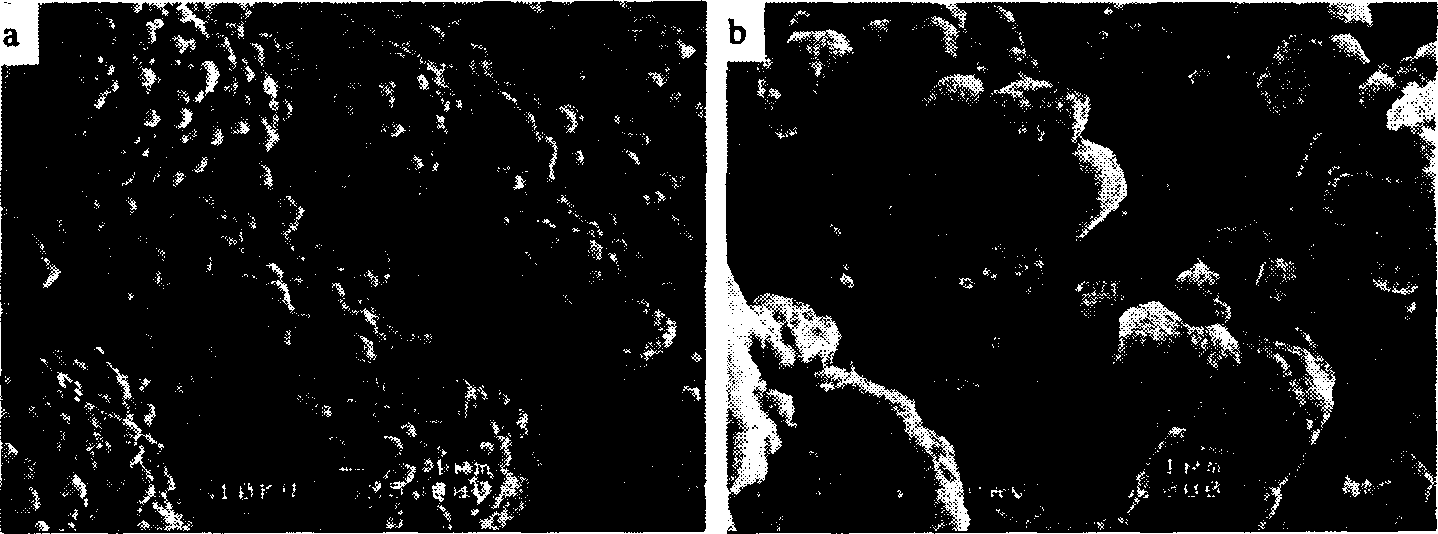
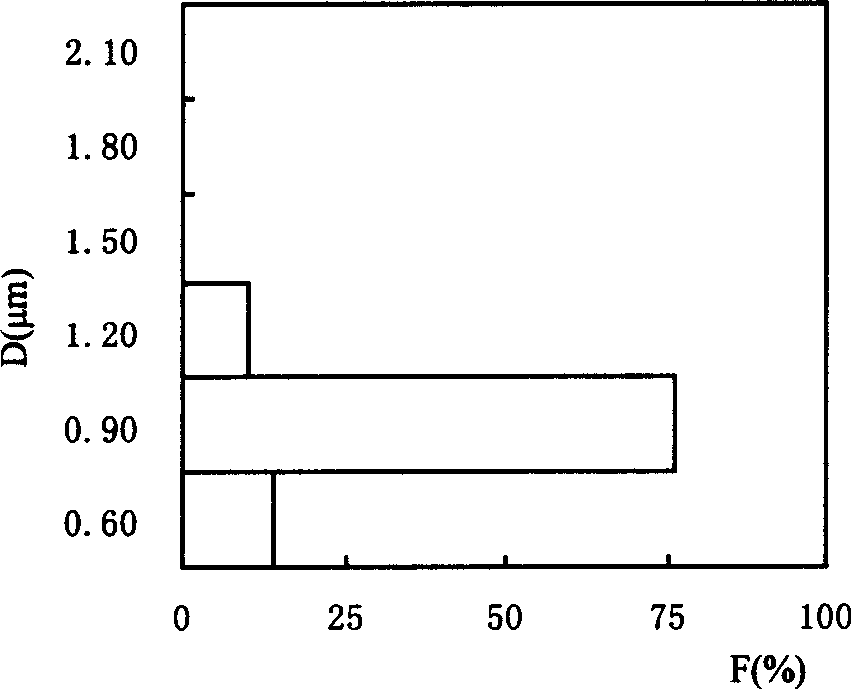
[0035] Example 3: The crystals obtained in Example 2 were recrystallized twice or three times according to the recrystallization process in Example 2, and respectively reacted with carbon dioxide at 75-85°C under the action of an ultrasonic system to obtain strontium carbonate The purities were 99.73% and 99.97% respectively (see Table 1). For the physical and chemical properties of strontium carbonate obtained by secondary recrystallization, see figure 2 (particle size and distribution), image 3 (particle microscopic morphology), Figure 4 (product phase analysis), Figure 5 (product thermal characteristics analysis). From the analysis of the chemical composition and physical and chemical characteristics of the product, it can be seen that the strontium carbonate product obtained by secondary or secondary recrystallization and under the action of ultrasonic waves is superior to the standard strontium carbonate for electronic ceramics in Japan and the United States.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com