In-situ treatment method of sapphire substrate for preparation of high-quality zinc oxide film
A zinc oxide thin film and sapphire substrate technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, ion implantation plating, coating, etc., can solve problems such as slow growth rate, difficult process control, and increased electron concentration in the background of zinc oxide thin film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
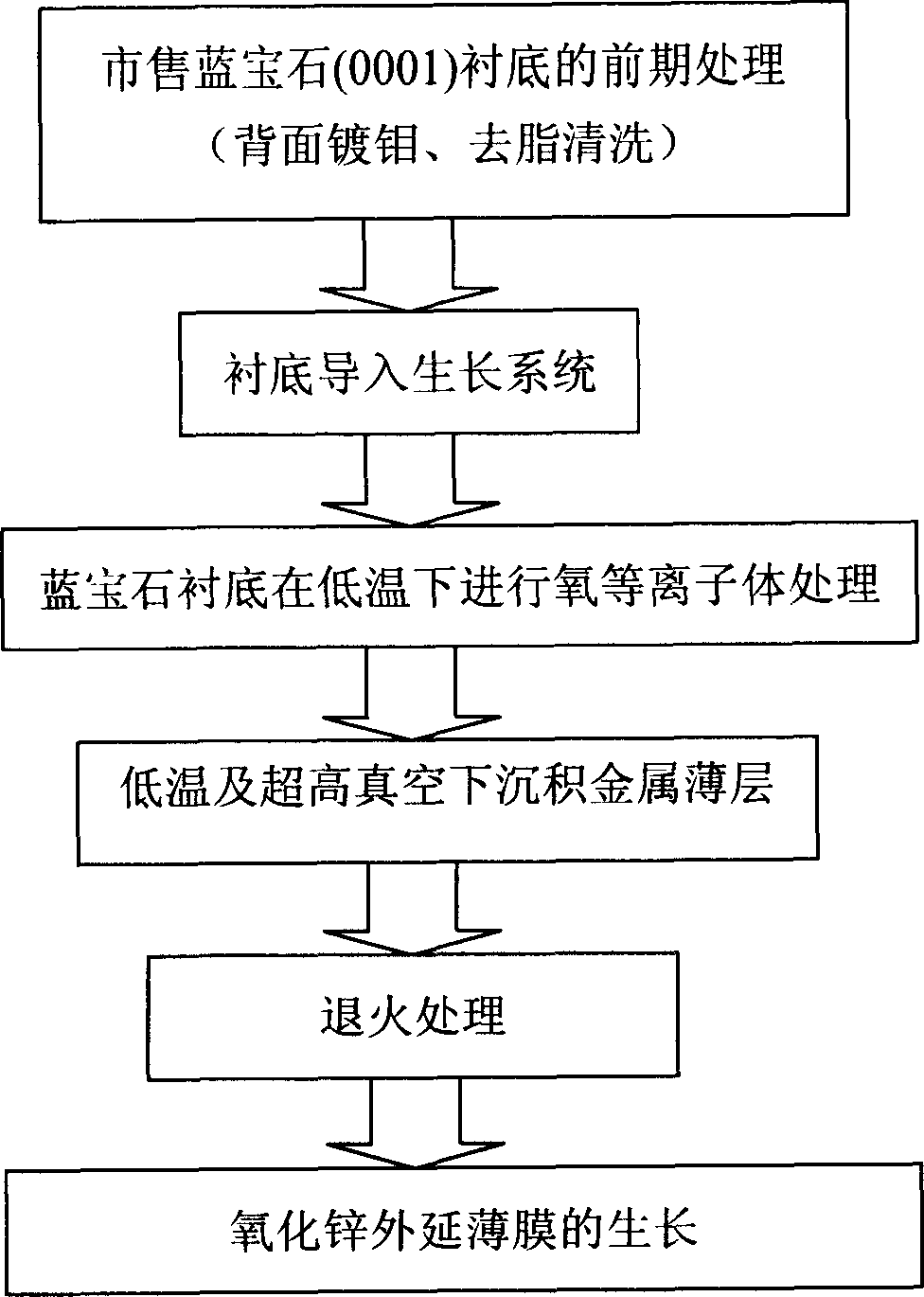
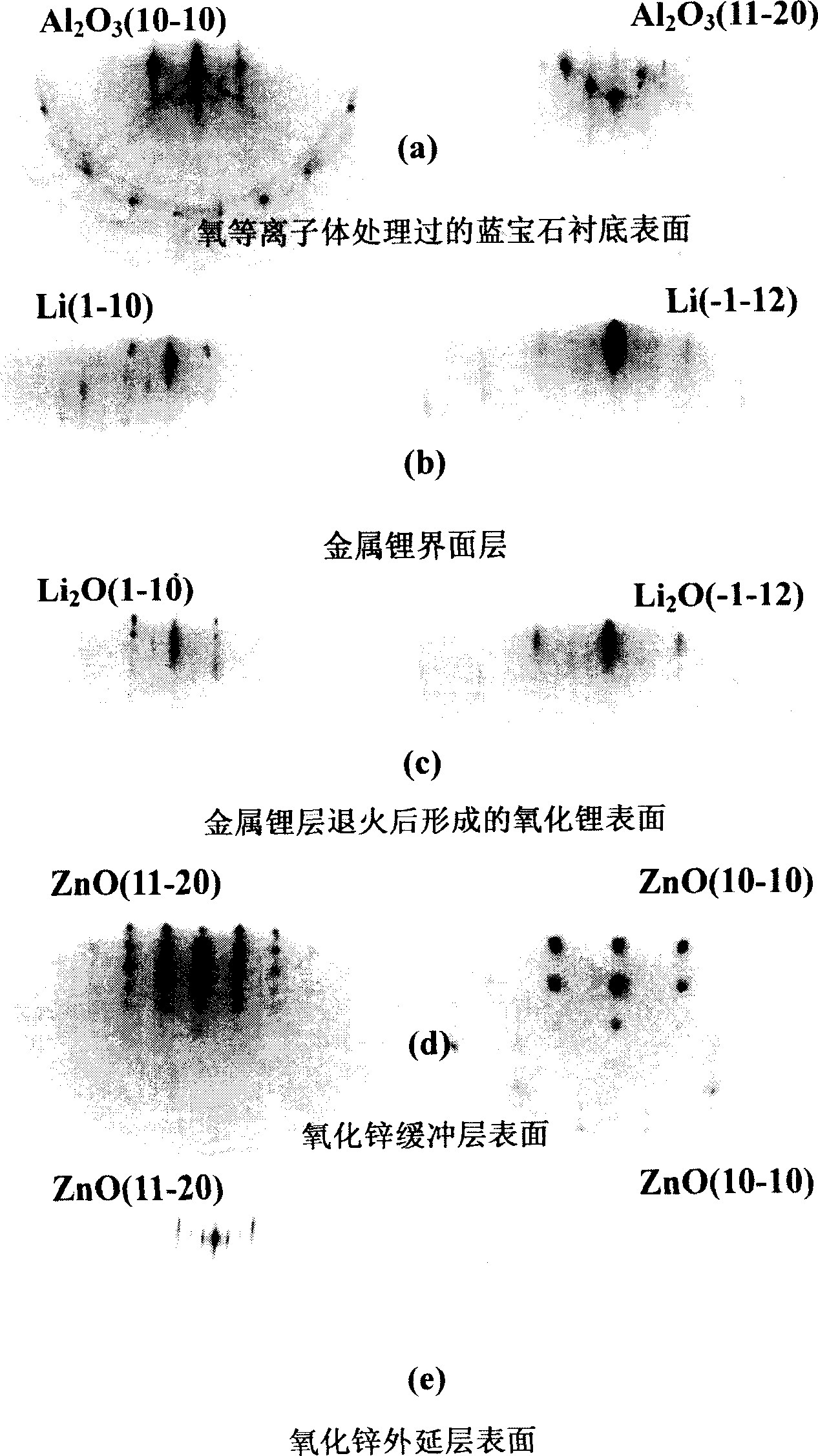
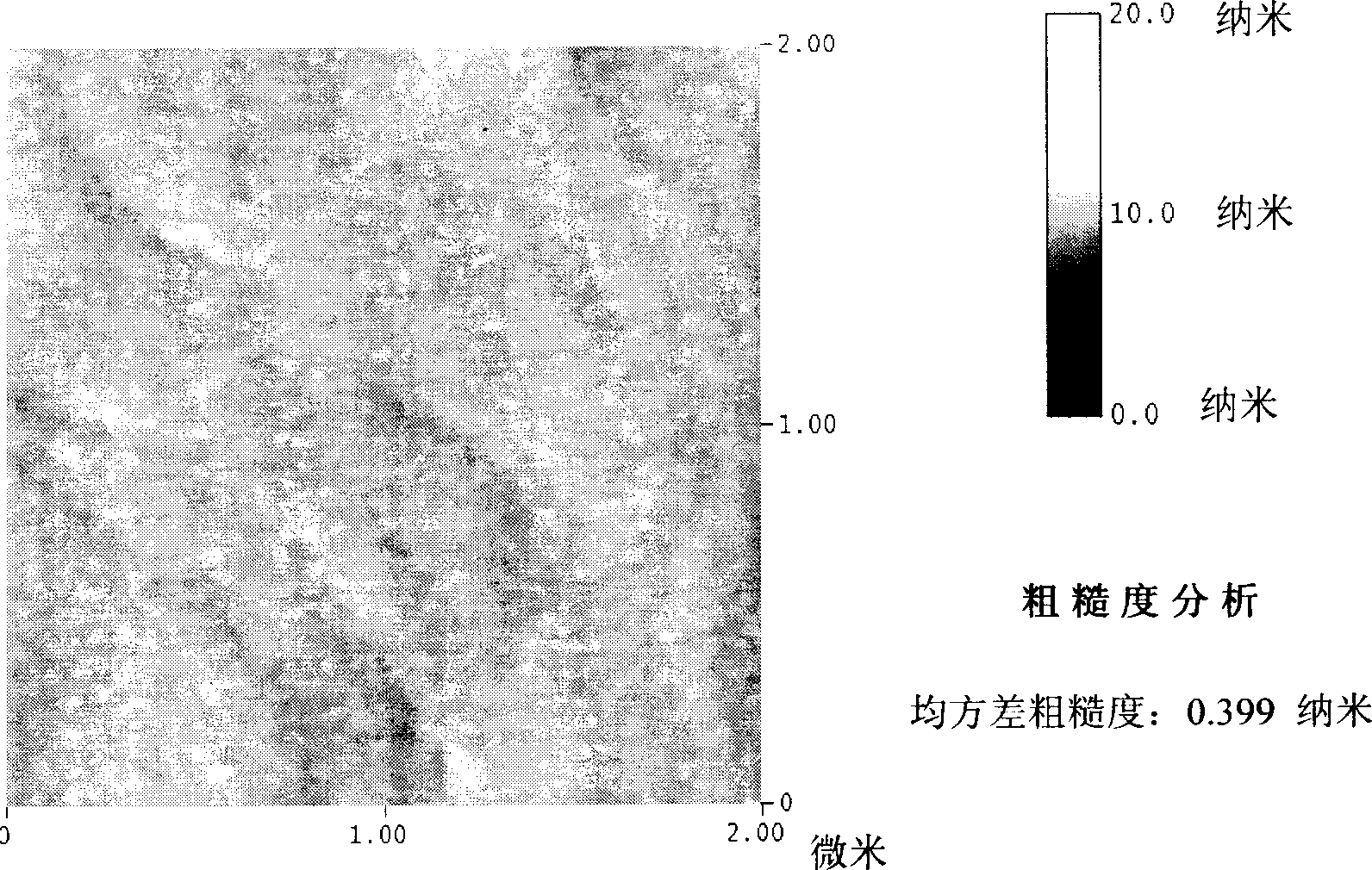
[0026] Such asfigure 1 As shown in the process flow diagram of the present invention, on the sapphire (0001) substrate, the specific steps for preparing high-quality ZnO single crystal film are as follows by utilizing oxygen plasma treatment and metal lithium interfacial layer modification technology:
[0027] 1) Plating molybdenum on the back of a commercially available sapphire (0001) substrate by a known method, cleaning it, and then introducing the substrate into a molecular beam epitaxy growth system;
[0028] 2) Perform radio frequency oxygen plasma treatment at a low temperature of 200°C for about 30 minutes, the radio frequency power is 400W, and the oxygen flow rate is 2.0 sccm to obtain an oxygen-terminated sapphire (0001) substrate; the purpose of choosing a low temperature is to prevent surface oxygen atoms from desorption;
[0029] 3) At air pressure -6 When the Pa and the substrate temperature are 80°C to deposit metallic lithium, the equivalent vapor pressure of...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Such as figure 1 Shown process flow diagram of the present invention, on sapphire (0001) substrate utilizes oxygen plasma treatment and metal magnesium interfacial layer modification surface to prepare the concrete steps of high-quality ZnO single crystal thin film as follows:
[0036] 1) Plating molybdenum on the back of a commercially available sapphire (0001) substrate by a known method, and cleaning, and then introducing the substrate into a molecular beam epitaxy growth system;
[0037] 2) Perform radio frequency oxygen plasma treatment at 80°C for about 30 minutes, the radio frequency power is 350W, and the oxygen flow rate is 2.5 sccm to obtain a sapphire (0001) substrate with an oxygen terminated surface. The purpose of choosing a low temperature is to prevent surface oxygen atoms from desorption;
[0038] 3) At air pressure -6 When the Pa and the substrate temperature are 80°C to deposit metallic magnesium, the equivalent vapor pressure of the magnesium beam i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com