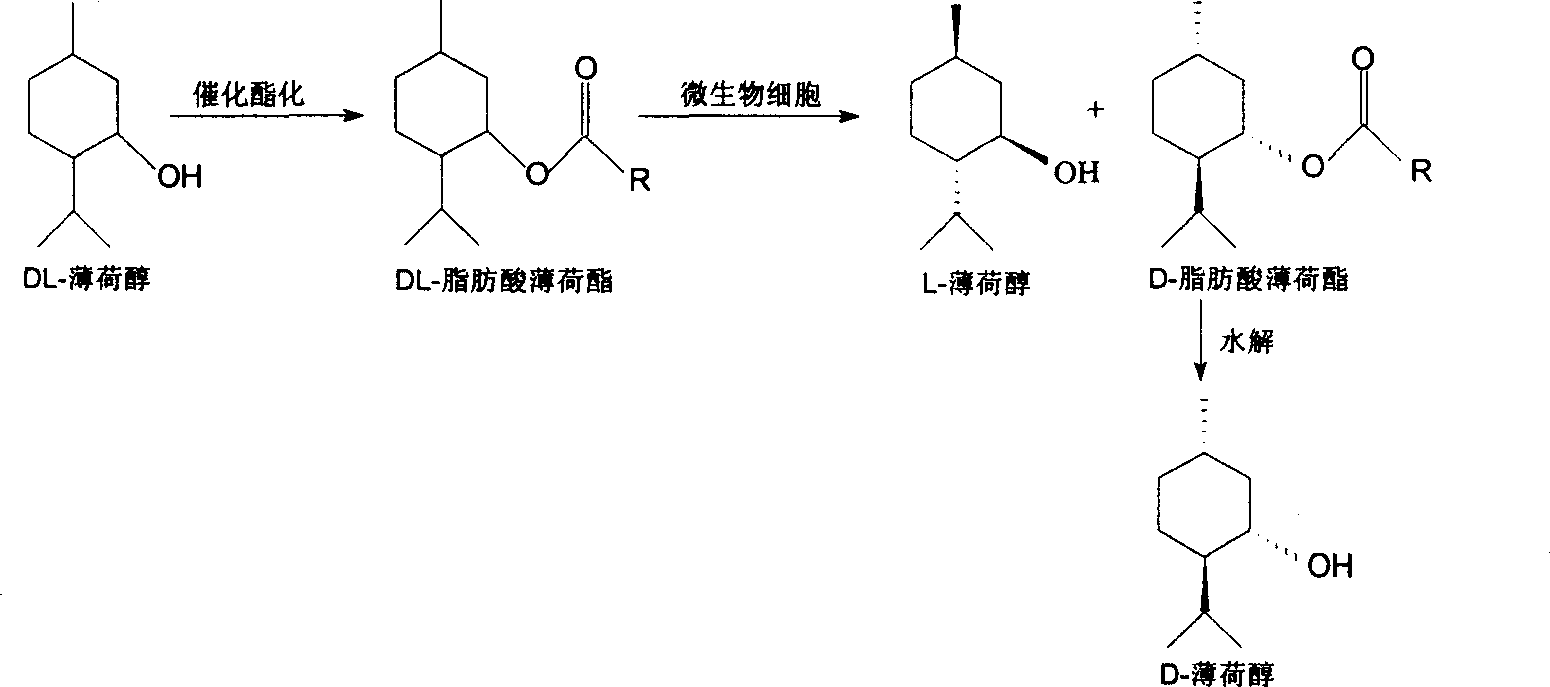
Method for preparing L-menthol from stereo-selective hydrolysis of DL fatty acid menthyl ester by whole-cell biological process
A stereoselective, whole-cell technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of difficult recycling, low reaction equilibrium conversion rate, low product purity, etc. Scope and operational stability, reduction of production cost, high reaction stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1D
[0063] The preparation of embodiment 1DL-menthyl acetate
[0064] Add 0.02mol menthol and 0.02mol acetic anhydride to a 100ml three-necked flask equipped with a condensing reflux device and a thermometer, and add 0.4mmol p-toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst, add n-heptane as a reaction solvent until the reaction volume is 10ml, stir and heat Reflux reaction 4h. After the reaction is completed, cool down to below 40°C, add 5% NaHCO 3 Neutralize the excess acid until no more bubbles are produced, let it stand for stratification, remove the water phase, wash the organic phase with saturated brine, separate the water phase and use anhydrous MgSO 4 Let dry overnight. After filtration, the mixed solution was rotatably evaporated to remove the solvent to obtain pure DL-menthyl acetate. The purity of DL-menthyl acetate detected by gas chromatography was 99.9%, and the yield (calculated as menthol) was 98.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0065] The hydrolysis situation of embodiment 2 different bacterial strains to DL-menthyl acetate
[0066] In 1ml, 50mmol / L potassium phosphate buffer solution (pH7.0), add 13mg of dry cells and 10mg of DL-menthyl acetate, shake and react on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C for 24 hours, after the reaction, the mixture is centrifuged to remove Bacteria, the supernatant was extracted with ethyl acetate to extract the product and substrate, and the e.e. value and conversion rate of the product were analyzed by chiral gas chromatography. The transformation status of each strain is shown in Table 1.
[0067] Table 1
[0068] microbial strain
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Asymmetric hydrolysis of DL-menthyl acetate with CCTCC M201021 whole cells
[0070] In 1ml, 50mmol / L potassium phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.0), add 13mg of dried bacteria and 10mg of DL-menthyl acetate, shake the reaction on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C for 12, 16, 20, 24, 36 , 48 hours, after the reaction, the mixture was centrifuged to remove bacteria, the supernatant was extracted with ethyl acetate to extract the product and substrate, and the e.e. value and conversion rate of the product were analyzed by chiral gas chromatography. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0071] Table 2
[0072] Response time (hours)
[0073] Table 2 shows that after 24 hours of reaction, the conversion rate is close to 50% of the theory, and the reaction time can be extended to 48 hours, and the optical purity of the product can still reach more than 90% e.e.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com