Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase 2 as a target in the regulation of fat and insulin action
A technology of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase, applied in the treatment of diabetic patients, regulating fatty acid accumulation and oxidation, in the field of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase ACC2 isoform, can solve problems such as deficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
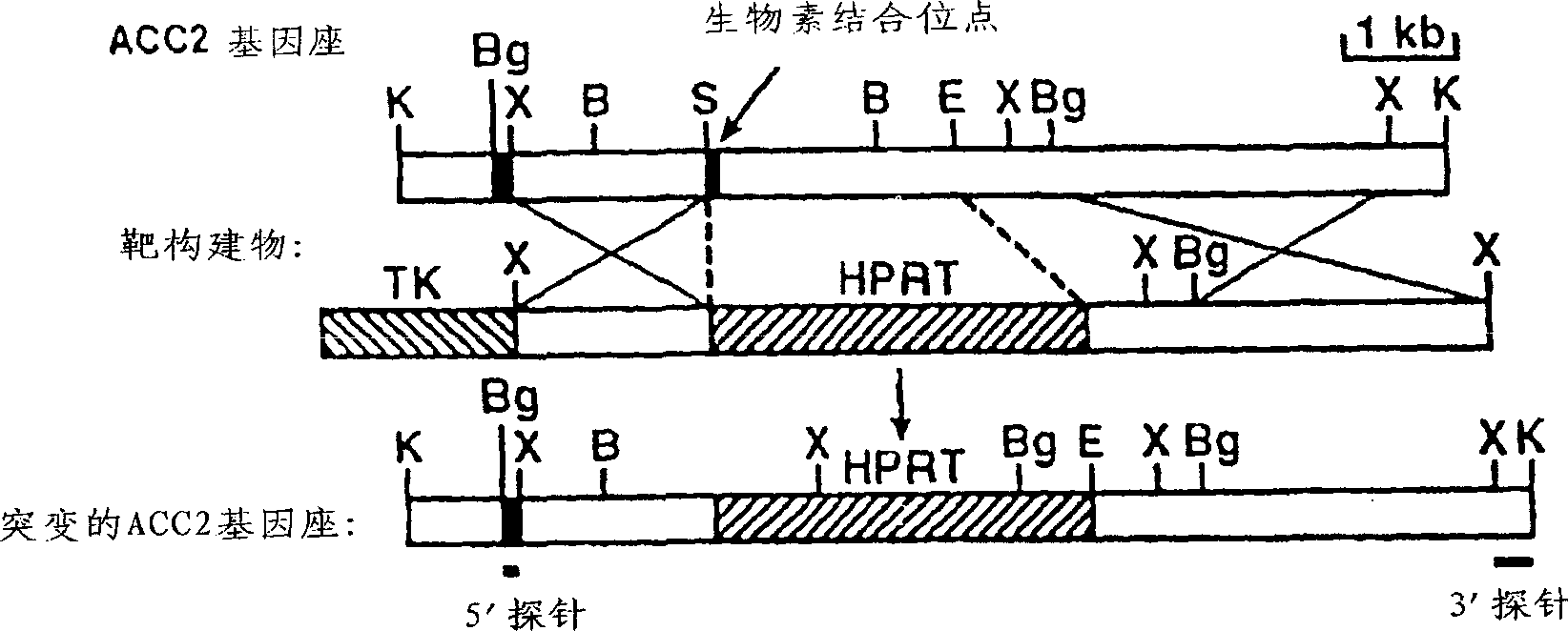
[0054] Acc2 - / - Generation of transgenic mice
[0055] Mouse Acc2 genomic clones were isolated using the Acc2 cDNA probe. Based on the homology between human and mouse ACC2 genes (Abu-Elheiga, L., Almaraz-Ortega, D.B., Baldini, A. and Wakil, S.J., J Biol Chem.272, 10669-10677, 1997), from Bio Two oligonucleotides in the binding region of the protein were designed based on the human ACC2 cDNA sequence: forward primer (5'-CTGAATGATGGGGGGCTCCTGCTCT-3'; nucleotides 2551-2575) (SEQ ID No.1) and reverse primer (5' - TTCAGCCGGGTGGACTTTAGCAAGG-3'; nucleotides 2890-2913) (SEQ ID No. 2). These primers were used to amplify cDNA from the Quick-Clone mouse heart cDNA library (Clontech) template.
[0056] The obtained cDNA fragments were sequenced and used to screen the 129 / SvEv mouse genome library to isolate a 16-kbp lambda genome clone. The 16-kbp lambda genomic clone was digested with different restriction enzymes to establish a restriction map and construct a gene targeting vec...
Embodiment 2
[0059] in Acc2 - / - Acc2 expression in transgenic mice
[0060] Northern blot analysis of total RNA from skeletal muscle tissue excised from wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous-null animals showed no detectable Acc2 mRNA in homozygous-null animals and, as expected, Acc2 mRNA in heterozygous animals. Acc2 mRNA level was half of the wild type ( Figure 1C ). Probing of biotin-containing Acc2 with avidin peroxidase / - Western blot analysis of heart, skeletal muscle, and liver tissues from mutant mice showed no expression of ACC2 protein ( Figure 1D ). ACC2 protein levels (280 kDa) were higher than ACC1 protein levels (265 kDa) in heart and skeletal muscle tissues of wild-type mice, although ACC1 proteins were more predominant in their liver tissues.
[0061] Acc2 - / - The absence of ACC2 protein in mutant mice was further confirmed by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy analysis using an affinity-purified anti-ACC2-specific antibody (Abu-Elheiga, L., W.R. Brinkley...
Embodiment 3
[0063] in Acc2 - / - Malonyl-CoA levels in transgenic mice
[0064] Since malonyl-CoA levels in animal tissues are due to the activity of ACC1 and ACC2, the consequences of the absence of ACC2 in malonyl-CoA levels in these tissues and whether ACC1 can be compensated to determine malonyl-CoA levels in these tissues improvement. Comparing wild type and Acc2 - / - There was no significant difference in malonyl-CoA levels and overall ACC activity in the liver tissues of mutant mice, indicating that almost all malonyl-CoA in the liver is provided by ACC1 ( figure 2 ).
[0065] On the other hand, comparing the skeletal muscle and heart tissues of the same two groups of mice, it was found that Acc2 - / - Malonyl-CoA levels in these tissues were approximately 30-fold and 10-fold lower in mutant mice than in wild-type mice, respectively. This suggests that ACC2 is the major provider of malonyl-CoA in skeletal muscle and heart ( figure 2 ).
[0066] During fasting, wild-type and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com