Filling composite welding flux vibrating liquid phase welding method for non-continuous strengthening aluminium base composite material
A technology for strengthening aluminum matrix and composite materials, which is applied in welding/cutting medium/material, welding medium, welding equipment, etc., and can solve the problems of high surface roughness to be welded, large difference in melting point of reinforcing phase, influence of joint strength, etc. , to improve the microscopic bonding interface, avoid enhanced phase segregation, and improve the performance of the joint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] The following examples describe the present invention in more detail:
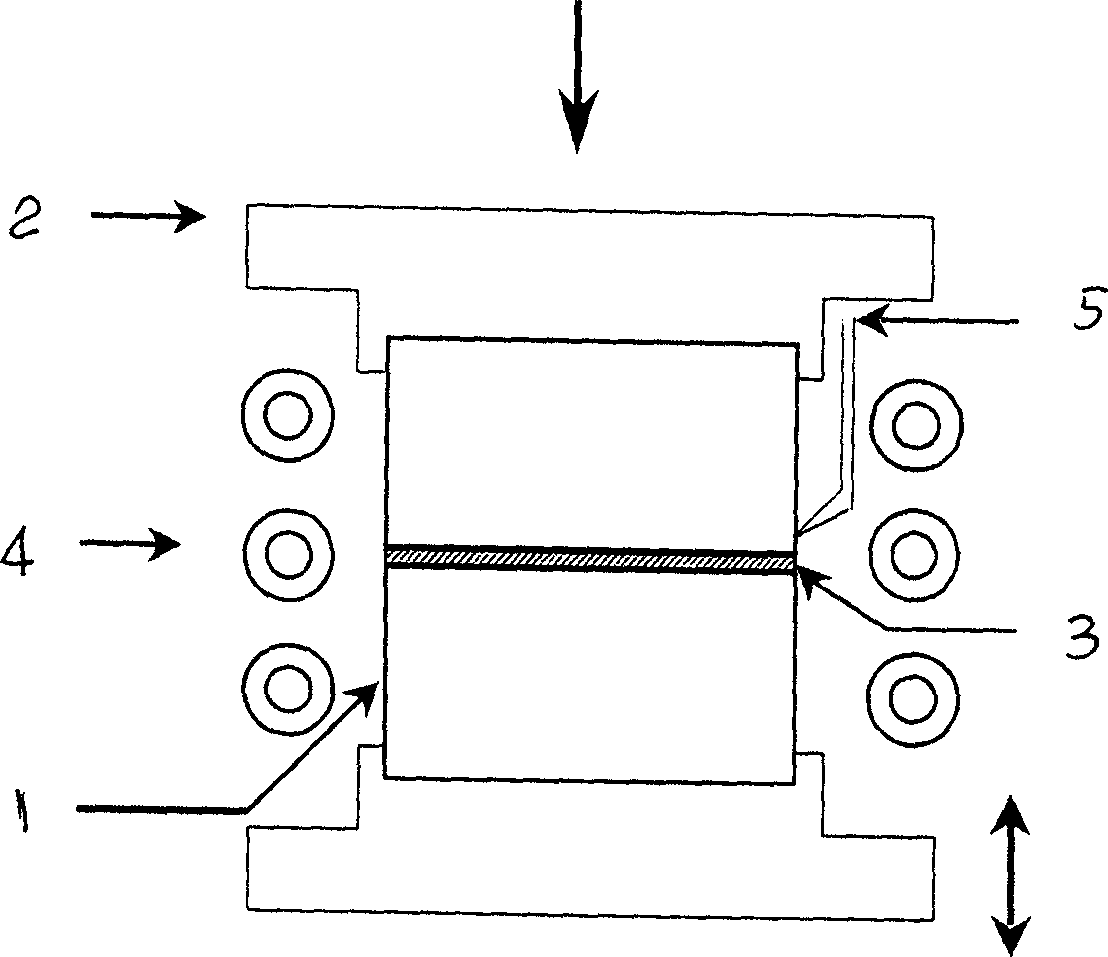
[0053] First use 400# sandpaper to polish the discontinuously reinforced aluminum matrix composite material, and perform ultrasonic cleaning in acetone. After the cleaned discontinuously reinforced aluminum matrix composite material 1 is dried, it is clamped in the form of a butt joint in the fixture 2 place the composite solder 3 between the surfaces of two discontinuous reinforced aluminum matrix composite materials to be welded, and heat the composite solder through the heater 4 to fully melt the composite solder. The heating temperature range is 380-620°C, and is controlled by the thermocouple 1. Keep the welding temperature, start the vibration device and apply pre-pressure. The vibration adopts one of the following two methods: use low-frequency vibration with a frequency of 50-4000 Hz and an amplitude of 0-1.5 mm, and the vibration time is 0.1-5 minutes. The pressure range is 0.25 ~ 10Mpa; or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com