Patents
Literature
85 results about "Lazulite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lazulite ((Mg,Fe²⁺)Al₂(PO₄)₂(OH)₂) is a blue, phosphate mineral containing magnesium, iron, and aluminium phosphate. Lazulite forms one endmember of a solid solution series with the darker iron rich scorzalite.
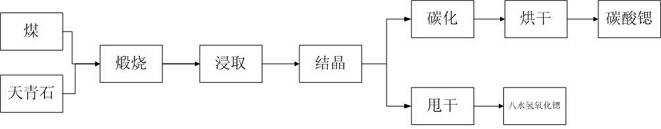
Preparation method of platy strontium carbonate particles
InactiveCN101559964AIncrease profitFully contactedCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesNanostructure manufactureCarbonizationStrontium chloride
The invention provides a preparation method of platy strontium carbonate particles. The steps include using reduced coal dust to roast reduced celestite ore at high temperature and prepare chamotte containing strontium sulfide; leaching the chamotte by hydrothermal to obtain strontium sulfide solution and simultaneously removing calcium, barium and other foreign ions from the strontium-containing solution; then carrying out oxidation treatment on the strontium-containing solution under the action of a catalyst and recovering sulphur side product and obtaining clean strontium solution; and finally preparing the strontium carbonate product with special platy structure by strictly controlling the carbonizing treatment condition of the strontium solution. The platy strontium carbonate product has uniform particles, high purity, and excellent flow property, dispersion property and fusion property with other materials. The preparation method avoids generating sulfureted hydrogen gas in carbonization process, thoroughly gets rid of sulfureted hydrogen pollution in the production process and can simultaneously separate solid sulphur to be beneficial to the strict control over the index of total sulphur in the product.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
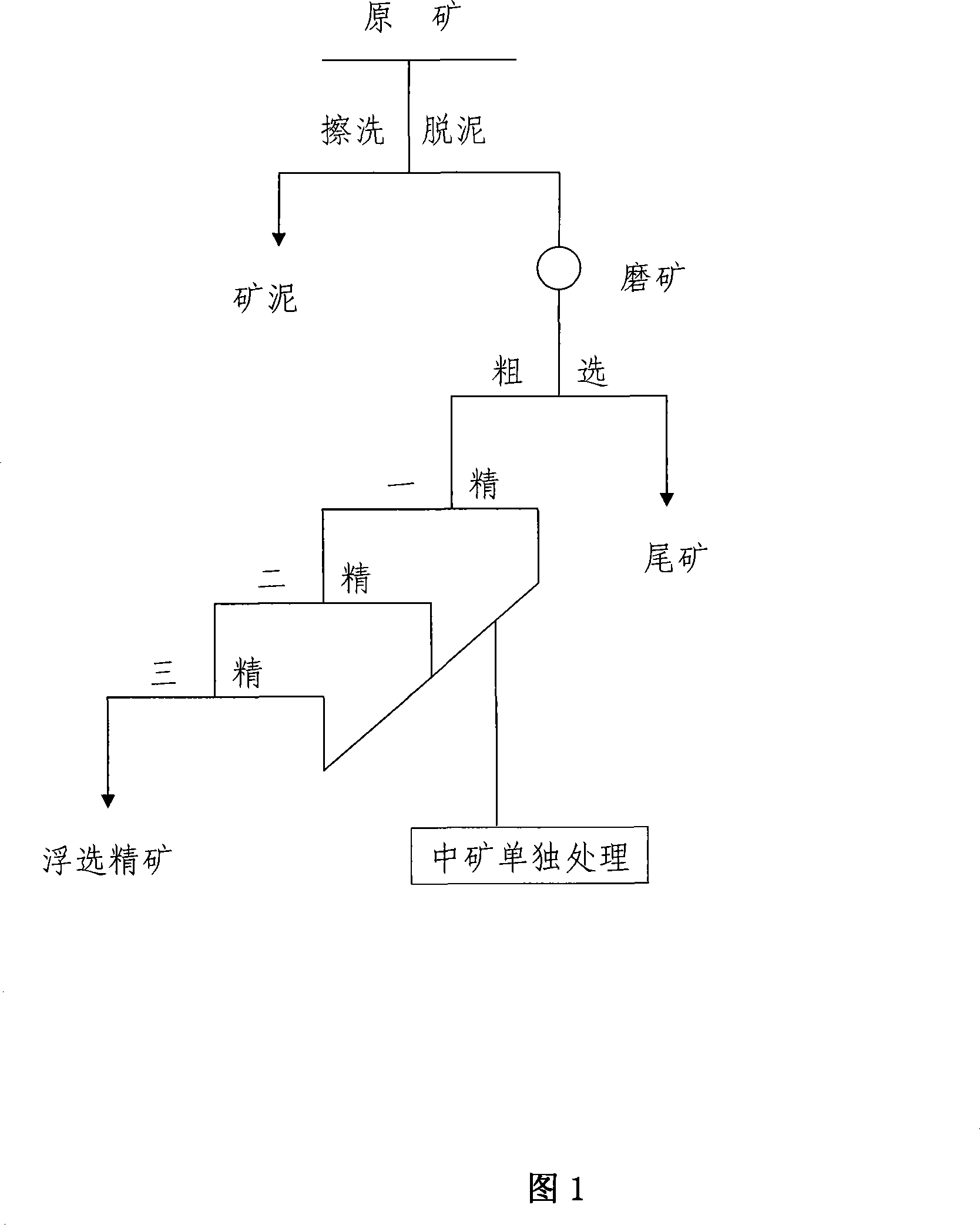
A milling enriched technics for celestine ore
ActiveCN101157066AHigh yieldReduce manufacturing costFlotationProcess efficiency improvementLower gradeLow graded
The invention relates to a beneficiation concentration process for celestite. The invention is characterized in that celestite ore is sent into a scrubbing desliming equipment to perform the desliming after being crushed to be smaller than 6 mm, the scrubbing desliming concentration is 40 to 50 percent, the obtained ore slime is sent into an ore slime pond to be stored, the obtained product after the desliming is delivered into a grinding system to be ground, the grinding concentration is 60 to 70 percent, to lead composite mineral to achieve the dissociation of a fundamental monomer, products in a roughing cell are flotation tailings to be discharged and stacked, the reflotation is performed to roughing froth products for three times, a reflotation froth product is also flotation concentrate for the last time, and the flotation concentrate is the finished product of the flotation concentrate after being concentrated, filtered, and dried; the products in a reflotation cell for each time of middlings are merged and singly treated. The flow is simple, the invention is easy to be realized, the operation and the controlling are easy, the product quality is high, the recovery ratio of the celestite is high, and the invention can be widely applied to the medium and low grade celestite concentration production.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
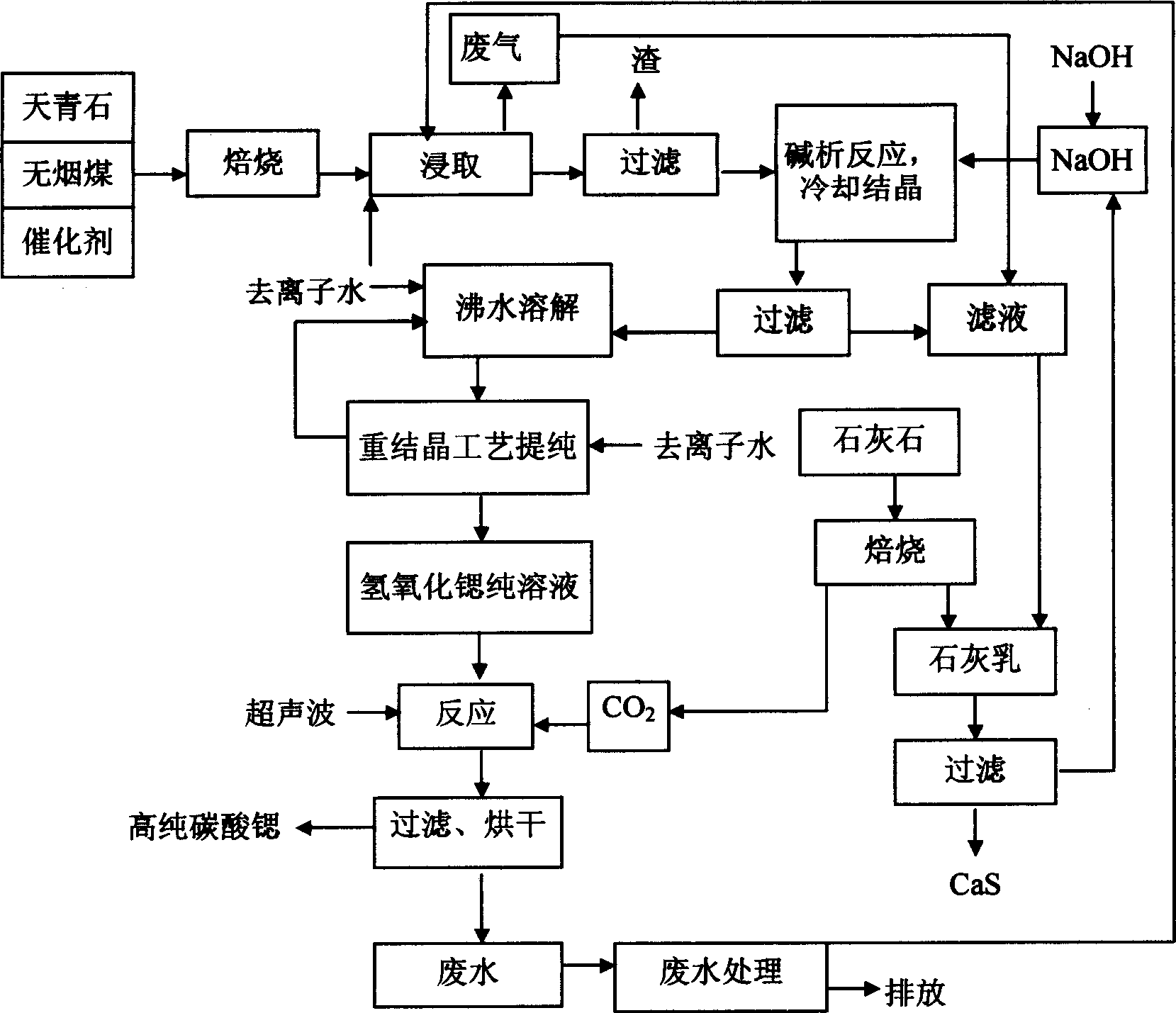
Process for preparing high purity strontium carbonate
InactiveCN1699178AImprove recovery rateImprove one-time yieldCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium sulfideStrontium carbonate
Disclosed is a process for preparing high purity strontium carbonate, which comprises mixing celestite, anthracite coal, calcium chloride as catalyst, high-temperature roasting for deacidizing strontium sulfide, filtering strontium monosulfide through heat leaching, charging sodium-hydroxide and strontium monosulfide to result in alkali analysis reaction, producing strontium hydroxide crystalline body, the purifying strontium hydroxide through recrystallization process, finally reacting pure strontium hydroxide solution with let-in carbon dioxide at the presence of ultrasonic wave action, thus producing high purity strontium carbonate powder, and reacting lime cream with strontium monosulfide to obtain sodium-hydroxide and strontium monosulfide precipitate, wherein sodium-hydroxide can be circulated in the alkali analysis reaction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for producing less-barium fine strontium salts from celestite
ActiveCN102602974ALow bariumLow costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesStrontium carbonateDecomposition
The invention mainly aims to provide a method for producing less-barium fine strontium salts from celestite, and the method is low in cost, which comprises the steps: refining: crushing or grinding the celestite to particles of less than 200 mesh; acid washing: reacting diluted hydrochloric acid with the levigated celestite, and removing a carbonate component in the celestite to obtain high-purity refined celestite; and double decomposition: adding the refined celestite to an ammonium carbonate aqueous solution, uniformly stirring, then reacting in an airtight condition at a reaction pressure of 0.2-0.3MPa and a reaction material temperature of 100-115 DEG C, stopping heating after the reaction is finished, filtering and washing obtained solid to obtain a strontium carbonate crude product, and further refining the strontium carbonate crude product to obtain a product. The method has the advantages that during the double decomposition reaction, when reacting with the celestite, ammonium carbonate only reacts with strontium sulfate in the celestite without reacting with barium sulfate, so that the barium content of the obtained strontium carbonate crude product is very low and lower than 0.05%; and the method is low in production cost and has wide market prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING YUANHE FINE CHEM
Method for preparing strontium carbonate
InactiveCN101318683ASimplify the manufacturing processAvoid emissionsCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing strontium carbonate, comprising the following steps: a. celestite and coal dust are roasted under the condition of a temperature between 850 and 1,000 DEG C; b. rough strontium carbonate is added with water and leached for 2 to 3 times, with 0.5 to 1 hour for each time, and then clarified; c. CO2 in industrial waste gas enters into a thionizer for desulfurization treatment; d. a clear leaching solution in the step b enters into a carbonizer, and the CO2 after the treatment in the step c enters into the carbonizer simultaneously for carbonization reaction; e. strontium carbonate serum obtained in the step d is added with alkali for desulfurization and dehydration, and strontium cakes are obtained; and f. deferrization of the strontium cakes is performed through a magnetic roller. The method not only saves the equipment required for manufacturing the CO2 but also greatly saves the human and material resources. More important, the method changes the waste into the valuable, thereby not only reducing the production cost but also simultaneously avoiding exhaust emission of other chemical enterprises and integrally improving the living environment of people.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG ZHENGDING JINSHI CHEM
Method for preparing strontium carbonate
InactiveCN1394809ATo achieve the purpose of removing bariumSimple processCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateSalt solution
The preparation method of strontium carbonate includes the following steps: pulverizing celestine in which the strontium carbonate content is 30-95%, making it react with soluble carbonate to obtain crude strontium carbonate, adding barium-removing agent to inhibit the conversion of barium sulfate into barium carbonate, then making the crude strontium carbonate react with acidifying reagent to obtain soluble strontium salt solution, removing impurity and making the strontium salt solution react with carbonization reagent to obtain the invented strontium carbonate.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Comprehensive utilization technique for hamartite and celestite paragenic ore
InactiveCN101157992AImprove recycling rateRaise the gradeProcess efficiency improvementSlagRare earth
The invention relates to a technique to comprehensively utilizing an intergrown ore of bastnaesite and celestite. The detailed steps of the technique comprises: firstly the raw material of intergrown ore of bastnaesite and celstite are crashed until the -200 orders taking up 60-90%; secondly proper collecting agent and alkalis inhibitor are added, and compound concentrate is obtained; thirdly under the temperature of 500-600 DEG C, the concentrate is roasted for 1.5 to 2.5 hours so as to obtain calcine; finally, the calcine is leached with concentrated hydrochloric acid in normal temperature for 0.5 to 3.0 hours, the leaching slag is celestite and the leaching solution is blended rare earth chloride solution. The invention can greatly increase the recycle rate of the rare earth and celestite and the grade of celestite concentrate, meet the further processing requirements of celestite; besides, the separation of the blended concentrate integrates closely with the existing rare earth production, no extra investment of equipments is needed, the existing roasting and leaching devices is expanded; furthermore, the invention simplifies gravity separation and flotation operation, which is good for the stability of the production.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Method for preparing high-quality strontium carbonate
InactiveCN101070177AReduce sulfur contentImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The invention offers a new kind of method producing strontium carbonate using lazurite mineral as raw material. Mix lazurite breeze with reduced iron powders in certain proportion to get black ash, dip black ash in water of opposite flow and get strontium carbonate solution; regard calcined soda as carburizer, make them reactivate at temperature of 90-100deg.C under mixing to form slurry including deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron, and get deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron through separating solid and liquid, absterge strontium carbonate with water of opposite flow for 3-5 times, dry it and get product of strontium carbonate of high quality; Mother liquor absterging strontium carbonate for the first time mixes with centrifugal mother liquor of slurry of strontium carbonate and the mixed solution is vaporized by cold boiler which regards heat transfer oil as medium, get byproduct of sodium sulfide of low iron. The producing craft of the invention is simple, the procedure is short with low cost, the investment of equipment is small, quality of main product and byproduct is high, it has a good economical effect.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite mineral crystal capable of improving water quality, strengthening immunity and facilitating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106219720AIncrease surface areaImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by substance additionDiseaseWater quality
The invention discloses a composite mineral crystal capable of improving water quality, strengthening immunity and facilitating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The composite mineral crystal is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10 to 15 parts of medical stone, 5 to 10 parts of wooden fish stone, 5 to 10 parts of tourmaline, 30 to 55 parts of activated zeolite, 5 to 10 parts of celestite and 15 to 40 parts of kaolin. Meanwhile, the invention provides a preparation method of the composite mineral crystal. The surface area of the composite mineral crystal is increased by using supplementary strontium element of the added celestite and a secondary honeycomb wrapping burning technology, and the mineralization speed and effect are greatly improved, so that the precipitation of trace elements, particularly the precipitation of the strontium element, is more abundant, heavy metals are absorbed, and the composite mineral crystal has the effects of promoting metabolism, strengthening immunity, improving water quality and facilitating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:刘乙霄
X-ray fluorescence spectrometry method for simultaneously analyzing fluorspar, barite and celestite
InactiveCN108051468AReduce consumptionPromote development and utilizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLithium metaborateRare earth
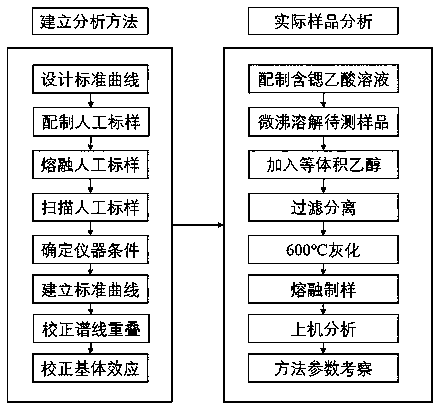
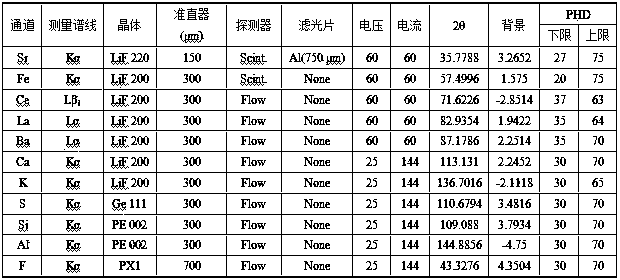
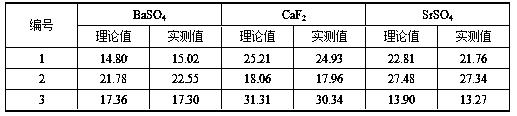
The invention discloses an X-ray fluorescence spectrometry method for simultaneously analyzing fluorspar, barite and celestite in ores quantitatively. The X-ray fluorescence spectrometry method comprises the following specific processes: preparing an artificial standard substance by mixing a barite standard substance, a fluorite standard substance, rare earth ore standard substance, strontium sulfate and strontium carbonate, fusing the artificial standard substance by using a mixed fusing agent (the ratio of lithium tetraborate to lithium metaborate is 12:22), scanning obtained standard samples to determine an instrument condition, correcting a matrix effect, and then establishing a standard curve; treating a sample to be tested by using a strontium-containing acetic acid solution, filtering, separating an interferent, ashing a precipitate and filter paper, then adding the mixed fusing agent (the ratio of lithium tetraborate to lithium metaborate is 12:22) for fusing, and analyzing according to the standard curve. An X-ray fluorescence spectrometer is selected as an analytical instrument, pretreatment operation is simplified, and simultaneous quantitative analysis of three components, namely the fluorite, the barite and the celestite, in the ore is achieved; the X-ray fluorescence spectrometry method is suitable for analyzing the single ore or the ore containing the fluorite, the barite and the celestite.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Preparation method of adsorbent for wastewater treatment
InactiveCN109759025ALarge specific surface areaHigh catalytic activityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsTreatment effectSorbent
Owner:南京思宇环保科技有限公司
Beneficiation method for comprehensively recycling strontium mineral from rare earth tailings
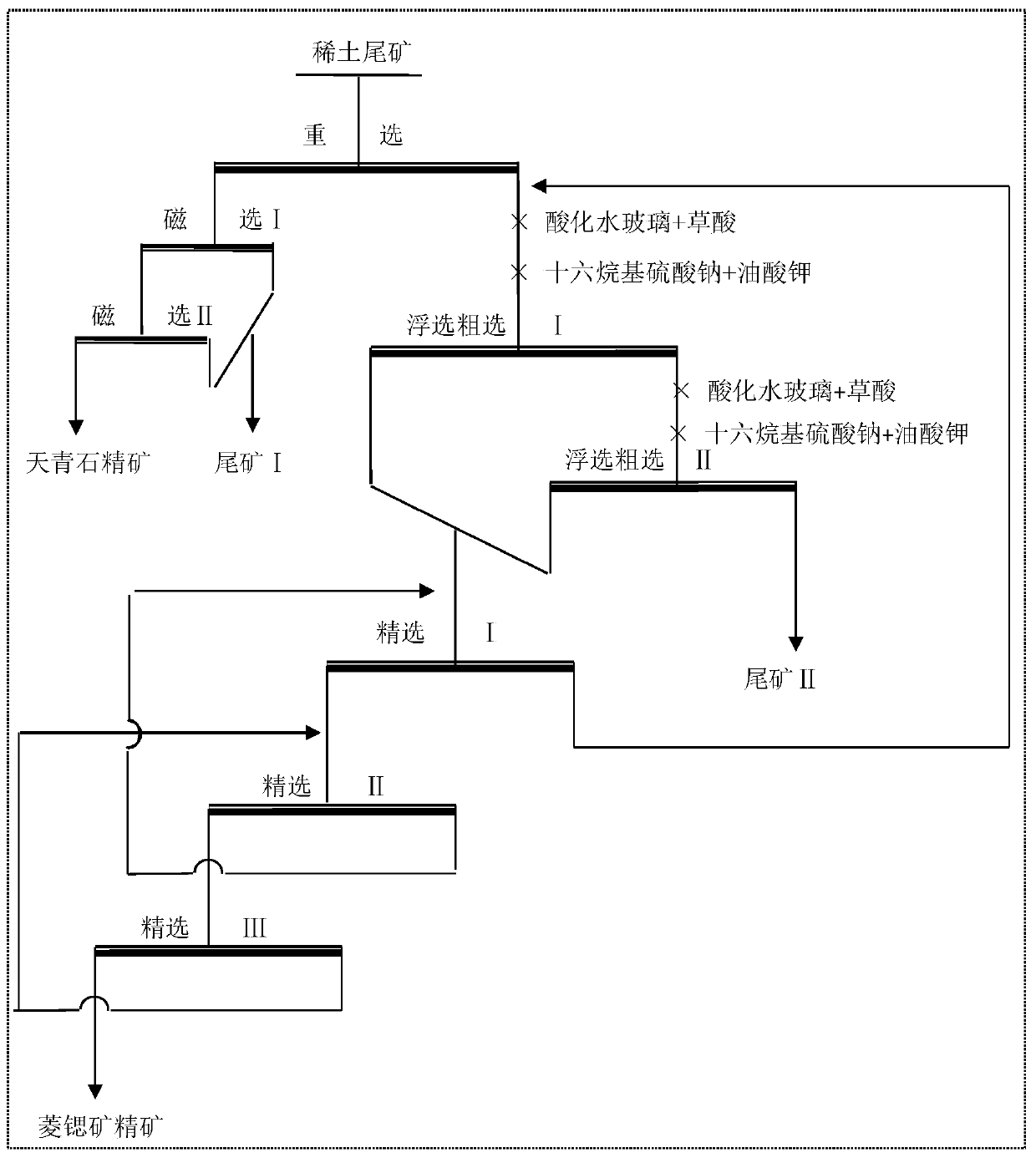
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for comprehensively recycling a strontium mineral from rare earth tailings and relates to a beneficiation method for the rare earth tailings containing celestite and strontianite. The beneficiation method comprises the following steps that (1) heavy minerals in the rare earth tailings are screened out through gravity concentration, so that gravity concentrate is obtained; (2) rare earth, iron and other magnetic minerals in the gravity concentrate in the step (1) are attracted out through strong magnetic separation, so that celestite concentrate isobtained; (3) the strontianite mineral in the gravity tailings in the step (1) is floated out through flotation, so that strontianite concentrate is obtained. The beneficiation method for comprehensively recycling the strontium mineral from the rare earth tailings has the beneficial effects of remarkably recycling the strontium mineral from the rare earth beneficiation tailings, improving the comprehensive utilization value of resources and greatly lowering the discharge amount of tailings.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
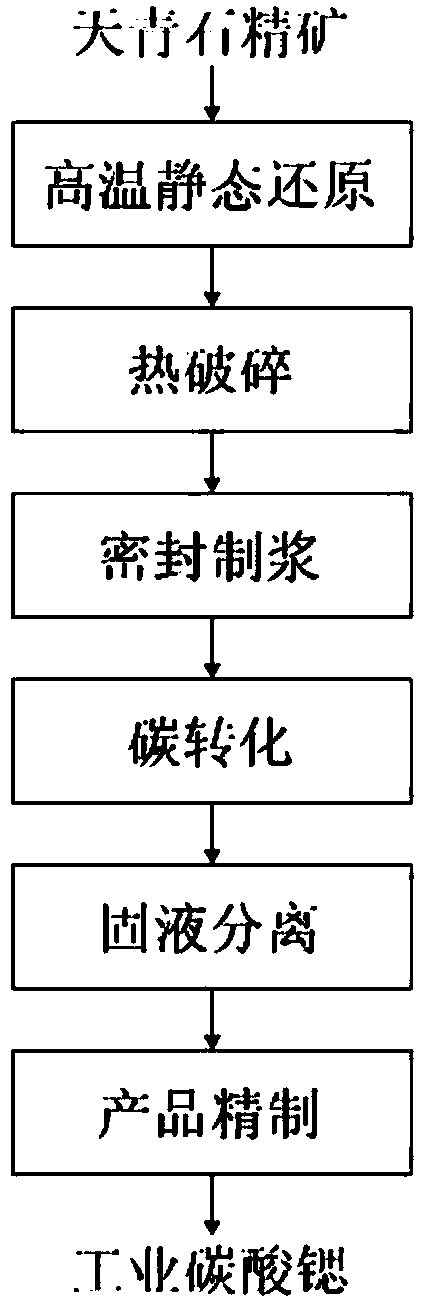
Method for synthesizing strontium carbonate from celestite by high-temperature static reduction-pressurization conversion
InactiveCN104192882AImprove solubilityQuick responseCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesFiltrationReaction rate
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing strontium carbonate from celestite by high-temperature static reduction-pressurization conversion. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing celestite concentrate and carbon into carbonous pellets, and carrying out reduction roasting in a rotary hearth furnace; 2) when the roasted product is cooled to 200-500 DEG C in a reducing atmosphere, crushing; 3) immediately introducing the crushing product into a high-pressure autoclave containing a conversion solution, immediately sealing to prepare the solution, and starting the conversion reaction when the temperature of the high-pressure autoclave reaches 50-150 DEG C; 4) carrying out solid-liquid separation on the converted ore slurry, sufficiently washing the filtration residue to obtain crude strontium carbonate, and sending the filtrate into an ammonia recovery system to perform ammonia steaming recovery so as to regenerate ammonium carbonate; and 5) carrying out impurity purification on the crude strontium carbonate to obtain high-purity strontium carbonate, sufficiently washing, drying, bagging, sealing and storing. The method solves the problem of hydrogen sulfide pollution, and enhances the reaction rate.
Owner:深圳市捷鑫资产管理有限公司
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN106984330AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersWater contaminantsUltrasound - actionLithium hypochlorite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst and belongs to the technical fields of environment protection and chemical engineering catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking porous materials attapulgite, diopside, talc, trona, aluminum hydroxide and celestite as a carrier, after chambering and modifying the carrier through lithium hypochlorite and di(acetylacetone) beryllium, adding a surfactant methyl trioctyl ammonium chloride for surface activating treatment under the action of ultrasonic waves; then performing a hydrothermal reaction on the ultrasonic surface activated carrier in a hydrothermal reaction kettle with a compound mineralizer borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic active auxiliary agent precursors of tri(3-trifluoroacetyl-D-camphor) praseodymium (III), tricyclopentadiene promethium, terbium triacetate hydrate and holmium oxalate decahydrate rare earth metal organic compounds catalytic active central compound precursor common traditional metal organic compounds of ferrous fumarate and nickel citrate, and noble metal compounds of potassium argentite dithiocyanide (I) and a terpyridyl ruthenium chloride hexahydrate under the action of an emulsifier trimethylaminoglycerol glycerol stearate; and after drying a reaction product to remove water, firing the reaction product in a muffle furnace at a certain temperature to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
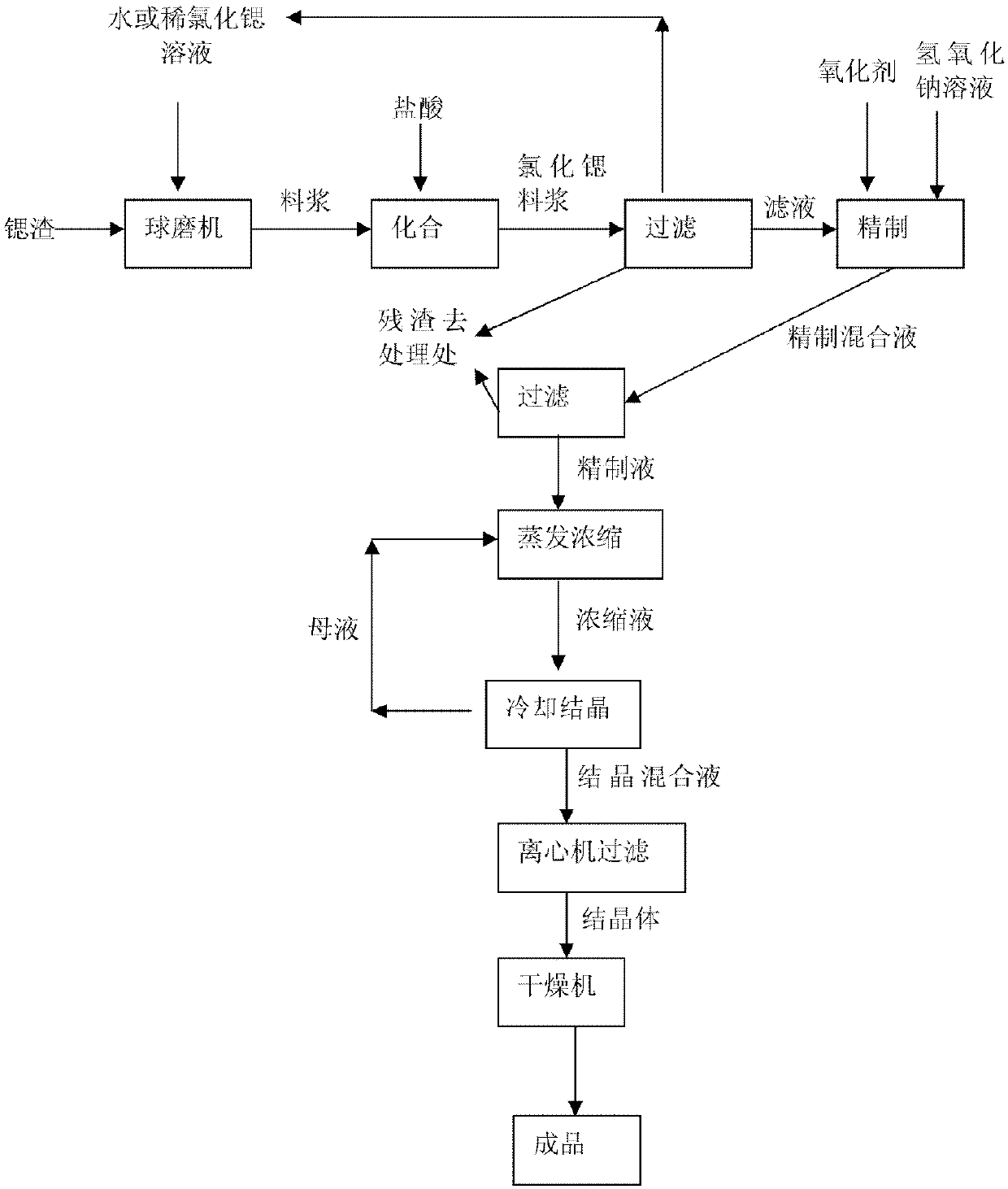
Method for producing strontium chloride by means of strontium slag, and strontium chloride prepared by using method
ActiveCN107673389AImprove qualityLow costCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesStrontium chloride hexahydrateSlag
The invention belongs to the field of chemical production, and discloses a method for producing strontium chloride by means of strontium slag, and the strontium chloride prepared by using the method.The invention provides the method for producing the strontium chloride by means of the strontium slag, and the strontium chloride prepared by using the method. The method for producing the strontium chloride by means of the strontium slag comprises the following steps: weighing 100-200kg of celestite and 50-250kg of feed coal, putting the weighed raw materials into a rotary kiln, carrying out reduction roasting under the high temperature condition, and grinding the strontium slag into slurry by means of a ball mill; adding hydrochloric acid into the slurry until solid particles in the slurry are no longer dissolved; filtering to remove residues, and refining filtrate; crystallizing, and filtering and washing crystals with a centrifugal machine to obtain strontium chloride hexahydrate. After the method is adopted, the quality of the strontium chloride is improved, the production efficiency is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:UPCHEM CHINA
Method for preparing nano strontium carbonate
ActiveCN106115760ASimple preparation stepsReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologyStrontium carbonatesCarbanionImpurity
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano strontium carbonate and belongs to the technical field of strontium carbonate preparation. Celestite serves as the raw material and is smashed and then dissolved with an excessive amount of diluted sulphuric acid to move calcium carbonate therein, then strontium sulfate in the celestite is dissolved with diluted hydrochloric acid, filtering is conducted to remove insoluble substances like barium sulfate, then the obtained strontium chloride solution is mixed with automatically cultured microorganism colonies on the surface of the celestite, and organic matter, with negative charges, on the surface of microorganism cell surfaces is chelated with strontium ions in the solution; urea serves as the carbon source of microorganisms, the urea is continuously decomposed so that the concentration of carbanions in the solution around the microorganisms can be increased continuously, accordingly the concentration of part of carbanions and strontium ions in the solution is increased, the carbanions and the strontium ions are combined into strontium carbonate crystal precipitate, and then the precipitate is filtered and dried to obtain the nano strontium carbonate. The method has the advantages that preparation steps are simple, the impurity content of the obtained product is reduced by 70-80%, and activity is improved by 25-30%.
Owner:重庆庆龙新材料科技有限公司
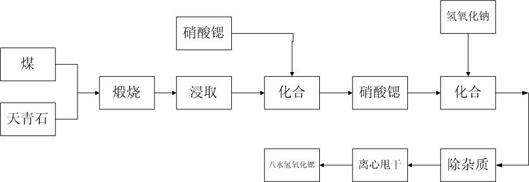
Method for preparing strontium hydroxide octahydrate granular crystals
InactiveCN102515235AReduce consumptionAvoid emissionsCalcium/strontium/barium oxides/hydroxidesStrontium carbonateStrontium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing strontium hydroxide octahydrate granular crystals, which includes steps: forging celestine and coal before leaching, obtaining crude strontium hydroxide octahydrate by chemical combination of the solution and sodium hydroxide, and recrystalizing the crude strontium hydroxide octahydrate at a certain temperature to obtain high-purity strontium hydroxide octahydrate granular crystals. Particles with diameter larger than 1000 micrometers account for more than 55% of the strontium hydroxide octahydrate granular crystals prepared by recrystalizing at temperature ranging from 72 DEG C to74 DEG C, the prepared strontium hydroxide octahydrate granular crystals are high in purity and low in impurity content. The conversion rate of Sr2+ in the celestine into strontium hydroxide is 100%, and economic benefit of the process is improved since the Sr2+ is converted into the strontium hydroxide to the greatest extent and the selling price of the strontium hydroxide is higher than that of the strontium carbonate.
Owner:HEBEI XINJI CHEM GRP
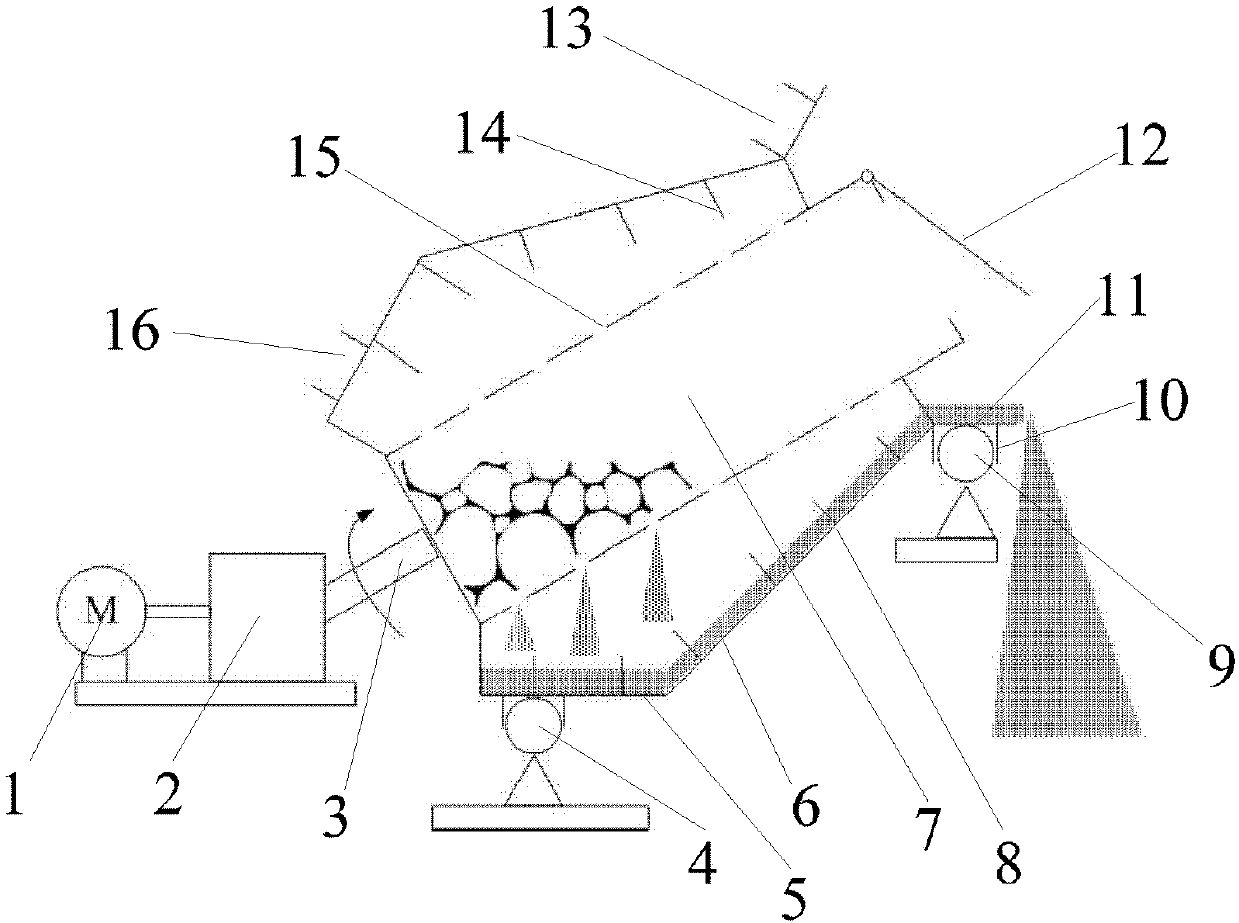
Agglomeration process of -200 mesh celestite concentrate
The invention relates the pulverulent material agglomerated technology, which is celestine agglomerated technology. The technological process of celestine finished ore agglomerated technology comprises the following steps: -200 mesh celestine finished ore and binding agent or addition agent - mixing ingredient homogeneously - preparing mother pellet - adding material and water - mother pellet growing - continuing rolling - compressing the pellet - drying and obtaining the celestine finished ore pellet. Because the invention adapts the method of pellet ore roll forming, the inner structure of the pellet is fine and close, and the materials, which hit against the pellet stick on the surface of the pellet to make the ball grow by layer. Merry-go-round agglomerated machine has the advantages of simple apparatus, light weight, automatic grading function and preparing the pelet epigranularly. The invention uses the addition agent to improve the incidence intensity of the pellet to 8.2 times per 0.5m.
Owner:QINGHAI JINRUI MINERAL DEV
Process for producing barium sulfate byproduct in process of removing barium from yellow water
InactiveCN102502750ASuppress generationImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesPolyacrylamideCoal
The invention relates to a process for producing a barium sulfate byproduct in the process of removing barium from yellow water. The process comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining the yellow water, namely calcining celestite and reducing coal to obtain black ash, and leaching the black ash by using water to obtain an aqueous solution of strontium sulfide, namely the yellow water; and performing natural sedimentation on the yellow water at the temperature of between 80 and 85 DEG C to remove impurities, namely acid-insoluble substances and calcium ions so as to obtain clear yellow water; (2) performing barium removal reaction, namely adding industrial dilute sulfuric acid into the clear yellow water, and performing barium removal reaction; and continuously stirring for 2 to 5 hours to convert barium ions into barium sulfate; (3) adding a flocculating agent, namely a polyacrylamide solution into the yellow water subjected to barium removal reaction, stirring, and filtering to obtain a filter cake and filtrate yellow water; and (4) carbonizing the filtrate yellow water by the conventional process to produce strontium carbonate; and washing the filter cake for one to two times, drying, and grinding to obtain the barium sulfate byproduct. The process is simple and low in cost, the clarity of the yellow water can be effectively improved, the content of the barium ions in the yellow water is reduced, and the environment-friendly barium sulfate byproduct is obtained.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
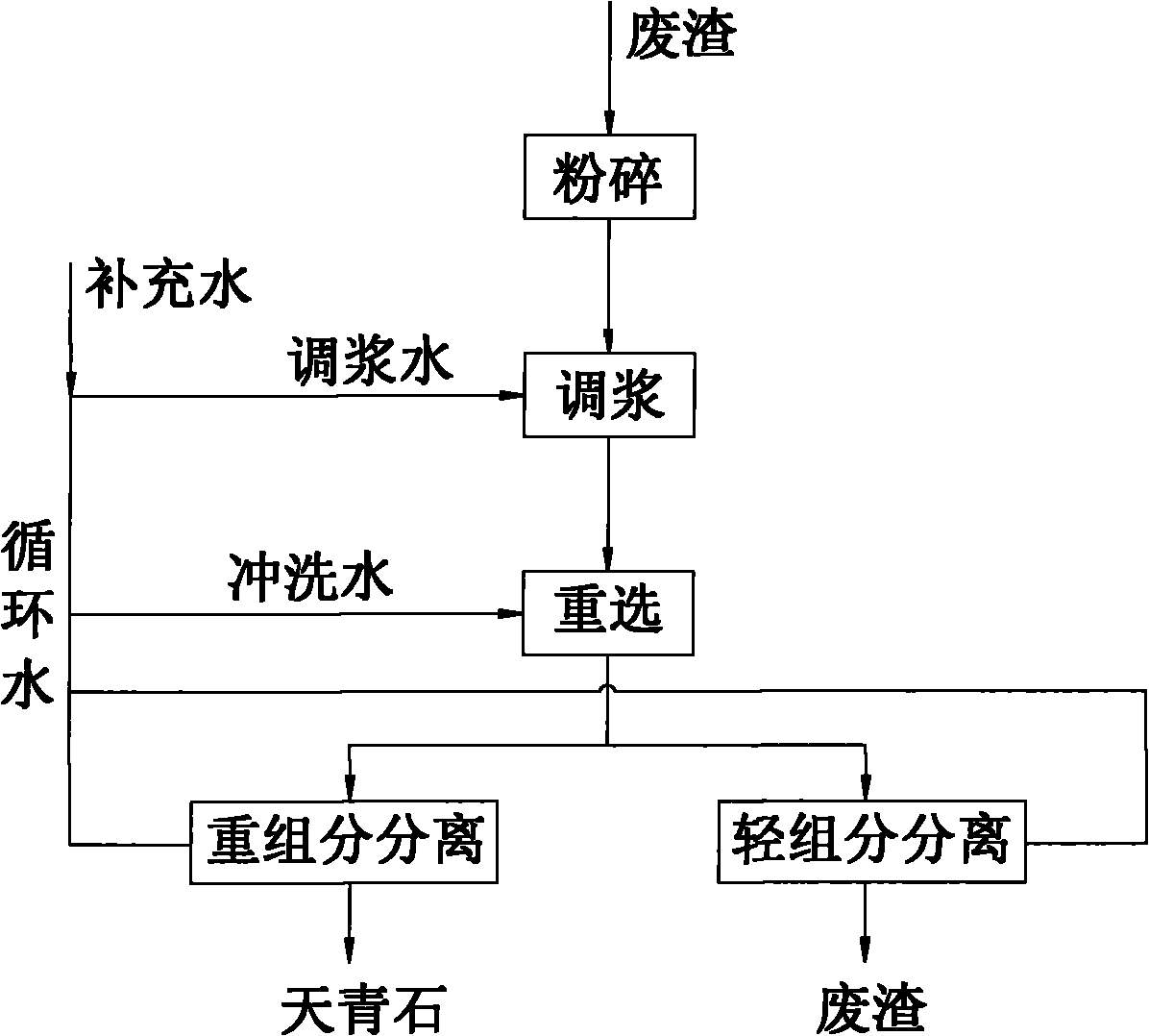
Method for recovering celestite from waste residue in strontium carbonate production by celestite back salt method
ActiveCN102060317ARaise the gradeHigh yieldSolid waste disposalCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesStrontium carbonateResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for recovering celestite from waste residue in strontium carbonate production by celestite back salt method, comprising the following steps: 1) crashing: crashing the waste residue to prepare waste residue powder; 2) sizing: mixing the waste residue powder with water to form residue slurry with a proper concentration; 3) reelecting: selecting unreacted celestite in the residue slurry by a shaker; and 4) dehydrating: dehydrating separated heavy and light components, wherein the heavy component is the celestite. In the invention, the unreacted celestite during the process of producing the strontium carbonate is recovered with a reelection method, thereby improving the resource utilization of strontium ore; and the method is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:重庆新申世纪新材料科技有限公司
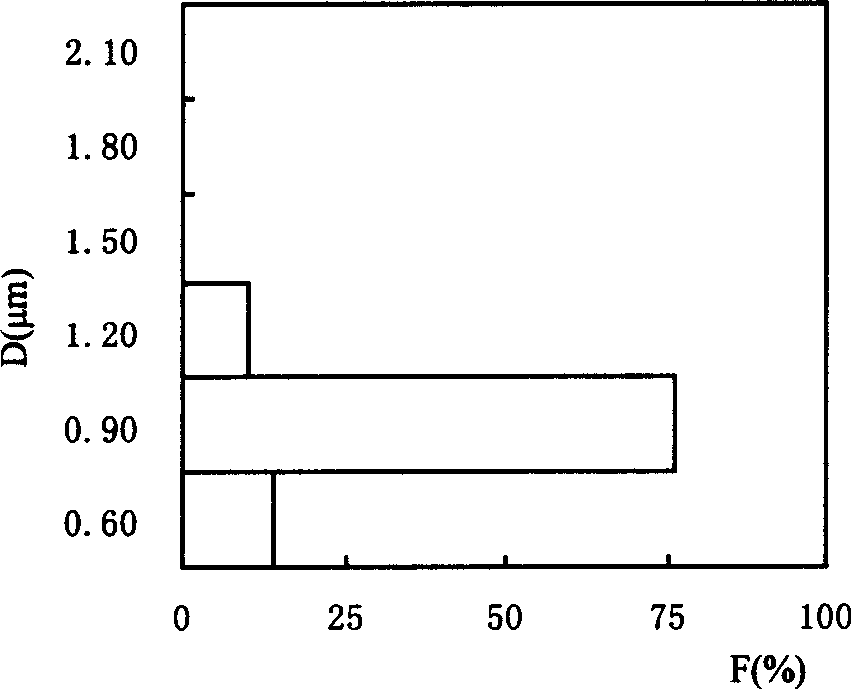
Preparation method of spherical nano-strontium carbonate
InactiveCN110451544AGood spherical effectUniform particlesStrontium carbonatesNanotechnologyStrontium carbonateHypergravity
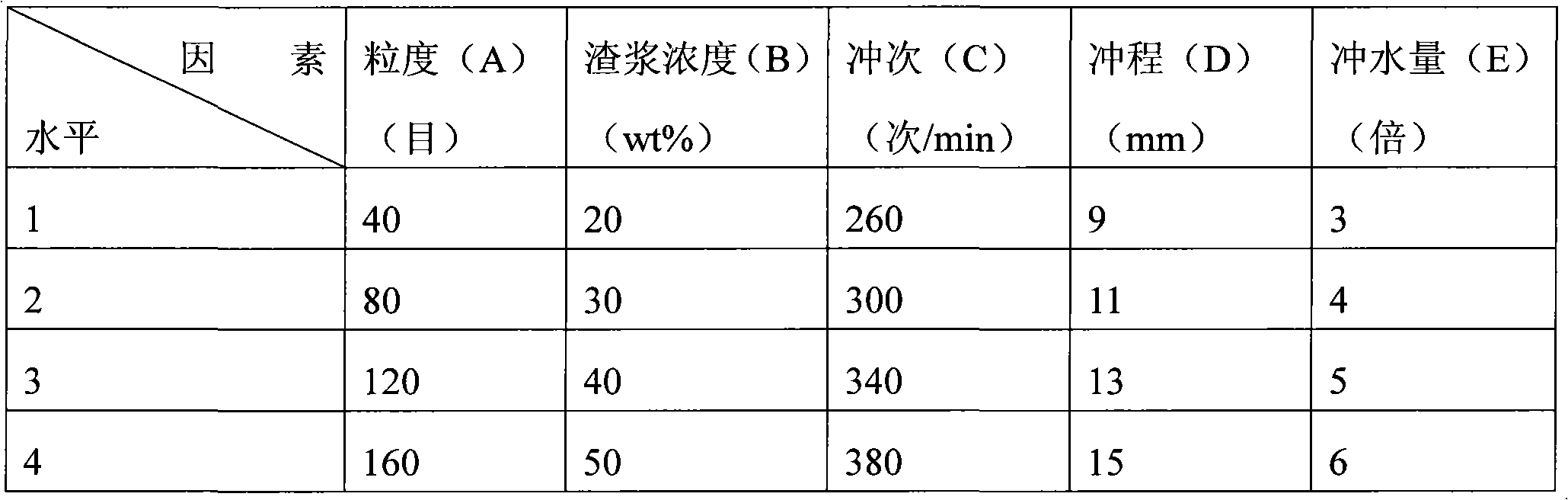
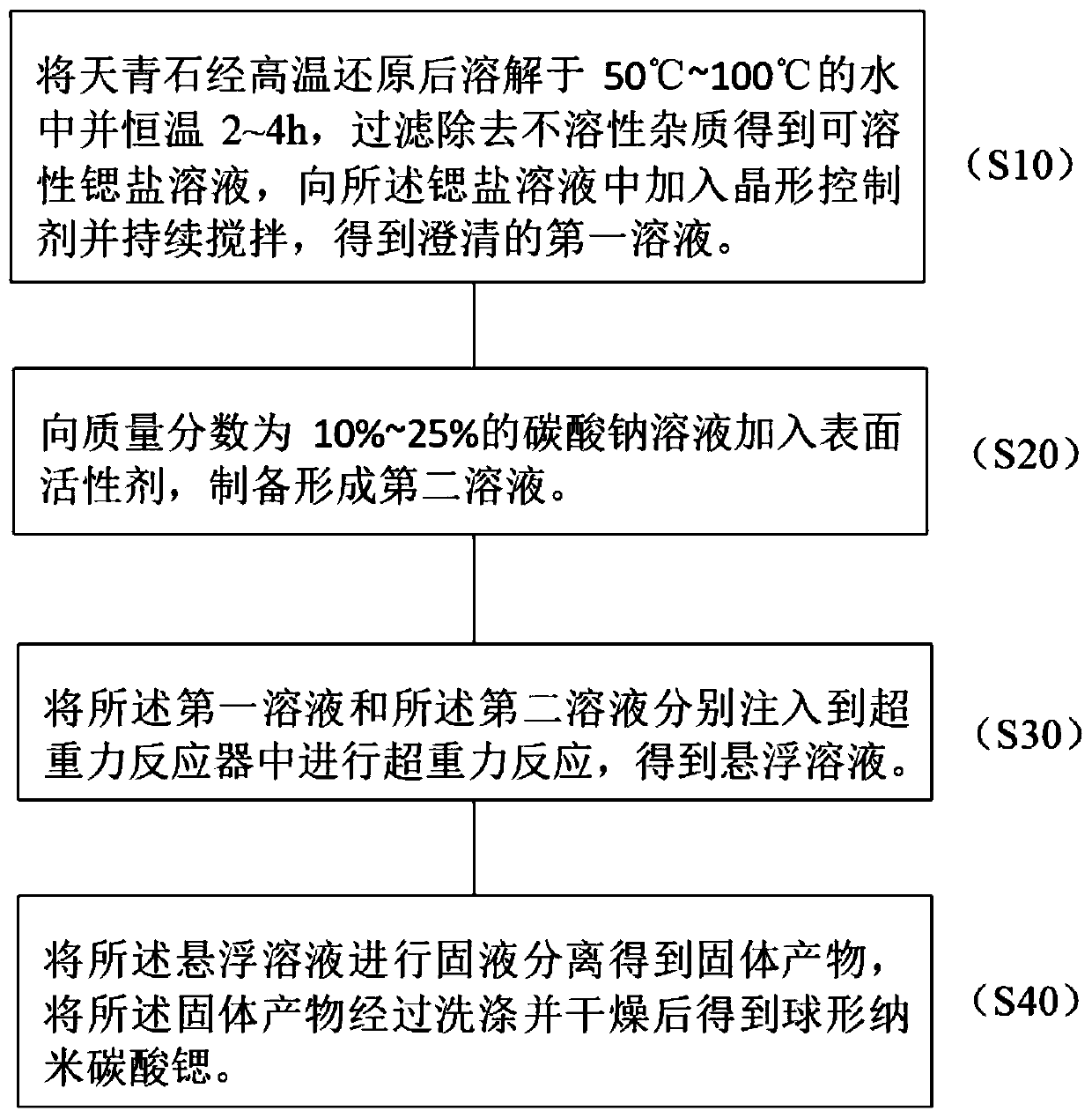
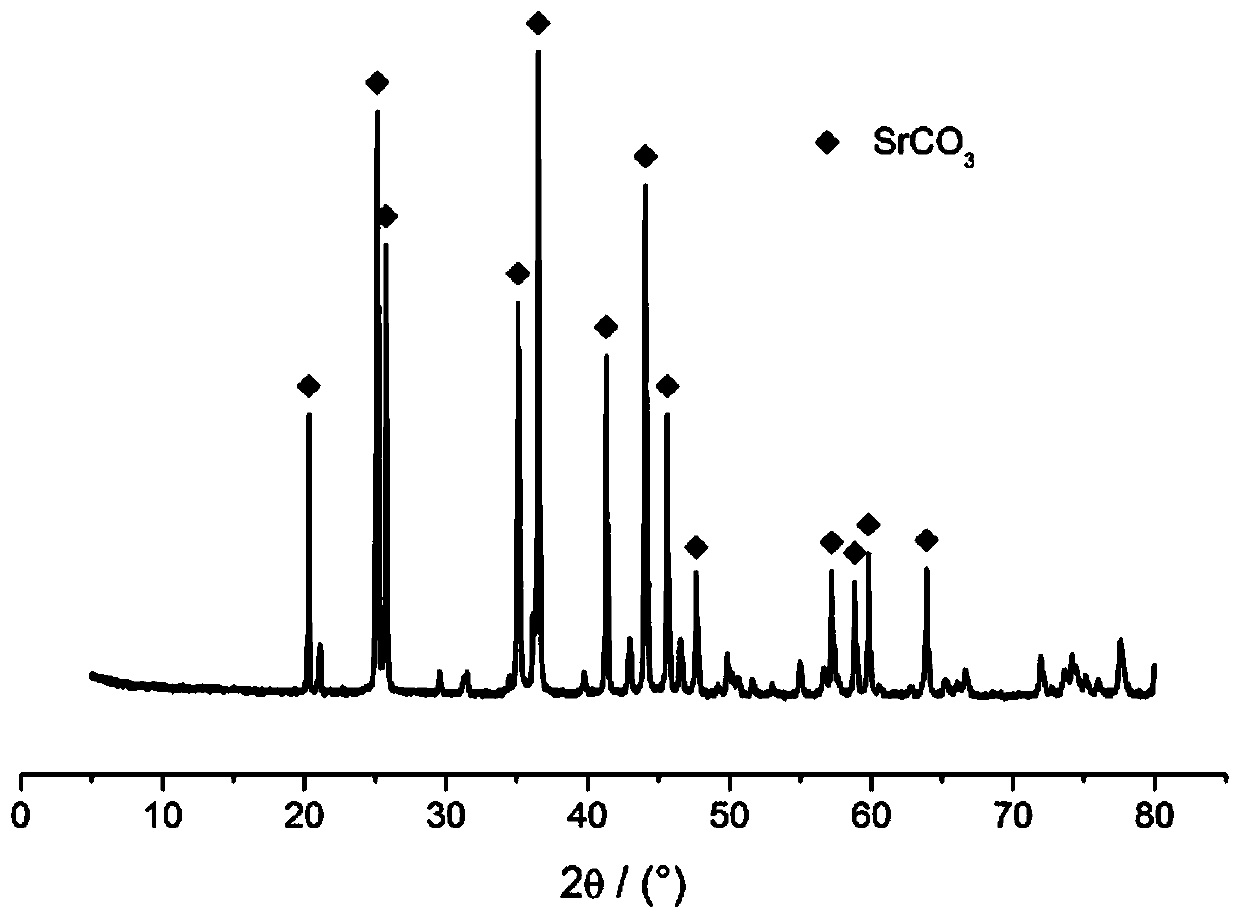
The invention discloses a preparation method of spherical nano-strontium carbonate. The method includes the steps of: S10. subjecting celestite to high temperature reduction, then dissolving the reduced celestite in water at 50DEG C-100DEG C and maintaining a constant temperature for 2-4h, filtering out insoluble impurities to obtain a soluble strontium salt solution, adding a crystal form controlagent into the strontium salt solution and performing stirring continuously to obtain a clarified first solution; S20. adding a surfactant into a sodium carbonate solution with a mass fraction of 10%-25% to prepare a second solution; S30. injecting a first solution and a second solution respectively into a hypergravity reactor for hypergravity reaction to obtain a slurry solution; and S40. subjecting the slurry solution to solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid product, and washing and drying the solid product to obtain spherical nano-strontium carbonate. The method provided by the invention can prepare spherical nano-strontium carbonate with good spherical effect, uniform particles and narrow particle size range.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Ceramic glaze applicable to robot glaze spraying process and preparation method of ceramic glaze applicable to robot glaze spraying process
Owner:GUANGDONG SITONG GROUP
High breaking resistant glass ceramic disc and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high breaking resistant glass ceramic disc and a preparation method thereof. The high breaking resistant glass ceramic disc is prepared from the following raw materials by weight part: 27-38 of broken glass, 15-25 of vesuvianite, 14-26 of kaliophilite, 10-15 of chromium slag, 17-29 of basalt, 4-6 of straw ash, 10-15 of titanaugite, 8-16 of dolomite, 9-18 of lazulite, 5-10 of magnesium zirconate, 3-6 of sodium carbonate, 2-3 of cobalt oxide, 3-5 of lithium silicate, and of 5-7 of an assistant. The glass ceramic disc prepared by the invention is prepared by compounding of vesuvianite, kaliophilite, chromium slag, basalt, straw ash, titanaugite, lazulite, magnesium zirconate, lithium silicate and other raw materials, has greatly enhanced mechanical properties, especially the breaking strength and fracture toughness, so that the glass ceramic disc has strong breaking resistance and durability, and is worthy of wide popularization and application.
Owner:安徽省德邦瓷业有限公司
Process for reducing celestine in rotary hearth furnace to produce strontium sulfide
InactiveCN106586975AReduce manufacturing costIncrease production capacityEnergy inputMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The invention relates to a production process for reducing celestine concentrate pellets with carbon in a rotary hearth furnace to produce strontium sulfide. The process comprises the following steps: subjecting celestine concentrate powder and anthracite duff or petroleum coke powder, used as main raw materials, to batching according to a certain ratio, weighing and mixing, adding a binder and water and carrying out blending so as to obtain a wet material; pressing the wet material with a ball press machine to obtain cold-bonded pellets with certain sizes; drying the pellets in a chain grate, then conveying the dried pellets to the rotary hearth furnace with a highest reduction temperature of 1200 to 1300 DEG C to convert strontium sulfate in celestine into strontium sulfide; and discharging the reduced hot pellets out from the rotary hearth furnace and directly quenching the hot pellets in a water leaching pool, wherein the waste heat of the pellets can be used for increasing water temperature so as to facilitate acceleration of a series of chemical reactions for subsequent preparation of strontium carbonate. The process for production of strontium sulfide via the rotary hearth furnace has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency, great output, low cost, no pollution, etc. Detection results show that the conversion rate of strontium sulfate in celestine reaches 95% or above through reduction of celestine with carbon in the rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
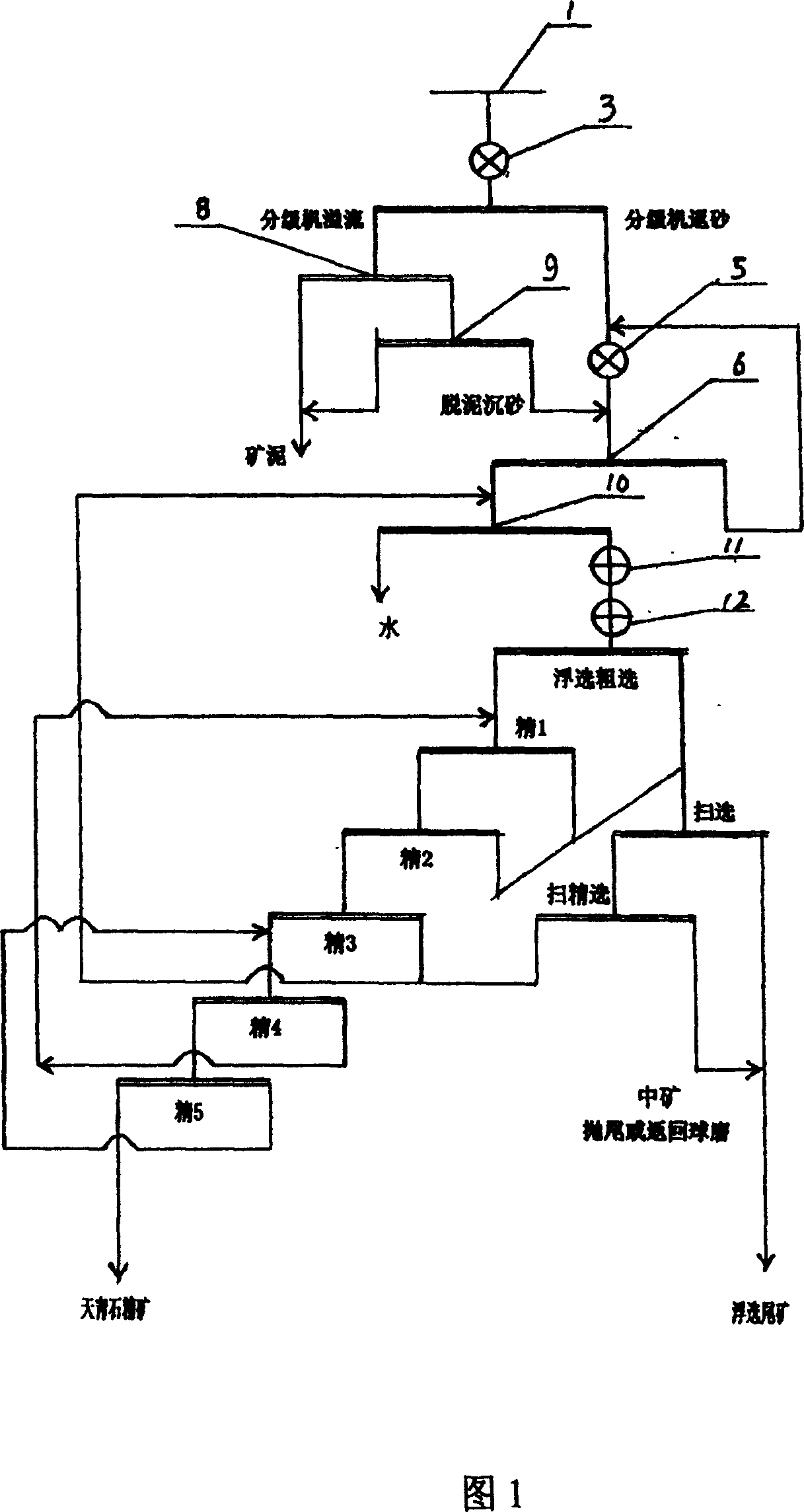
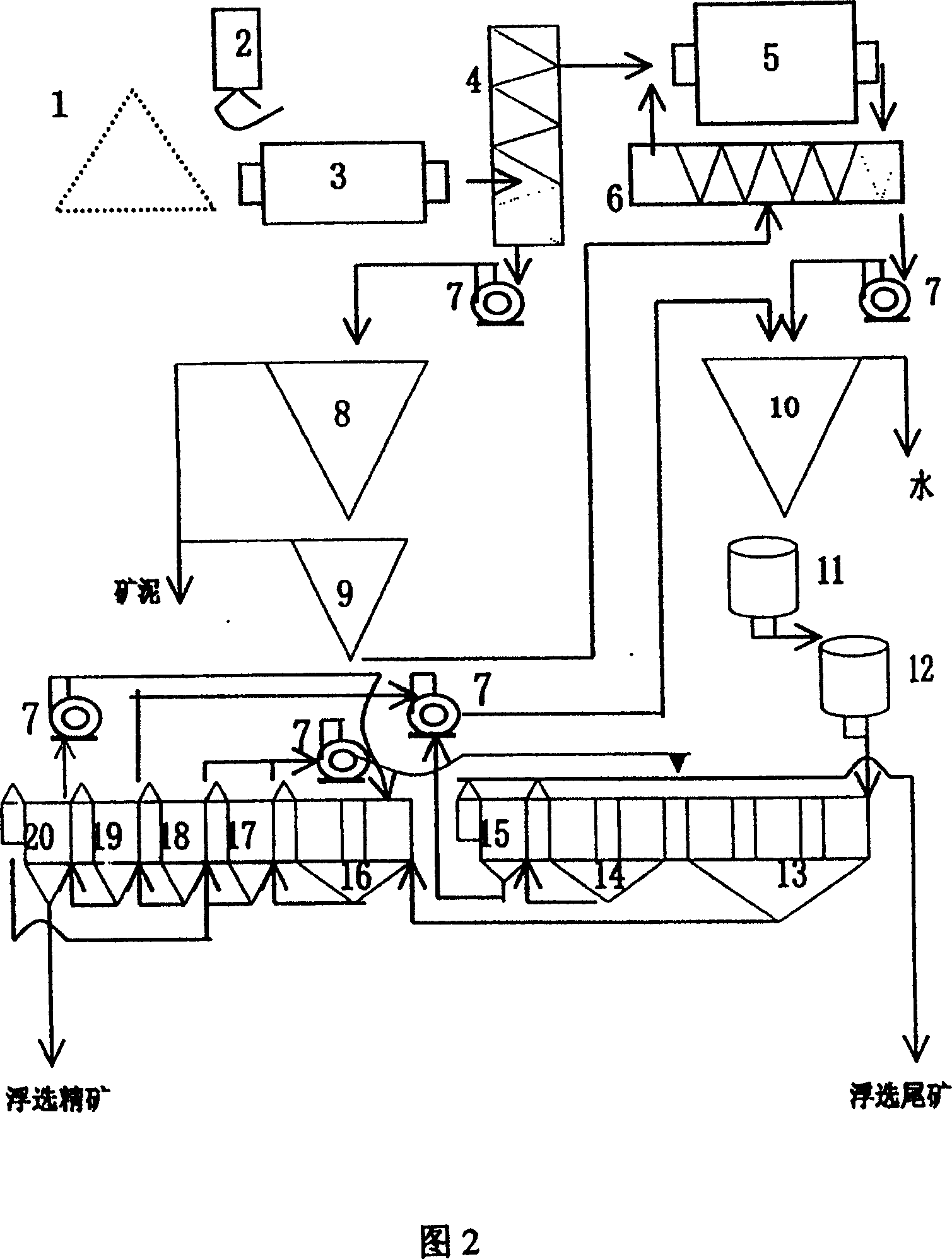
Deslim-floatation celestite inished ore process
InactiveCN1321746CRaise the gradeLarge amount of processingFlotationGrain treatmentsStrontium carbonateScavenger
The invention relates to a process for separating mineral of Celestine, especially relating to a finished ore process of desliming-multiple selection. The inventive method comprises: the ore is processed with rod milling, secondary desmliming, spiral classifying, floatation-roughing separation, secondary scavenger, and fifth classifying. The invention comprises following advantages: the inventive process has better mineral separation index when it is used to classify the Celestine with large content of low-grade mud, while the finished ore productivity is 37.82-42.09%, the content of SrSO4 is 75.75-80.10% and the recovery ratio is 75.17-79.59%; the fifth floatation device has large handling capacity, lower water consumption, lower cost of finishing ore, and lower medicament consumption with simple device. The invention has stable process, simple operation and wide application in the finishing-separation production of Celestine, while it can supply high grade Celestine finished ore for producing strontium carbonate.
Owner:QINGHAI JINRUI MINERAL DEV
Method for preparing ozone heterogeneous phase oxidized solid catalyst
InactiveCN107042115AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesUltrasound - actionBrucite
The invention relates to a method for preparing an ozone heterogeneous phase oxidized solid catalyst, which belongs to the technical fields of environmental protection and a chemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: diatom pure, kyanite, brucite, serpentine, aluminium hydroxide and a celestine porous material are taken as carriers, the carriers are subjected to hole-reaming modification through lithium hypochlorite and dis(acetylacetone)beryllium, a surfactant dodecyl dimethyl hydroxyethyl ammonium chloride is added, surface activation treatment is carried out under supersonic wave effect, then the carriers after ultrasonic surface activation are subjected to a hydro-thermal reaction with a composite mineralizer borax and potassium sulfate, a catalytic activity auxiliary agent predecessor tri(hexafluoroacetylacetone)yttrium (III)dehydrate, tricyclopentadiene promethium, holmium nitrate decahydrate, a tri(strifluoromethanesulfonimidate)ytterbium rare earth metallorganic compound, a catalytic activity central composite predecessor common transition metallorganic compound pyruvate iso-nicotinoylhydrazone vanadium, cobalt gluconate and a precious metal compound tetraammine dichloropalladium, tetrachloro iridium hydrate in a hydro-thermal reaction vessel under effect of an emulsifier dioctadecalkyl ammonium bromide, the reaction products are dried to remove the moisture, in a muffle furnace, and the product is calcinated at certain temperature to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidized solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high-purity strontium carbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity strontium carbonate, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of strontium carbonate. The method comprises the steps: firstly, soaking calcined celestite in hydrochloric acid, supplementing with hydrogen peroxide, extracting strontium ions, followed by extracting probiotics in celestite surface soil, screening, culturing, mixing with a strontium ion-containing mixed solution, supplementing with sodium carbonate, under action of probiotics self enzymes, continuously carrying out enzymatic action with surrounding media to generate carbonate ions, and carrying out a reaction with strontium ions to produce strontium carbonate crystals. The prepared strontium carbonate contains low impurity level, has high purity up to more than or equal to 99.5%, has high activity, and cannot produce secondary pollution in the process of preparation.
Owner:TRUSYN CHEM TECH
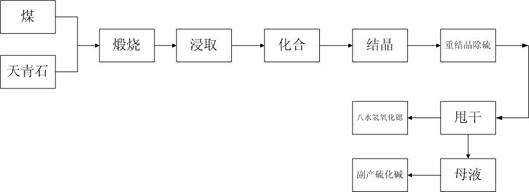
Strontium carbonate production method
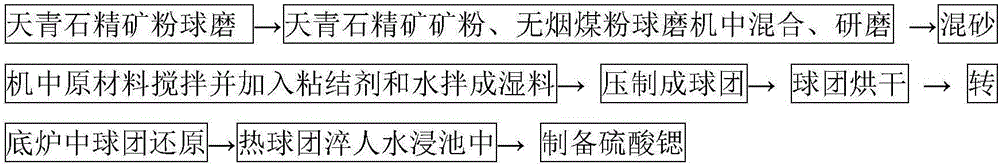
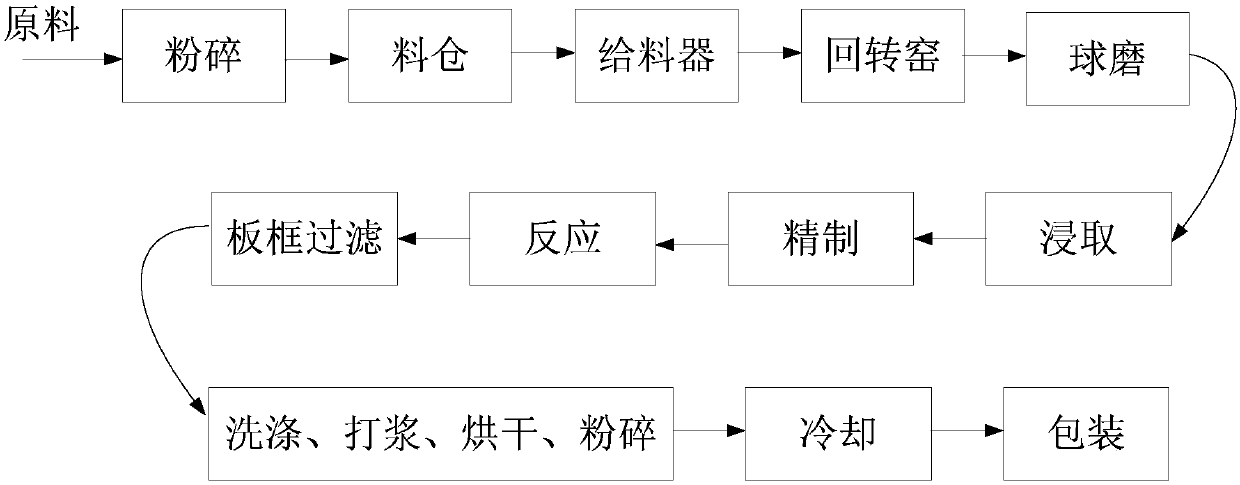
InactiveCN109574054AReduce manufacturing costLow impurity contentStrontium carbonatesEngineeringCrusher
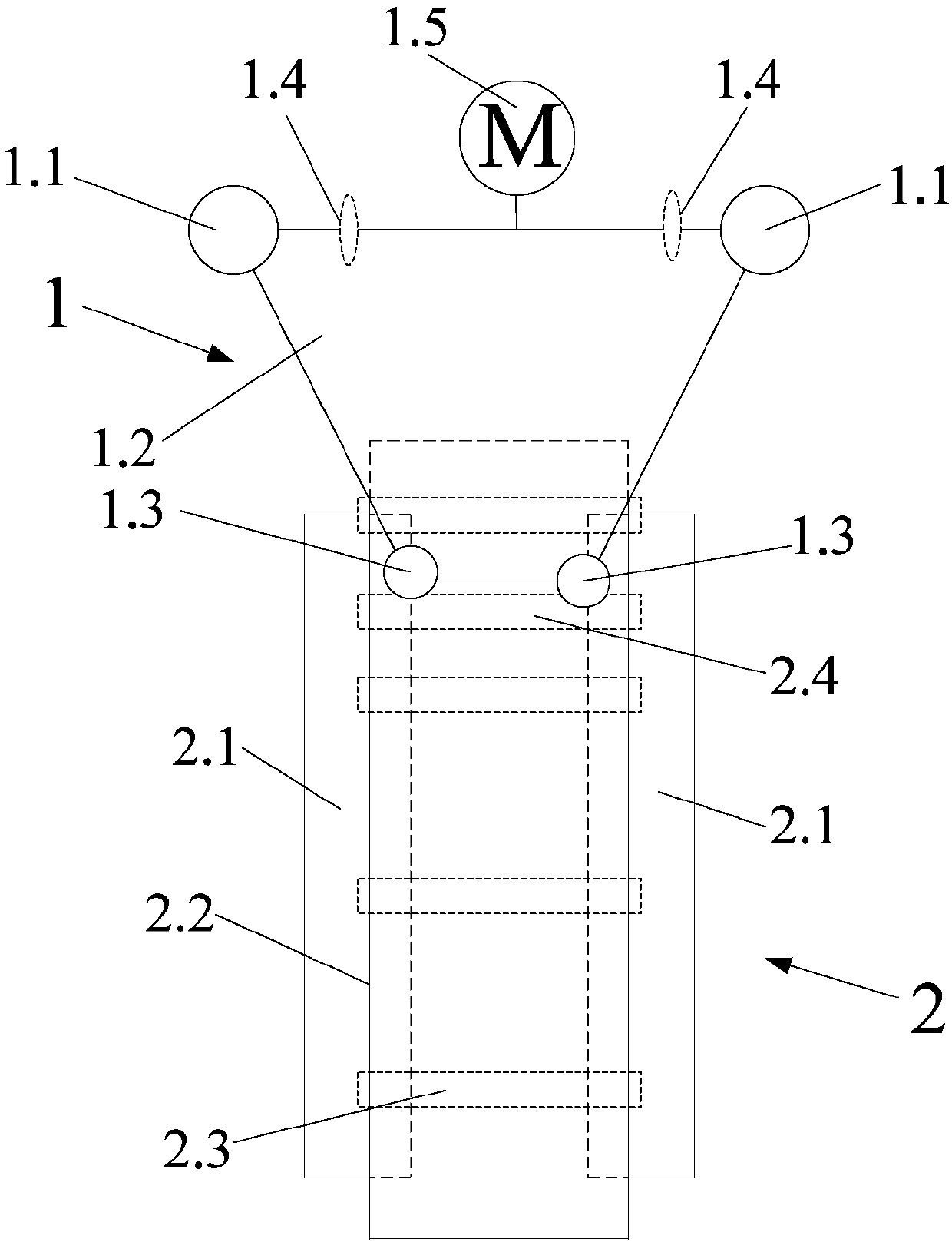
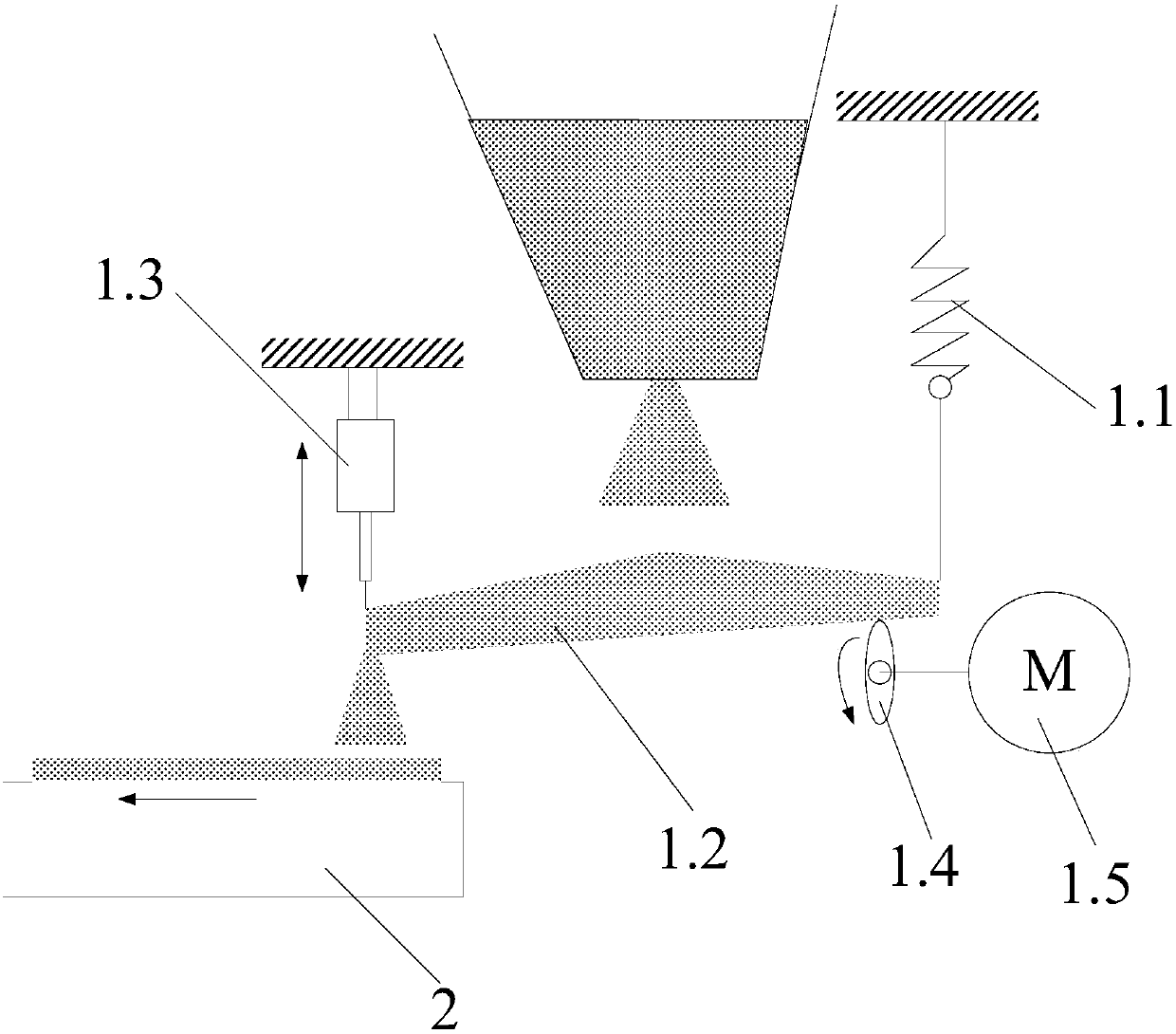
The invention discloses a strontium carbonate production method. The strontium carbonate production method comprises the following steps: S100: after smashing celestite and raw coal via a smashing machine, feeding the smashed celestite and raw coal into a bin; S200: feeding raw materials in the bin into a rotary kiln through an oscillating feeder (1) and a conveying device (2); S300, ball-millingrough strontium sulfide into powder through a ball-miller; S400: leaching to obtain leaching liquid containing strontium ions; S500: refining; S600: carrying out chemical combination to generate a strontium carbonate precipitate and sodium sulfide mixture; S700: washing, pulping, drying and smashing sodium carbonate obtained by filtering and separating to obtain strontium carbonate particles; andS800, cooling and packing to obtain a final strontium carbonate product. The quality of the strontium carbonate product is improved, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:URUMQI VOCATIONAL UNIV
Anti-crease elastic breathable fabric
InactiveCN109322145AAttachment homogenizationBiochemical fibre treatmentVegetal fibresFiberCooking & baking
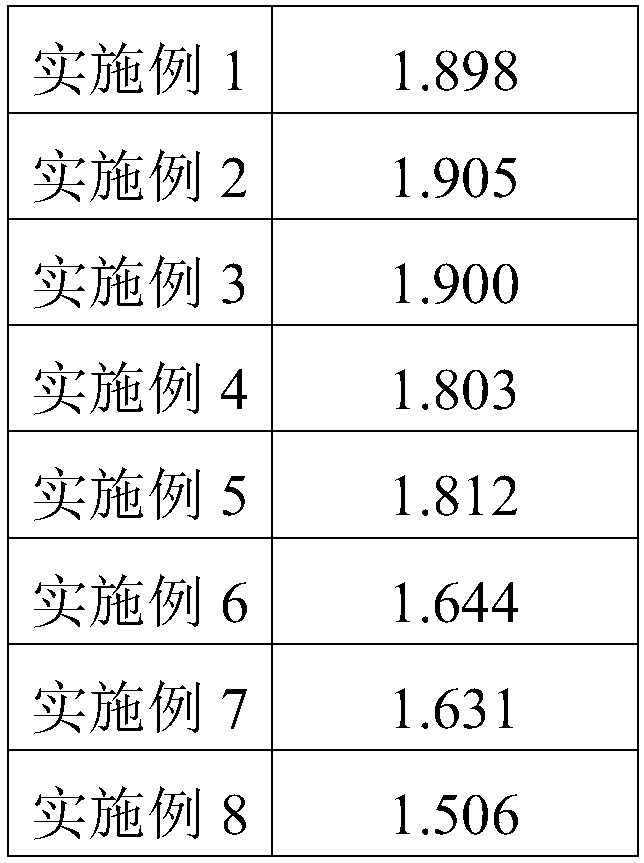
The invention provides an anti-crease elastic breathable fabric, and belongs to the field of fiber products. The crease resistance, elasticity and breathability of the fabric are improved. The fabricis a tussah silk / ramie fabric obtained by finishing through a lapis lazuli finishing agent, wherein the lapis lazuli finishing agent is prepared from lapis lazuli powder, ethydiaminedhephen acetic-Na,glycerin, 4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid or a derivative thereof, a penetration aid, and water. The anti-crease elastic fabric is prepared by the steps of two-dipping two-rolling, pre-baking, baking, spraying, washing and drying, and balancing. The obtained anti-crease elastic fabric has a maximum dry crease recovery angle of 259 degrees and a minimum bending length of 1.506 cm.
Owner:潢川县圣宇服饰科技有限公司
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107008420AEvenly dopedEnhanced anti-toxicityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesUltrasound - actionLithium hypochlorite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, belonging to the technical field of environment-friendly and chemical catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking attapulgite, diopside, illite, ulexite, aluminum hydroxide and celestine porous materials as carriers, performing pore expansion and modification to the carriers through lithium hypochlorite and beryllium bis(acetylacetonate), adding a surfactant methyl trioctylammonium chloride and performing surface activation treatment under ultrasonic wave effect, then leading the ultrasonically surface-activated carriers to have hydrothermal reaction with a complex mineralizer, namely borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic activity assistant precursors, namely praseodymium(III) tris[3-(trifluoromethylhydroxymethylene)-D-camphorate], promethium tricyclopentadienide, tris(4,4,4-trifluoro-1-(2-thienyl)-1,3-butanediono) europium and lutetium carbonate hydrate rare earth metal organic compound, and catalytic active site component precursors, namely common transitional metal organic compound ferrous fumarate, nickel citrate and tungsten catechol ethylenediamine complex and precious metal compound potassium bis(thiocyanate) argentate (I) in a hydrothermal reactor under the action of an emulsifier dodecyl dimethyl (2-hydroxyl) ethylamine chloride, drying reactive products to remove moisture, and firing in a muffle furnace at certain temperature, to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com