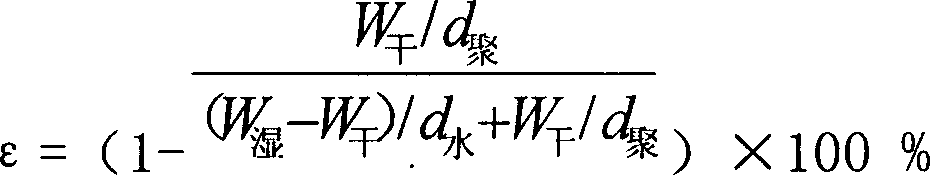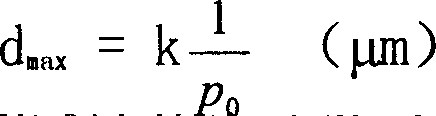Method for producing hollow fiber film
A fiber membrane and hollow technology, which is applied in the field of hollow fiber membrane production, can solve the problems of small water permeability of membrane, uneven pore size distribution of porous membrane, and inability to meet needs, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform pore formation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: with 1500 gram calcium carbonate (2~5 microns of particle diameter) particle, 2000 gram polyvinylidene fluoride resin, 500 gram polyethylene glycol 20000, 100 gram soil temperature-20, 1500 gram dibutyl phthalate The ester is uniformly dispersed at 220°C, blended and granulated, and melt-spun. Soak in 10wt% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution for 2 hours to remove calcium carbonate in the polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber, and soak in isopropanol for 3 hours to remove dibutyl phthalate, and the obtained polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber porous membrane has an inner diameter of 0.4mm , outer diameter 0.6mm, rupture strength 0.91MPa, pure water transmission rate 1210L / m 2 ·h@0.1MPa 20℃, membrane separation pore size 0.10μm, porosity 74%.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: 500 grams of aluminum oxide 20-80 nanoparticles, 500 grams of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 2000 grams of polyvinylidene fluoride resin, 100 grams of Tween-80, and 1500 grams of diethylene glycol dimethyl ether were heated at 215 ° C. Twin-screw blending, melt spinning. Soak in 10wt% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution for 4 hours to remove aluminum oxide in polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber, soak in isopropanol for 3 hours to remove diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and the obtained external pressure polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber The inner diameter of the porous membrane is 0.5mm, the wall thickness is 0.15mm, the rupture strength is 0.62MPa, and the pure water transmission rate is 1570L / m 2 ·h@0.1MPa 20℃, membrane separation pore size 0.20μm, porosity 78%.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Blending 800 grams of calcium carbonate nanoparticles, 1800 grams of polyvinylidene fluoride resin, 780 grams of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 20 grams of fluorosurfactant FC-4, and 1000 grams of diethylene glycol dimethyl ether at 220 ° C Granulation, melt spinning. Soak in 10wt% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution for 2 hours to remove calcium carbonate in polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fibers, soak in isopropanol for 3 hours to remove diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and obtain polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber porous membranes with an inner diameter of 0.9mm, Outer diameter 1.4mm, rupture strength 1.03MPa, pure water transmission rate 1510L / m 2 ·h@0.1MPa 20℃, membrane separation pore size 0.45μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com