Method for separating cell from biological tissue
a biological tissue and cell technology, applied in cell dissociation methods, instruments, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to identify the specific type of collagen and difficult to produce antibodies, and achieve the effect of high biological activity and efficient and stable cell separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
Identification of Major Protein-Degrading Enzyme to be Used in Separating Cells or the Like from Biological Tissue>
[0069][Identification of Enzyme for Use in Separating Pancreatic Islets from Rat's Pancreas Tissue]
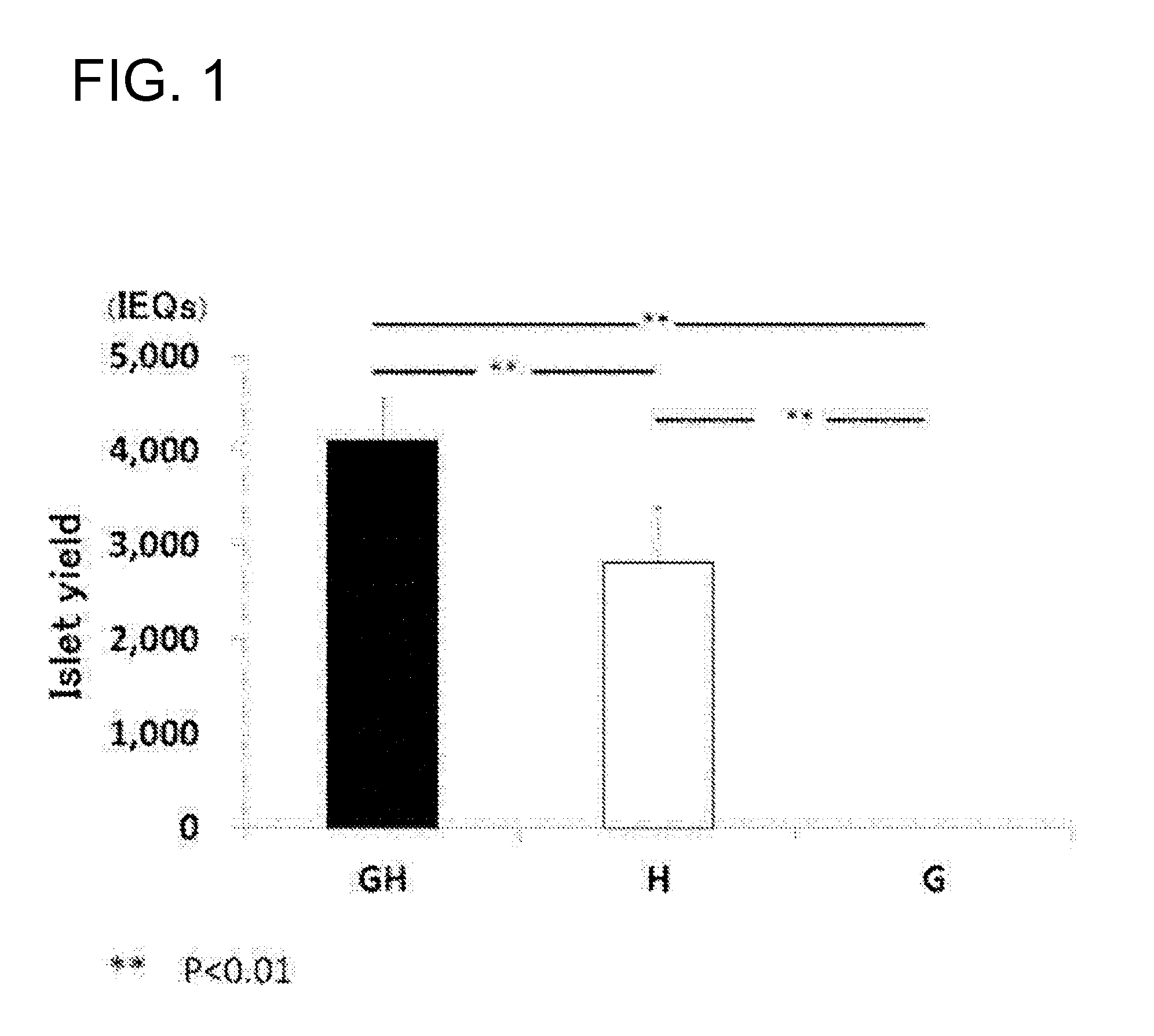
[0070]A male Lewis rat (10 to 13 weeks old) was used. Before the pancreas was excised out, the duodenum was clamped. A degrading-enzyme composition (10 mL, cold Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS)), which contains at least one of a protein-degrading enzyme: recombinant collagenase G (8.4 mg) and collagenase H (2.9 mg), and a neutral protease: thermolysin (0.3 mg), was injected through the bile duct. After a treatment was performed at 37° C. for 14 minutes, density gradient centrifugation was performed to obtain a fraction of pancreatic islets.
[0071]The case (GH group) where thermolysin, collagenase G and collagenase H were simultaneously added, the case (G group) where thermolysin and collagenase G alone were added, and the case (H group) where thermolysin and collagenase...
reference example 2
Identification of Substrate for Major Protein-Degrading Enzyme
[Identification of Substrate for Collagenase H]
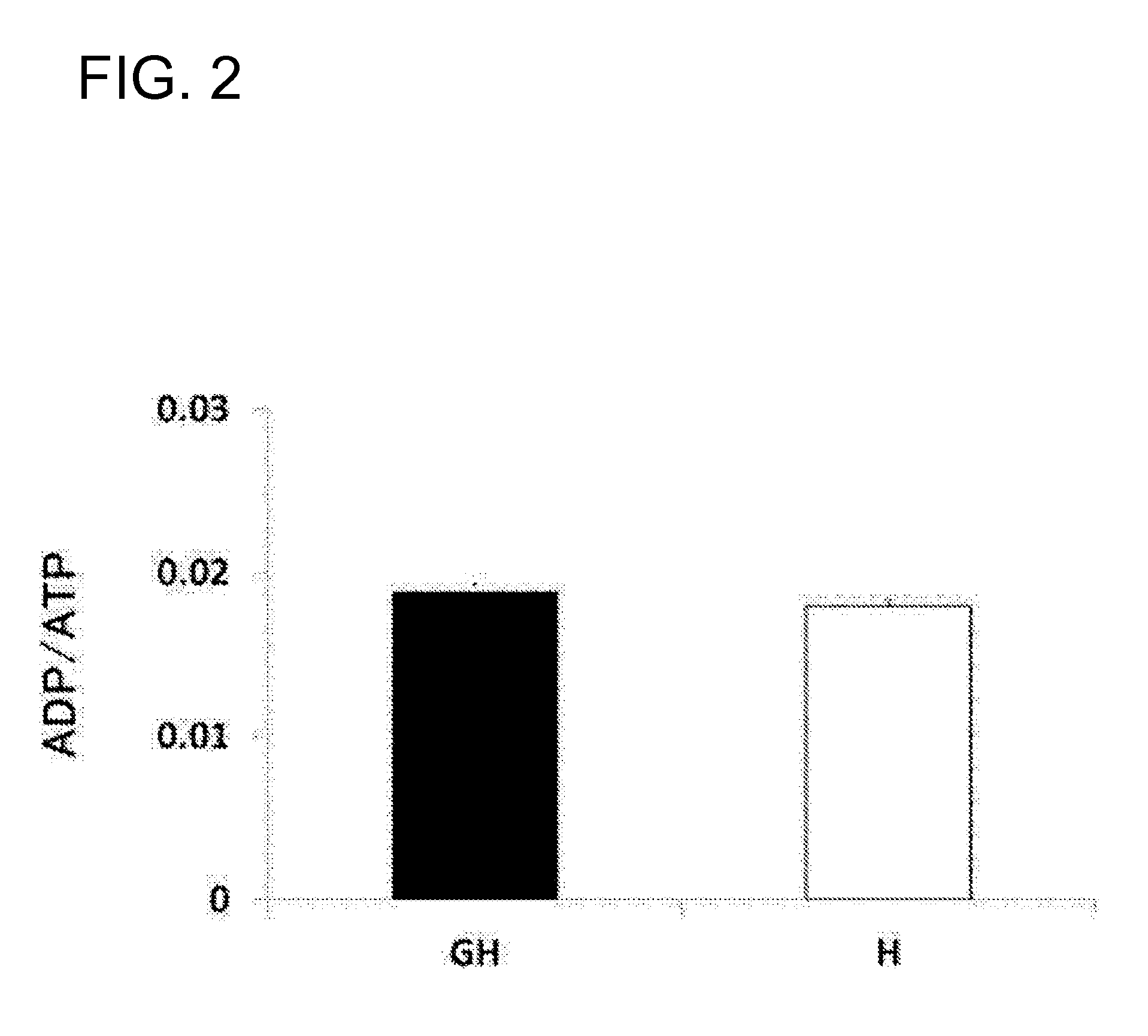
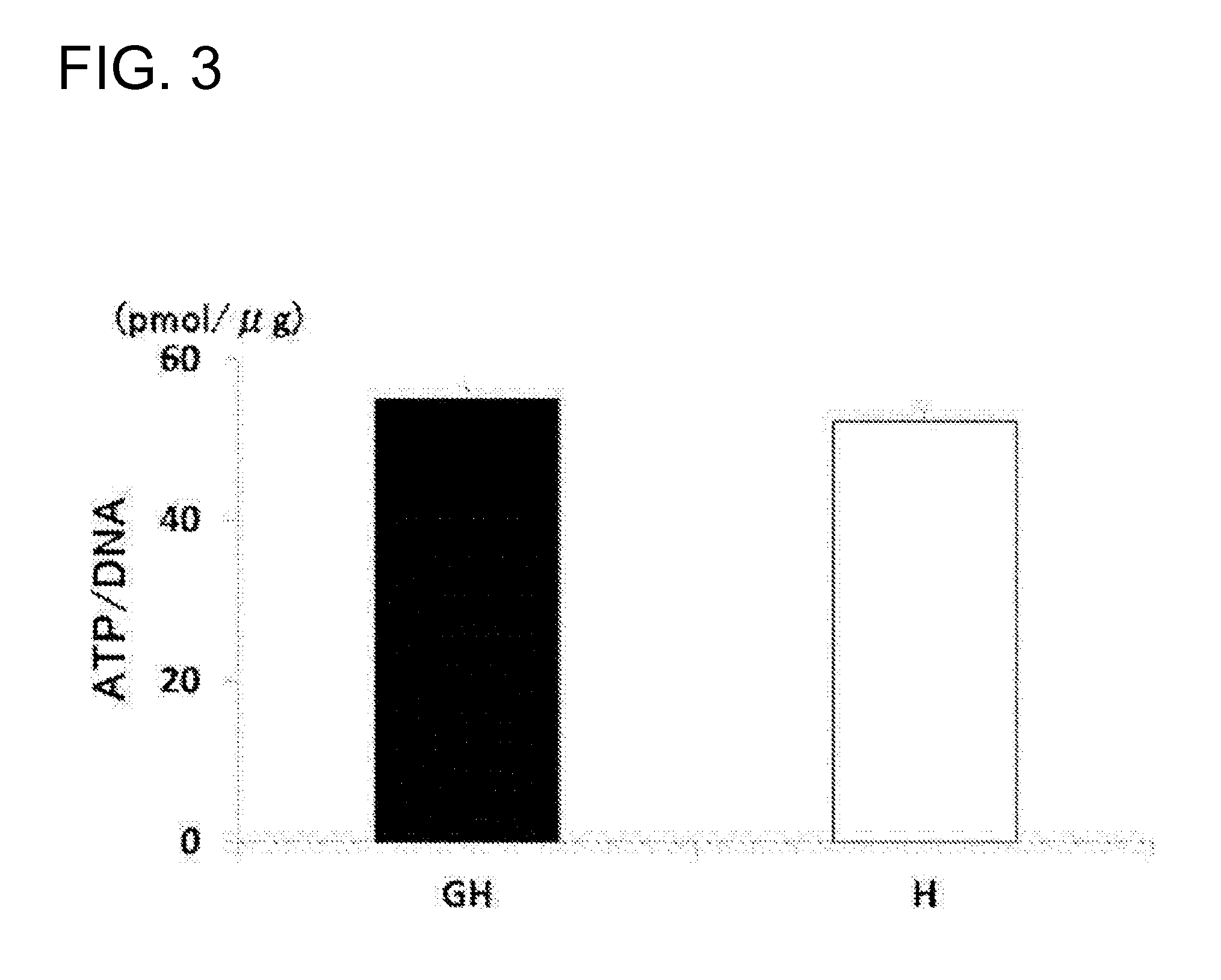
[0075]The pancreas tissue slices (100 mg) of a Lewis rat were treated with 20 mM HEPES (pH 8.0) containing a protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and 1 mM CaCl2 at 37° C. overnight. Thereafter, the tissue slices were washed with a buffer and subjected to enzyme degradation with a buffer containing collagenase H (0.1 mg / mL) for 10 hours at 37° C.
[0076]After the enzyme degradation, incubation was performed in 50% acetonitrile containing 100 mM TMPP (Sigma-Aldrich) (10 μL) for 30 minutes. Then, acetone precipitation was performed with cold acetone and thereafter centrifugation was performed. The resultant precipitate was dried and digested with trypsin (10 μL / mg) in a 100 mM ammonium carbonate solution, overnight.
[0077]After the digest was treated by ZipTip (Millipore), the resultant peptides were eluted by concentration gradient with 2.5-40% acetonitrile in 10% formic acid and s...
example 1
Separation of Cells Depending Upon the Composition of Major Protein of Biological Tissue
[Quantification of Collagen III and Collagen I in Pancreas Tissue and Liver Tissue of Rat]
[0080]Tissue slices of a Lewis rat (10 to 13 weeks old) were prepared. Enzymatic immunoassay using labeled antibodies (Chemicon Merck Millipore) against collagen III and collagen I was performed to compare expression of collagen III and collagen I in the pancreas tissue and liver tissue. As a result, the number of positive staining obtained by immunohistostaining of collagen III and collagen I in the liver tissue was significantly lower than that in the pancreas tissue.
[Separation of Cells from Pancreas Tissue and Liver Tissue of Rat]
[0081]It was predicted that the major protein of a liver tissue may be a protein other than collagen III and collagen I, and thus the amount of collagenase H in the degrading-enzyme composition for liver cell separation may be low compared to for pancreatic islet separation.
[008...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| protein composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com