Anti-Inflammatory, Radioprotective, and Longevity Enhancing Capabilities of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
a technology of cerium oxide and nanoparticles, applied in the field of nanoparticles, can solve the problems of high variability between batches, uncontrollable particle size, and difficulty in the process of sonic gel, and achieve the effect of prolonging the life of living cells, reducing or eliminating damage to cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Extension of Cell and Organism Longevity
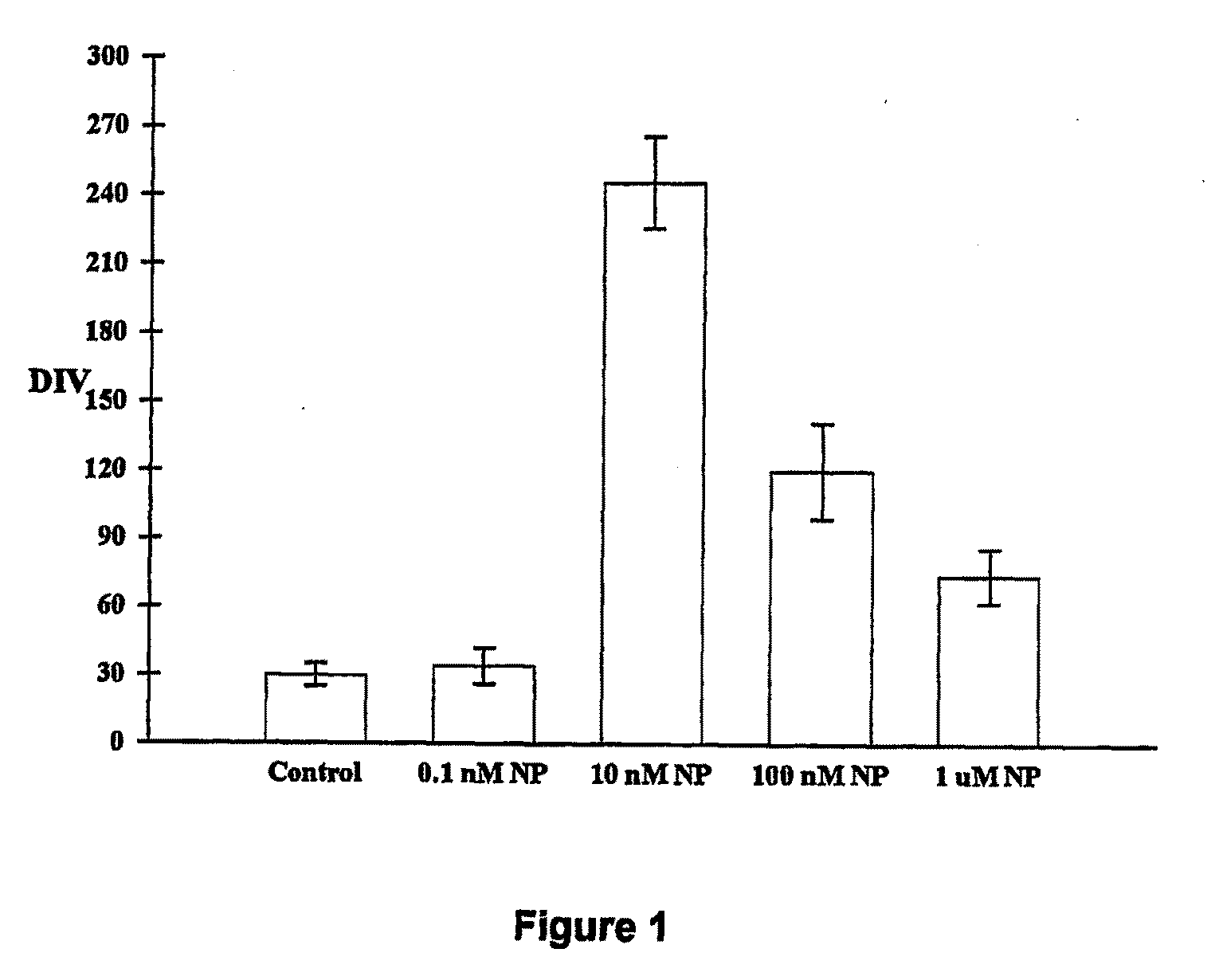
[0079]A single 10 nM dose of cerium oxide nanoparticles extended the life span of cultured rat brain cells (neurons, astrocytes, microglia) from 28 to 182 days (6 months). For delivery, the nanoparticles were in a non-agglomerated form. To accomplish this, stock solutions of about 10% by weight were sonicated in ultra-high purity water (16 megaohms) or in normal saline prepared with ultra high purity water. Stocks were sonicated with a probe sonicator for 3 minutes. Dilutions were made, beginning with 10 mM, down to 100 nM or lower. No phosphate or other ionic buffers were used because these were found to increase agglomeration. All serial dilutions were sonicated for 3 minutes prior to use or to further dilution. Importantly, aged neurons and astrocytes were functionally equivalent to their younger, untreated, counterparts. Neurotransmission in response to glutamate, GABA, and acetylcholine in cerium oxide nanoparticle-treated aged cultures w...
example 2
Free Radical Scavenging Capacity of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
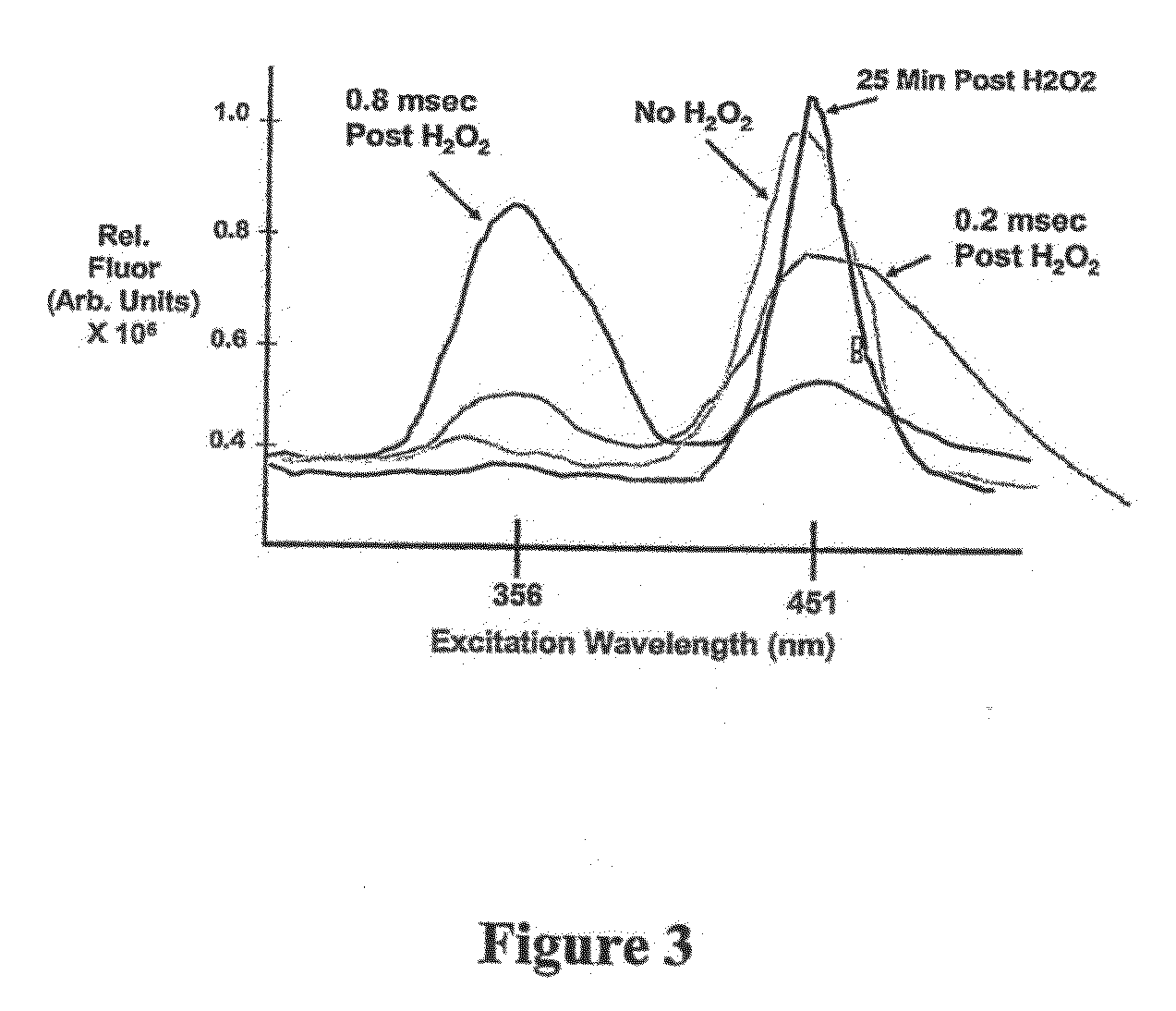
[0082]Given the structure of cerium oxide nanoparticles, we hypothesized that cerium oxide nanoparticles promoted cell longevity by acting as free radical scavengers. To test this hypothesis, we exposed cultured brain cells to lethal and sub-lethal doses of the free radical generating agents, hydrogen peroxide, and UV light. Exposure to cerium oxide nanoparticles afforded significant protection against both of these free radical generating agents, and reduced cell death in excess of 60%. Protection against UV and hydrogen peroxide-mediated injury was preserved in 3 month old cultures that had been treated with cerium oxide nanoparticles on day 10 in culture. Thus, the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles are long-lasting, following a single dose.
[0083]Studies comparing the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles to the traditional free radical scavengers Vitamin E, melatonin, and N-acetyl-cysteine demonstrated that only ce...
example 3
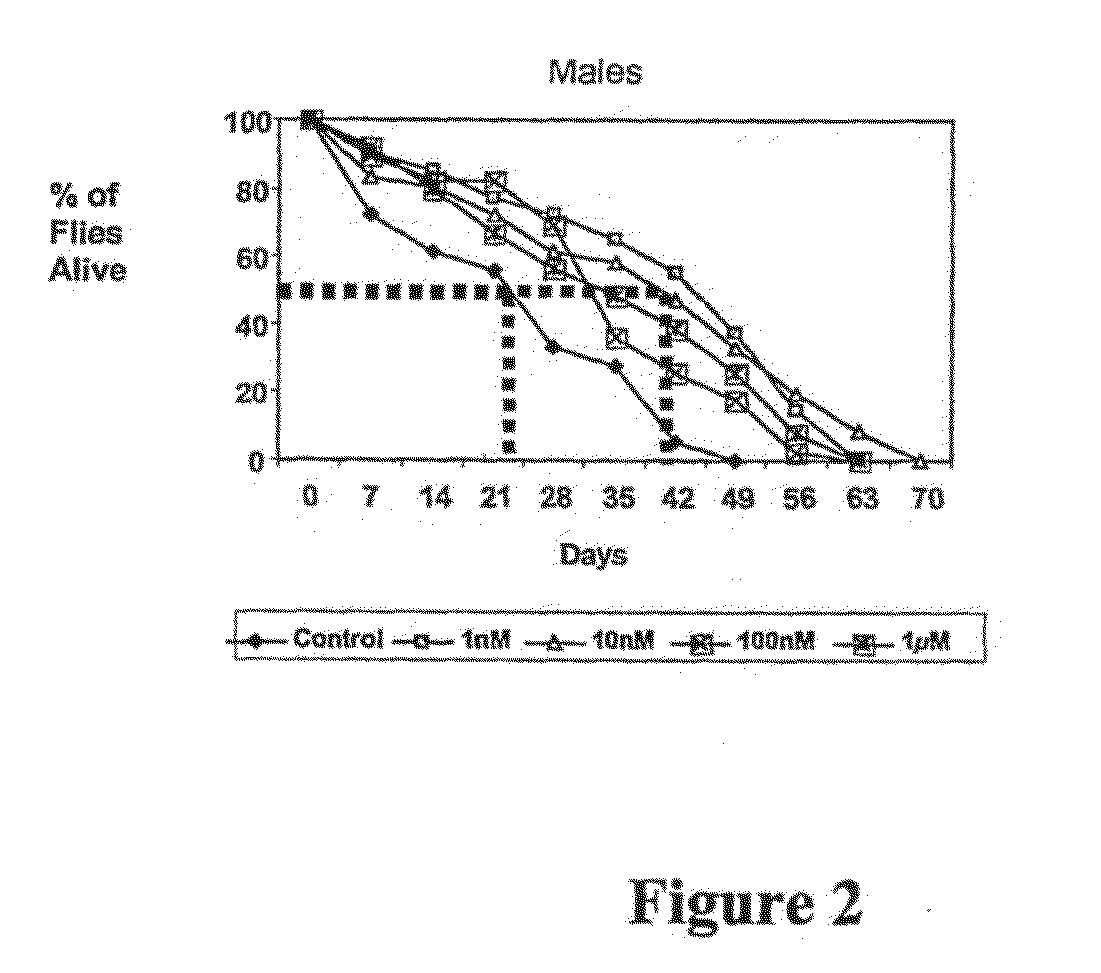
[0086]Using electron microscopy, microspectrophotometry, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, we found that cerium oxide nanoparticles of size less than 20 nm readily enter cultured cells and cells of living organisms. Further, doses as high as 100-fold of that which extend cell culture lifespan exhibited no overt toxicity in Drosophila. A single tail vein injection of 0.3-3 mM in the mouse produced no overt organ or behavioral abnormalities. Cerium oxide nanoparticles were found to accumulate preferentially in brain, heart, and lung with little excretion over a 6 month time period. At the 0.3 mM dose, tissue cerium levels approximately doubled (as compared to background), but remained in the parts per billion range.
[0087]FIG. 4 depicts the results of tissue cerium measurements of mice treated with nanoparticles. More specifically, Balb / c mice were administered 5-10 ul tail vein injections each containing 300 nmoles cerium oxide nanoparticles...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com