Method For Manufacturing High Purity Tin, Electrowinning Apparatus For High Purity Tin And High Purity Tin
a technology of high purity tin and electrowinning apparatus, which is applied in the direction of electrolysis components, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of complicated method for manufacturing high purity tin disclosed in patent literature 1, and always taking into the cathode. , to achieve the effect of improving the productivity of tin, reducing manufacturing cost, and high purity tin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
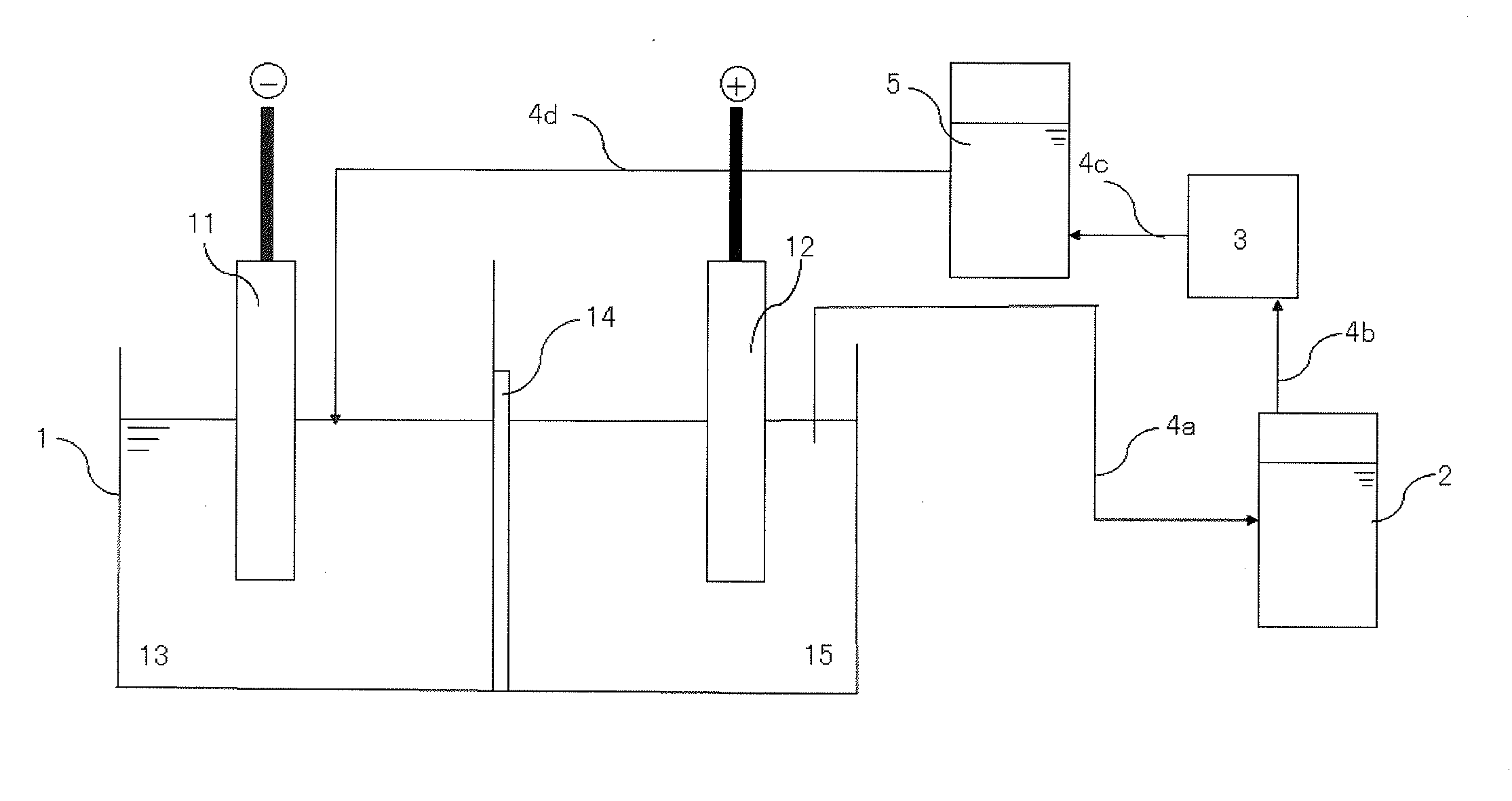
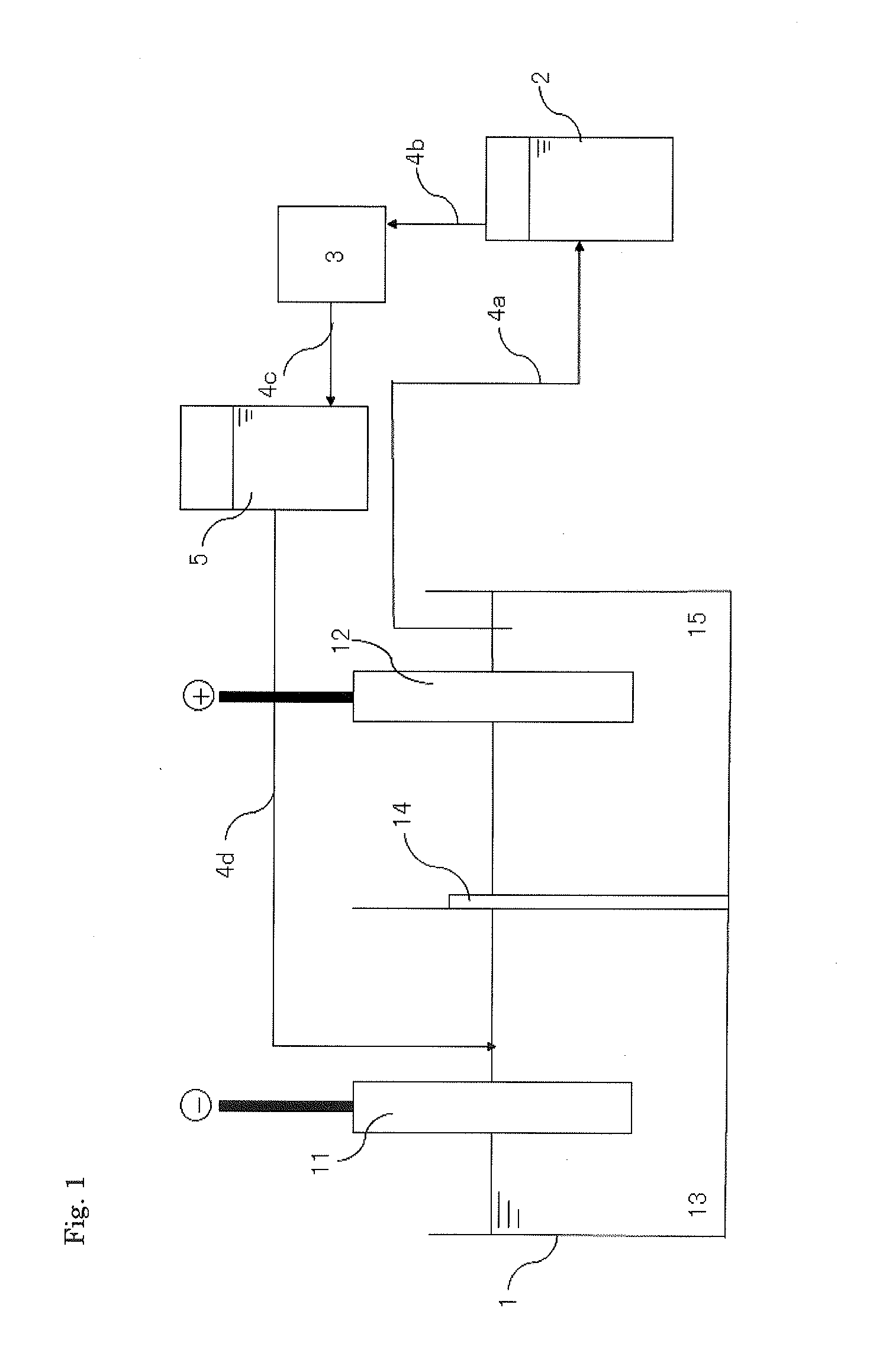
[0066]A predetermined amount of a sulfuric acid solution was added to a cathode side and a dilute sulfuric acid solution of pH 0.5 was added to an anode side of an electrolytic bath of which a cathode and an anode were partitioned by an anion exchange membrane (SELEMION AMV manufactured by ASAHI GLASS CO., LTD.). In addition, hydroquinone was added as an antioxidant into an anode side electrolytic solution such that the concentration was 5 g / L in the electrolytic solution. An anode obtained by casting a raw material for tin and a cathode made of titanium were placed in the electrolytic bath, respectively, and electrolytically leaching was performed at a current density of 2 A / dm2 and a solution temperature of 33° C. to give an electrolytic solution of tin sulfate (with a concentration of tin of 105 g / L).
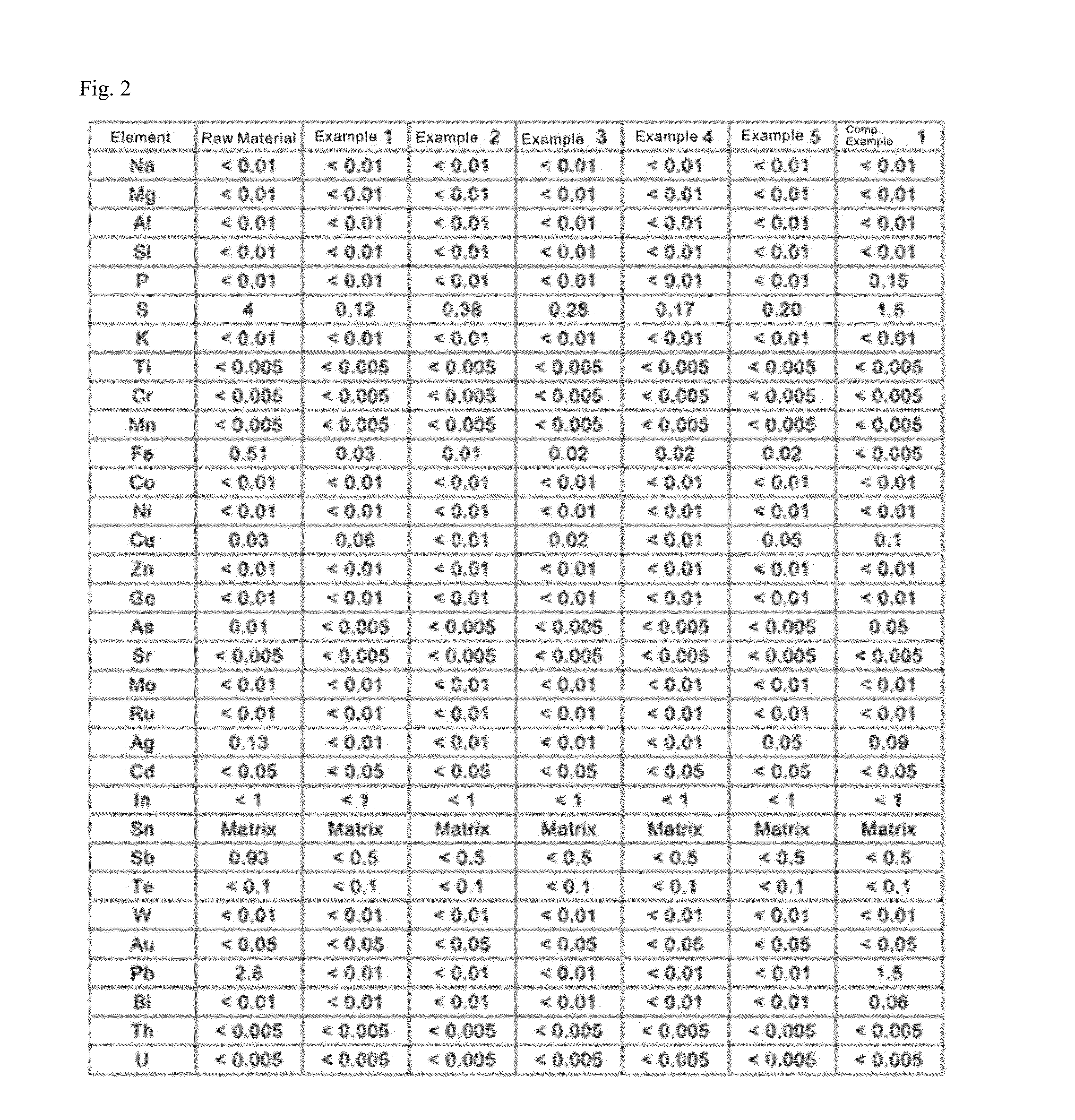
[0067]A result of analysis of the raw material for tin (raw material) used as the anode is shown in FIG. 2.
[0068]A portion of the electrolytic solution in the anode chamber was disch...
example 2
[0072]In Example 1, the concentration of tin in the electrolytic solution in the anode chamber after completing electrowinning was 94 g / L and pH of this solution was pH 0.54. This electrolytic solution in the anode chamber was discharged, and was supplied to the tank for solution purification in which lead is removed. Powdery strontium carbonate was added to the tank for solution purification such that the concentration of strontium carbonate was 5 g / L in the electrolytic solution, and the resulting solution was stirred for 16 hours. After stirring, the electrolytic solution was subjected to solid-liquid separation by sucking filtration in order to remove lead as a precipitate in the electrolytic solution.
[0073]Next, a post treatment solution containing the smoothing agent which had been obtained in the cathode chamber by electrowinning of Example 1 was added back to the anode side of the electrolytic bath such that the reduced amount corresponding to the discharged electrolytic sol...
example 3
[0075]In Example 2, the concentration of tin in the electrolytic solution in the anode chamber was 100 g / L and pH of this solution was pH 0.63 after completing electrowinning. The solution purification processing was performed in a similar manner to Example 2 except that the added amount of strontium carbonate was 10 g / L. The electrolytic solution from which lead had been removed had the concentration of lead of less than 0.1 mg / L.
[0076]Next, a post treatment solution containing the smoothing agent which had been obtained in the cathode chamber by electrowinning of Example 2 was added back to the anode side of the electrolytic bath such that the reduced amount corresponding to the discharged electrolytic solution was supplemented.
[0077]Then, the electrolytic solution from which lead had been removed in the tank for solution purification was added into the cathode side chamber. The smoothing agent added in Example 1 was not decomposed in the cathode chamber in the electrolytic bath a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com