Patents
Literature
36 results about "Upper Case Letter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
One of the large alphabetic characters used as the first letter in writing or printing proper names and sometimes for emphasis.
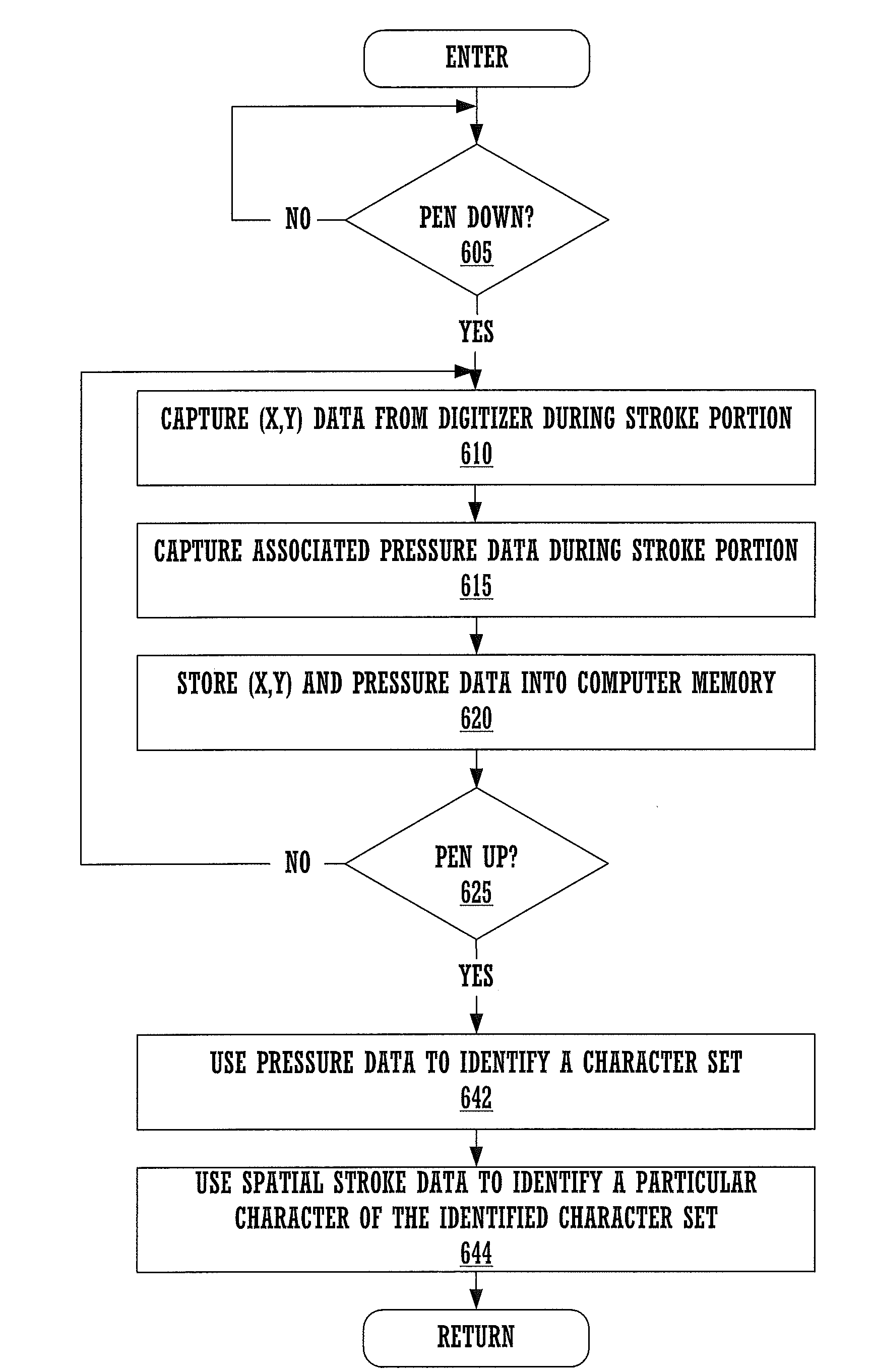
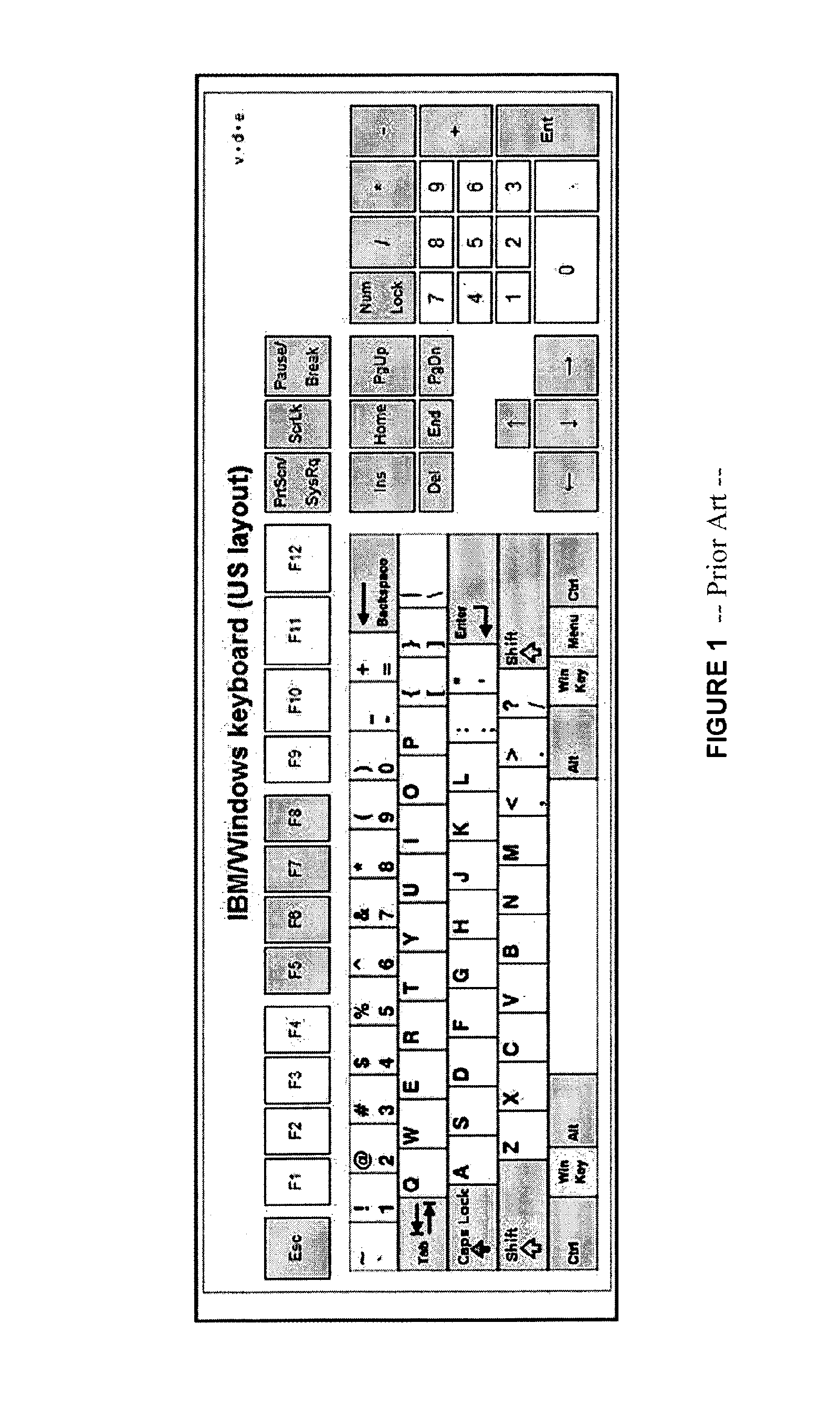
Method and apparatus for using pressure information for improved computer controlled handwriting recognition data entry and user authentication
InactiveUS20090202153A1Data augmentationNot alleviating taskProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsHandwritingHeuristic
A method and system utilizing both (x, y) coordinate (“spatial”) stroke data and associated pressure information for improved handwriting recognition. The method and system can also be applied to all types of handwriting-based data entry applications and also to user authentication. The digitizer pad used in the computer system gives both spatial information and associated pressure data when a stroke is being drawn thereon, e.g., by a stylus. Pressure information can be used to differentiate between different character sets, e.g., upper case and lower case characters for certain alphabetic characters. The spatial stroke data then identifies the particular character. The pressure information can also be used to adjust any display attribute, such as character font size, font selection, color, italic, bold, underline, shadow, language, etc. The associated pressure information can also be used for recognizing a signature. In this case, a user is allowed to sign a name on the digitizer pad. This provides non-character based user authentication that relies not only on the spatial stroke data but also on the pressure applied at different points in the signed name or image. Pressure information can also be used to provide improved handwriting-based data entry. For instance, in a drafting program, the pressure of a drawn line can be used to determine its width. Generally, pressure data can also be used to improve handwriting recognition tasks and heuristics.
Owner:ACCESS SYSTEMS AMERICAS
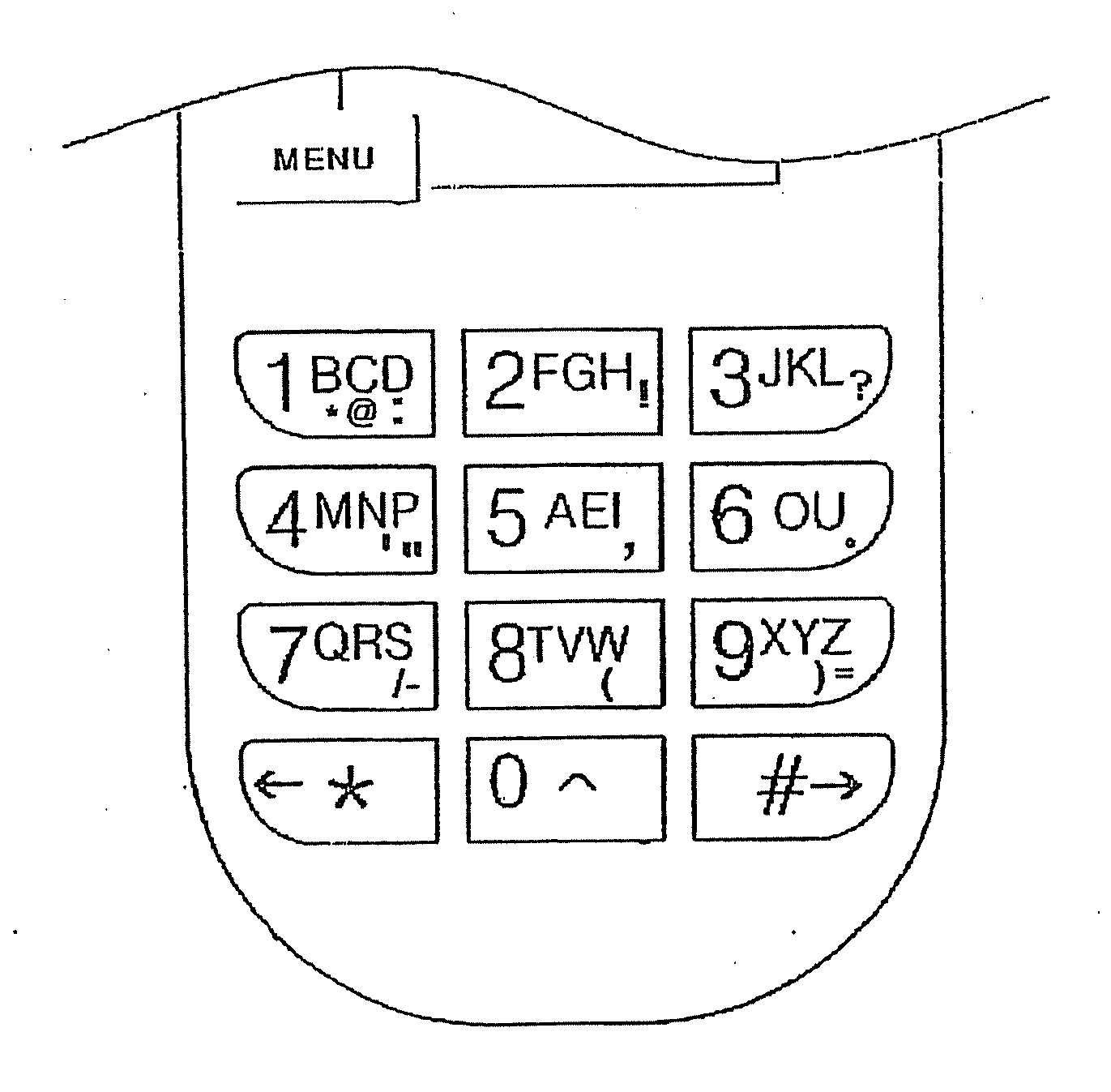
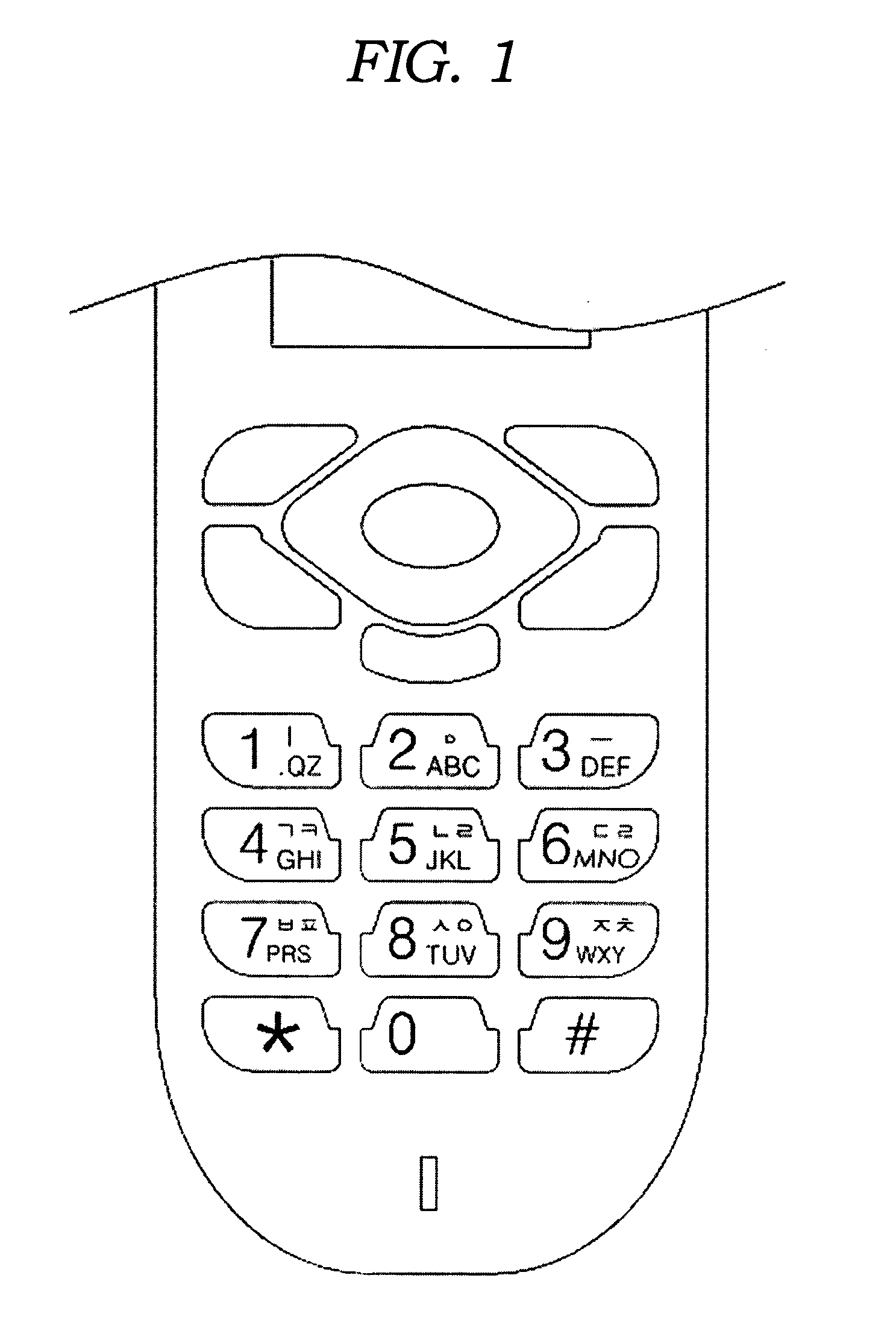
Device for inputting english characters for a mobile communication terminal, and method for same
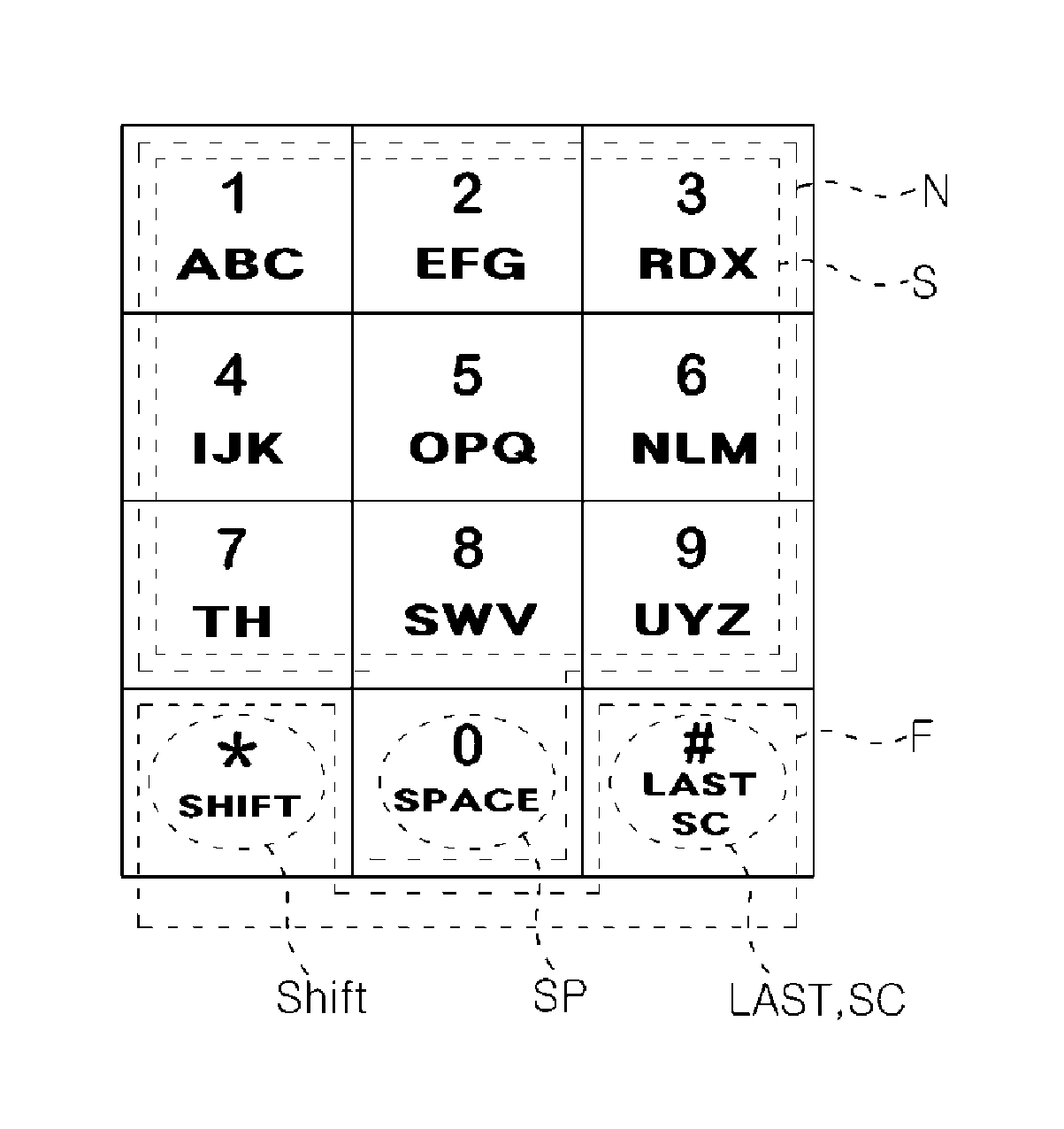
InactiveUS20120188168A1Easy and fast mannerConveniently positionInput/output for user-computer interactionAlphabetical characters enteringEmbedded systemInput device
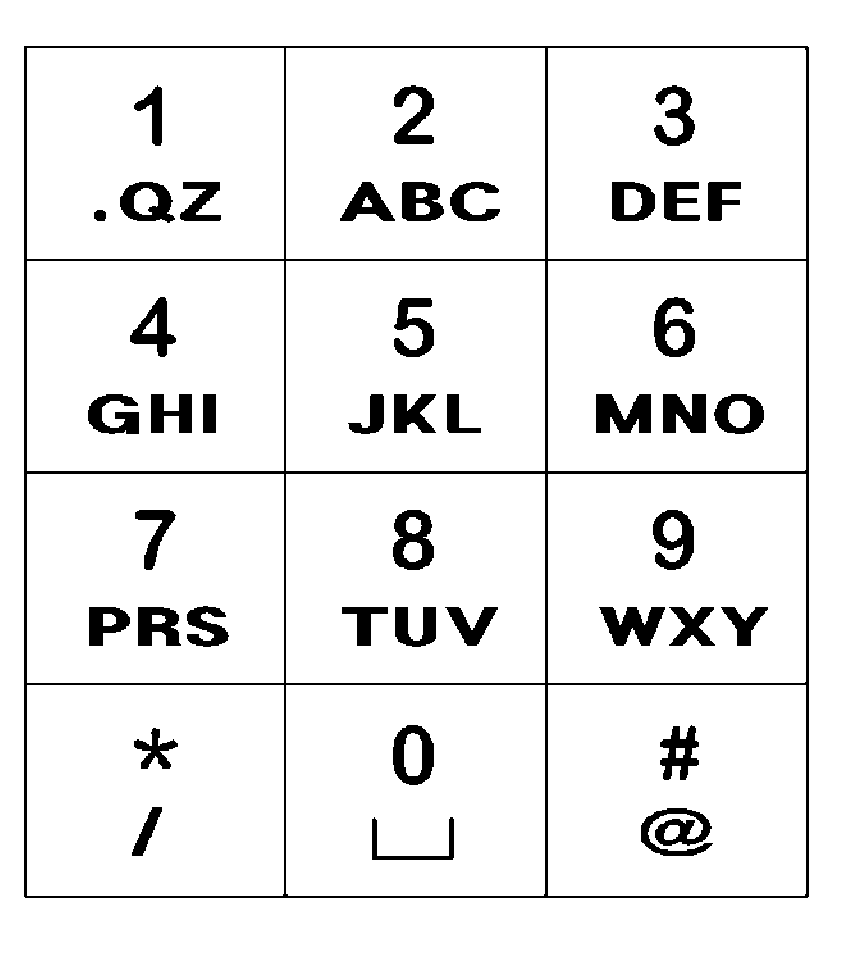
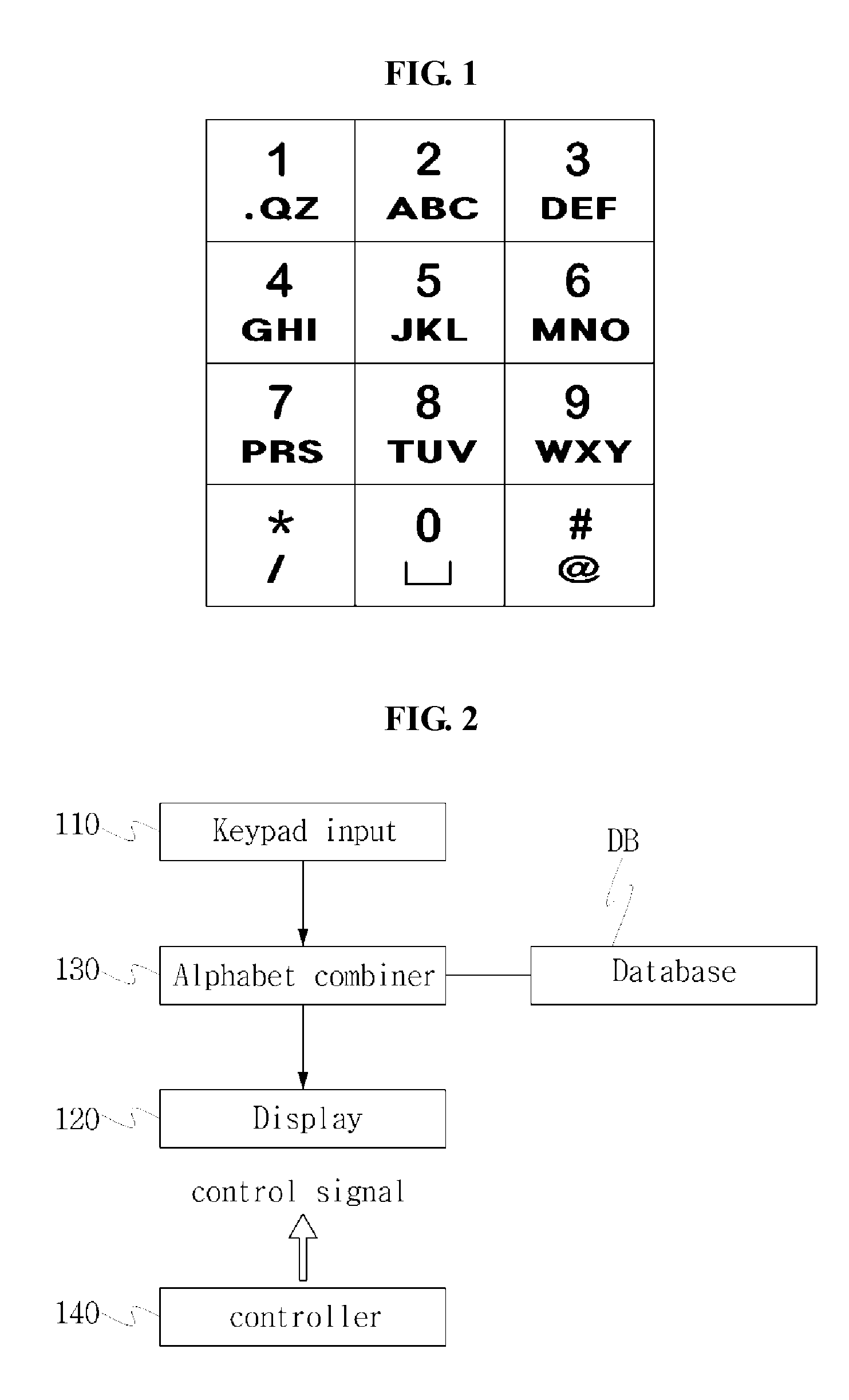
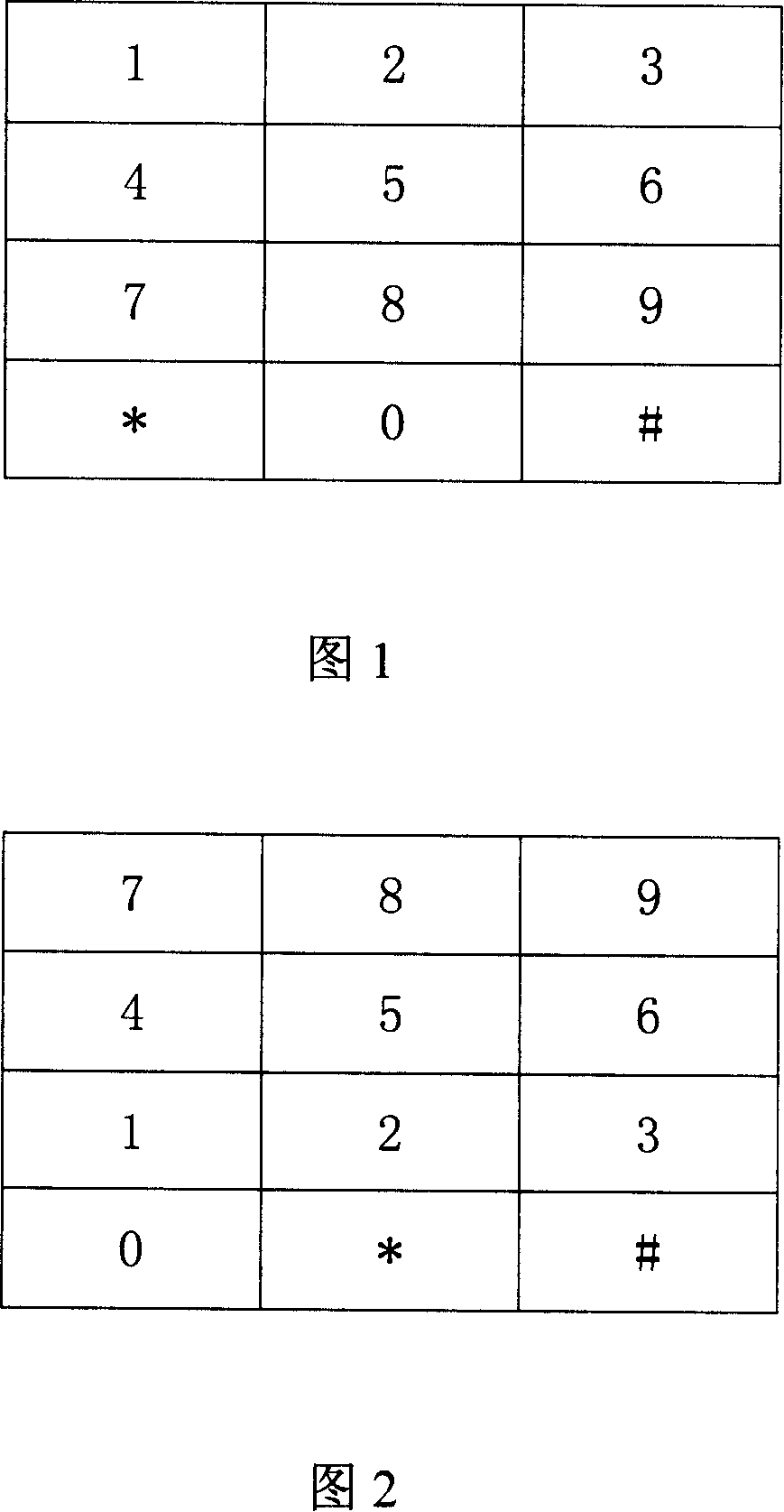
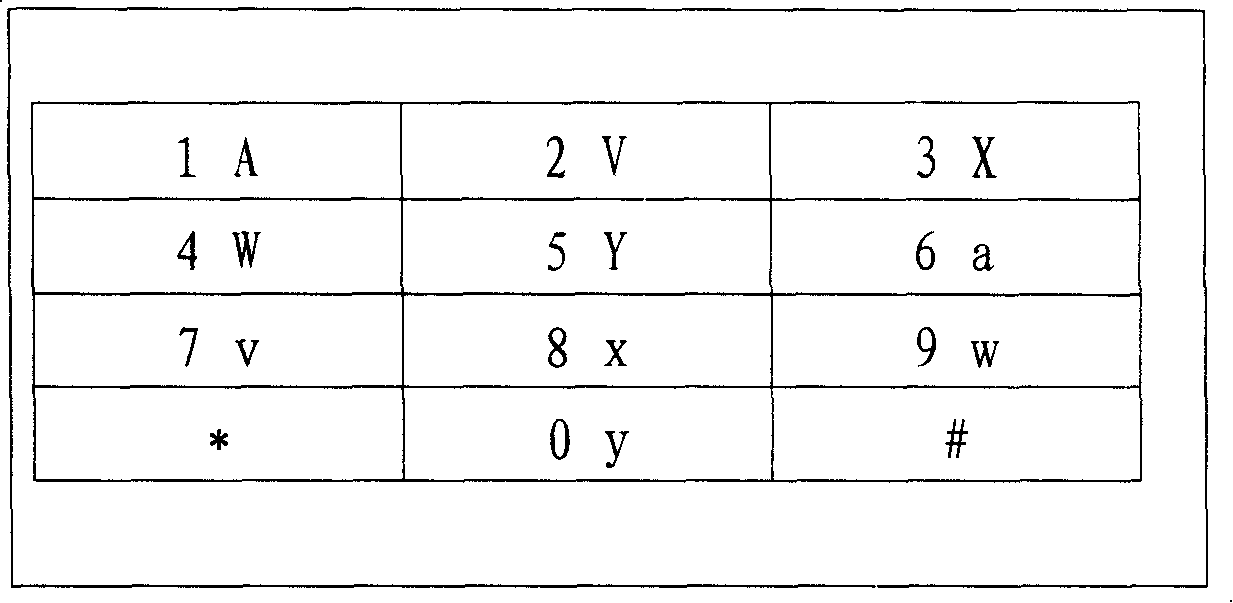
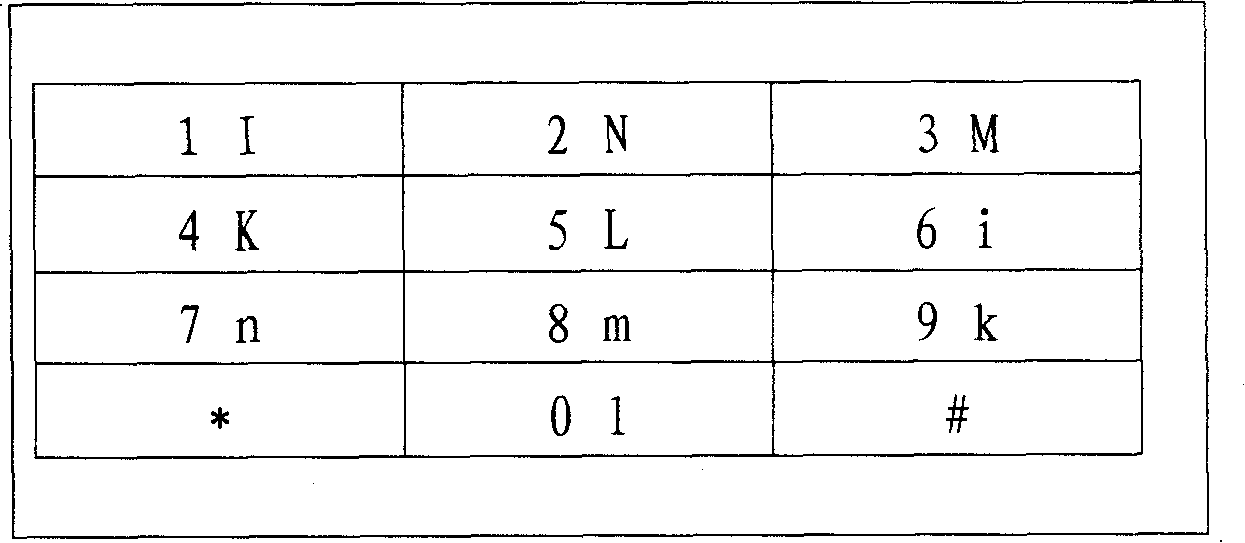
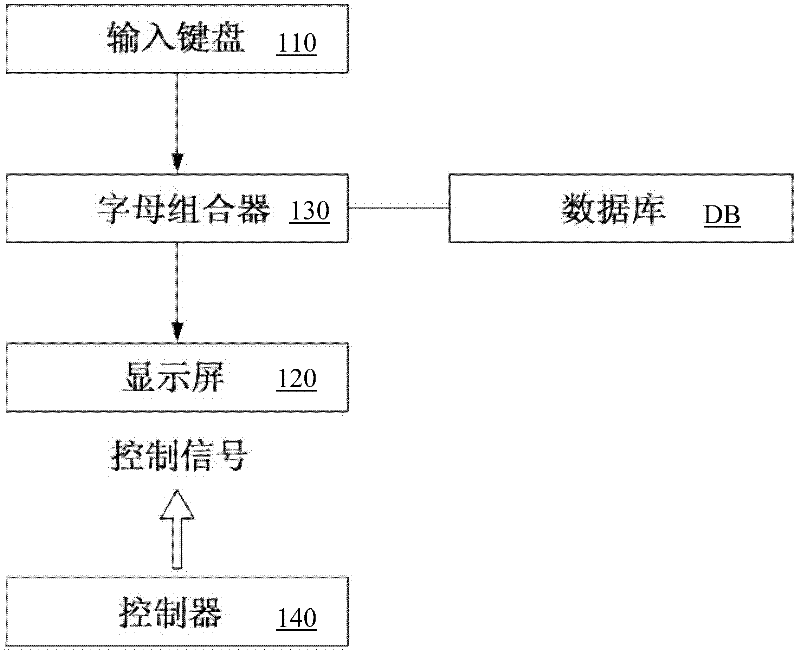
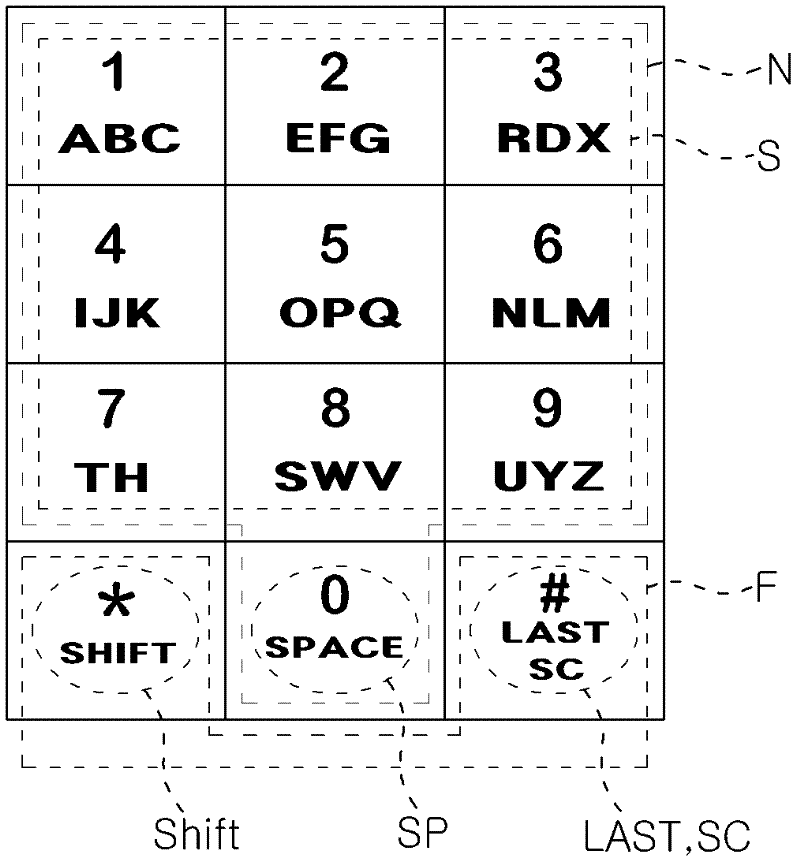
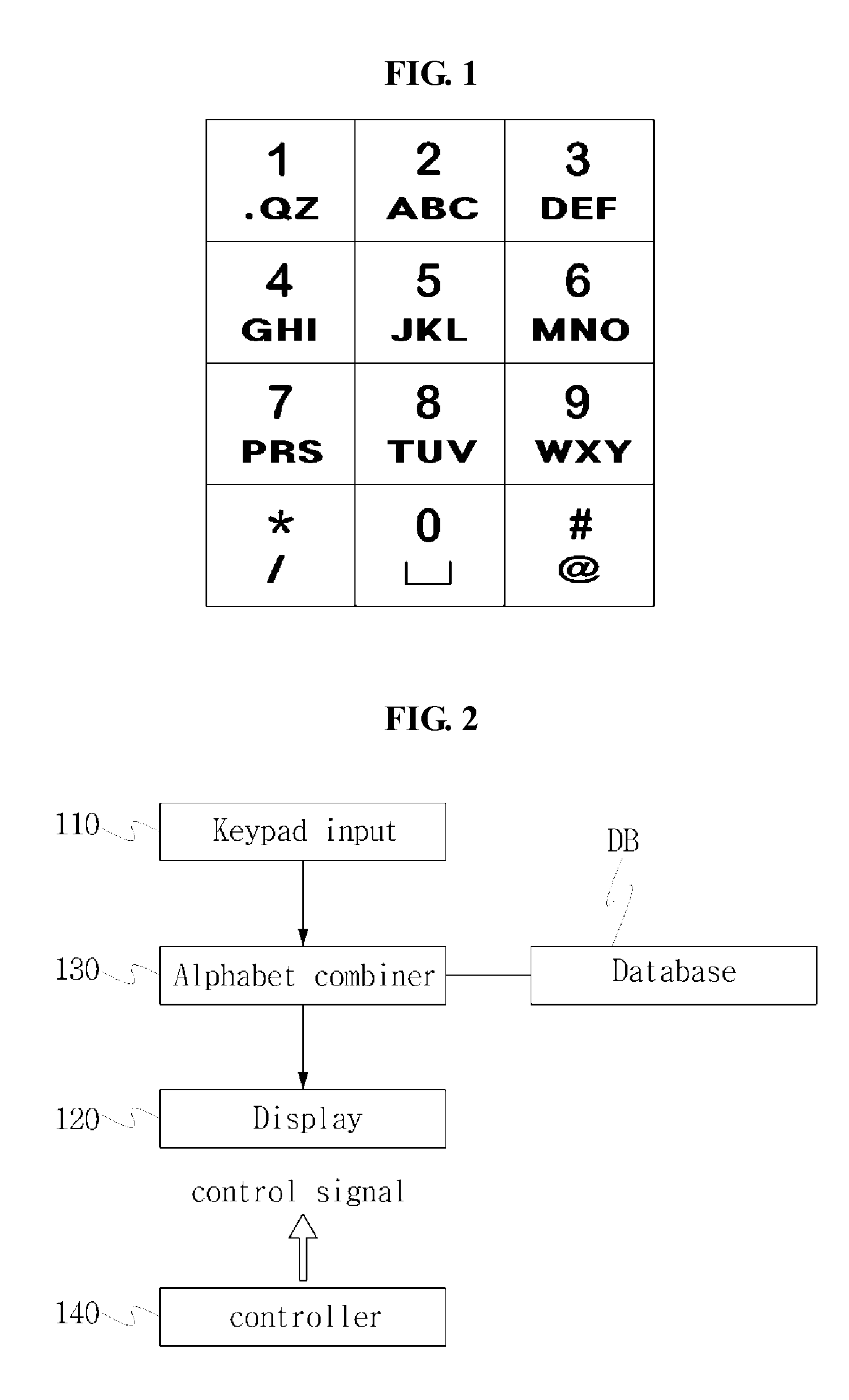
According to the present invention, an alphabet input device of a mobile communication comprises a keypad input including a plurality of keys for inputting alphabets; a display for displaying alphabets inputted by said keypad input; an alphabet combiner for reading the alphabet corresponding to the input of the keypad input from pre-stored database and providing the display with said alphabet from said database; and, a controller coupled to said keypad input, said display and said alphabet combiner so as to control thereof, wherein said keypad input has a 3×4 matrix which includes numeric keys distinguished by the numbers ‘0’ to ‘9’ and function keys distinguished by the characters ‘*’ and ‘#’, and said numeric keys for ‘1 ’ to ‘9’ are assigned with a plurality of alphabet buttons for inputting alphabets, wherein said numeric key for ‘0’ is assigned with a space button for inputting a blank, wherein one of said function keys for ‘*’ and ‘#’ is assigned with a last button for successive inputting of the alphabet and a special character button for inputting a special character, wherein the other of said function keys that does not assigned with said last button and said special character button is assigned with a shift button, which performs a function of character input mode-setting and word-shifting for setting a character input mode so as to allow inputting of the capital / small letter of alphabet and for shifting a word inputted beforehand between the capital letter and the small letter, and a function of character-shifting for shifting characters inputted beforehand one at a time.
Owner:YOON KI SUP
Electronic mail distribution via a network of computer controlled display terminals with interactive display interfaces offering a sender creating an E-mail message proposed recipients based upon E-mail wording
Sending E-Mail including the conventional implementation enabling the sender of an electronic mail document to specify users to receive the document; but, in addition, the process invites the sender creating the E-Mail to prompt the sender with more potential recipients as the sender, proceeds with the creation of the E-Mail message. An address book is maintained including the E-Mail addresses of a set of names of selected recipients who regularly receive E-Mail from the sender. Then, there is monitoring the text being entered for words with initial capital letters combined with an implementation responsive to the monitoring for determining if a located word with an initial capital corresponds to a name in said address book. The corresponding name to the designated recipients of the E-Mail message provided the sender interactively agrees to do so. Optionally, the system may be set up so the monitoring is for two consecutive words with initial capitals corresponding to the first and last name of a recipient in said address book.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method to animate on a computer screen a virtual pen which writes and draws
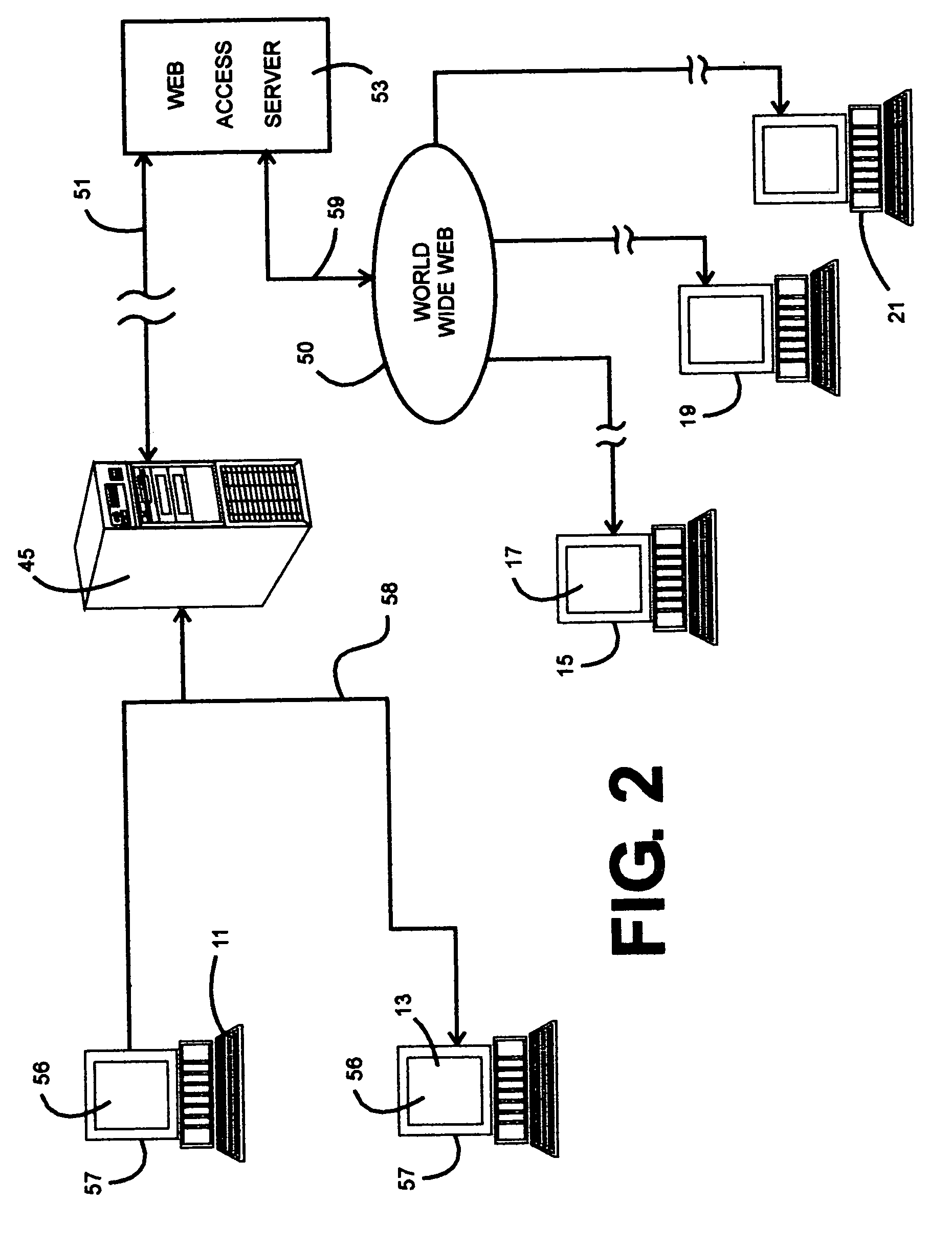
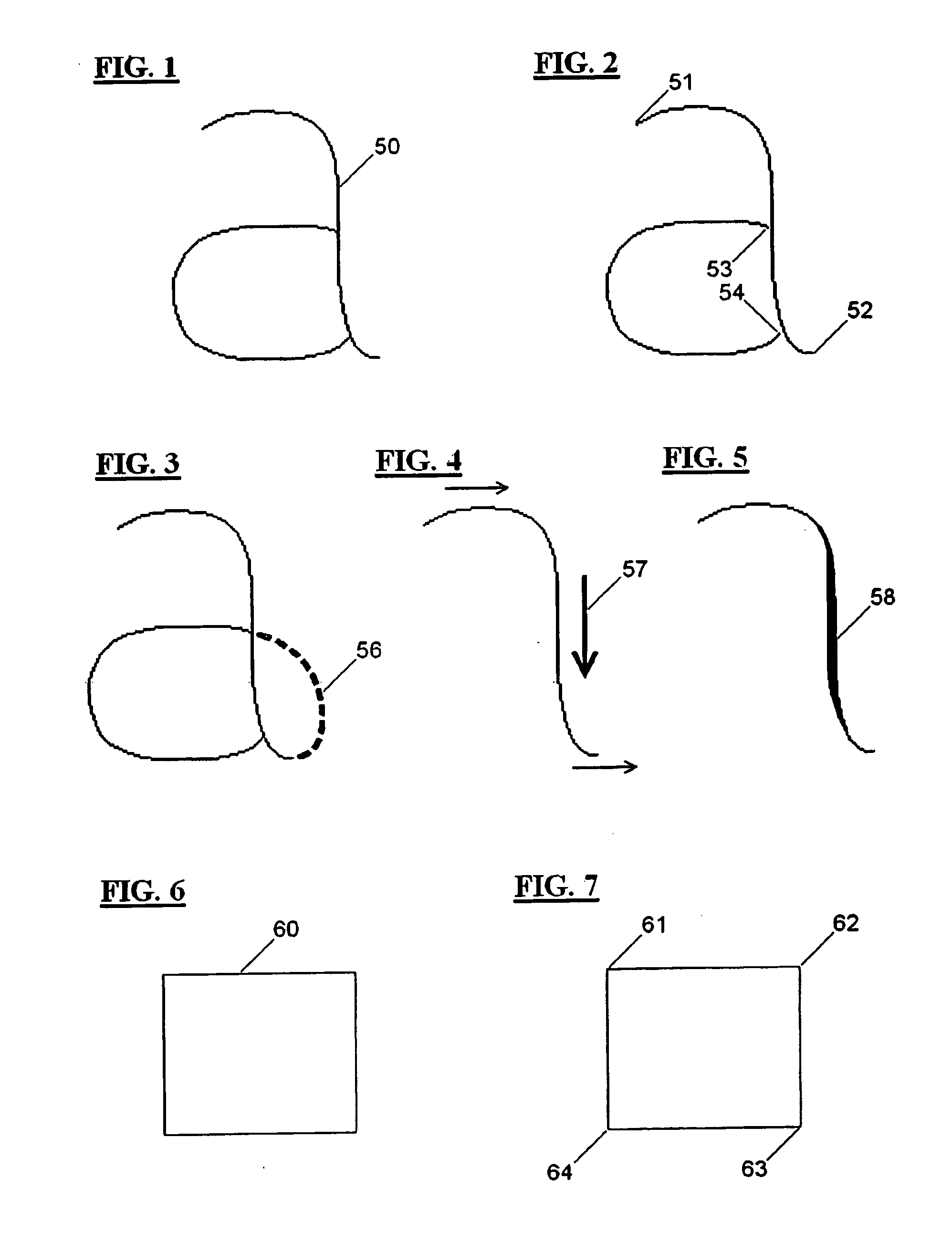
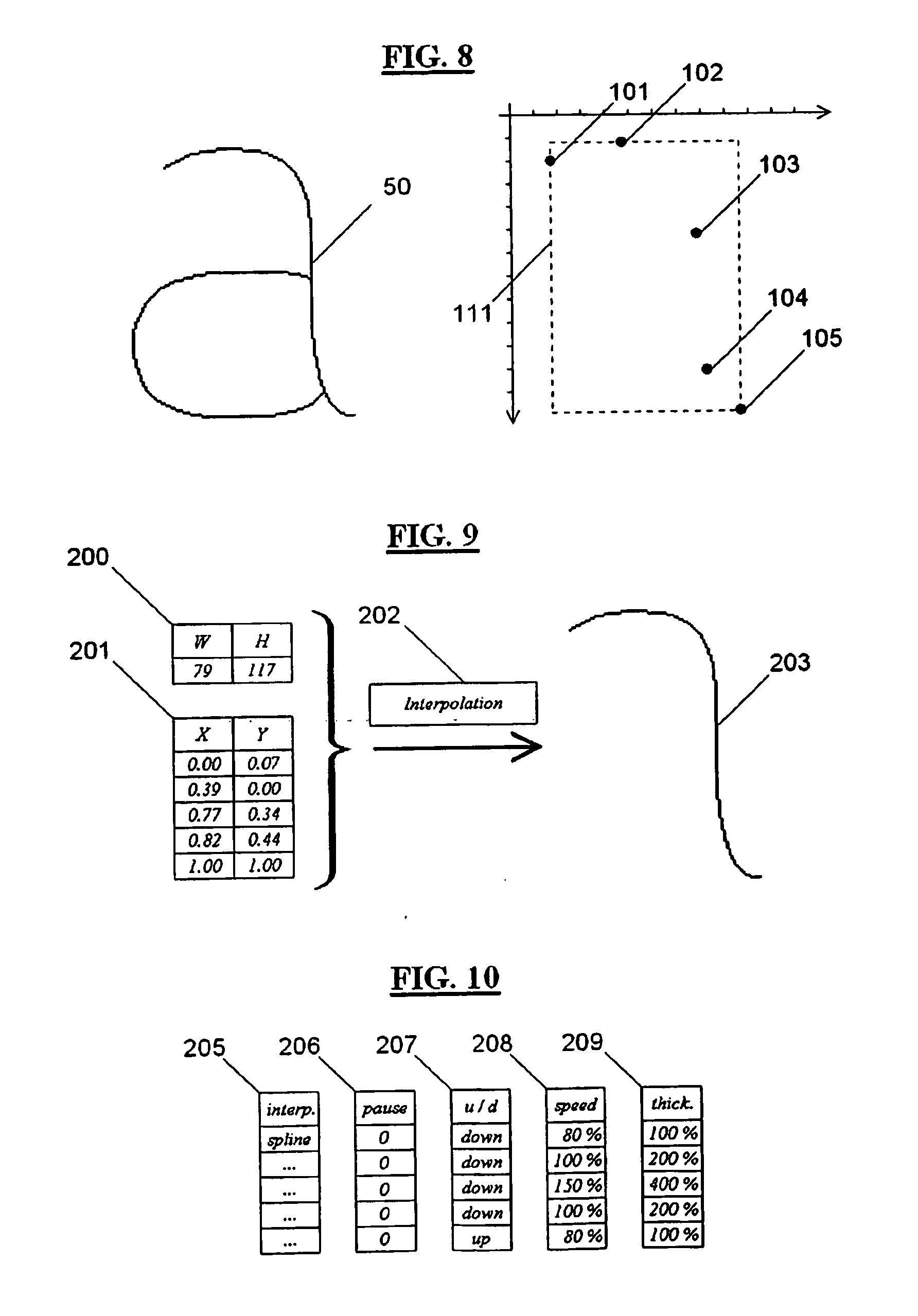
A method to animate on a computer screen a virtual pen which writes and draws on a virtual blackboard in order to simulate a real pen writing on a real blackboard. Graphemes and drawings (50) are created by specifying a subset of knot points (106, 107, 108, 109) from the set of points forming the lines (50) to draw. All the attributes concerning the knot points, as coordinates (201), pauses, speed, thickness, etc., are stored in a file. Subsequently the user types on the keyboard the word to write or selects from a list the drawing to draw. At this point all the attributes of the knot points of the graphemes to write or of the drawing to draw are retrieved from the file and interpolated, and the data obtained are used to animate a virtual pen in such a way it writes and draws looking like a real pen, pausing at the sharp angles, detaching from and landing on the writing surface of the virtual blackboard, varying the thickness and the speed of drawing, using block letters or joined-up writing.
Owner:PIRCHIO MARIO
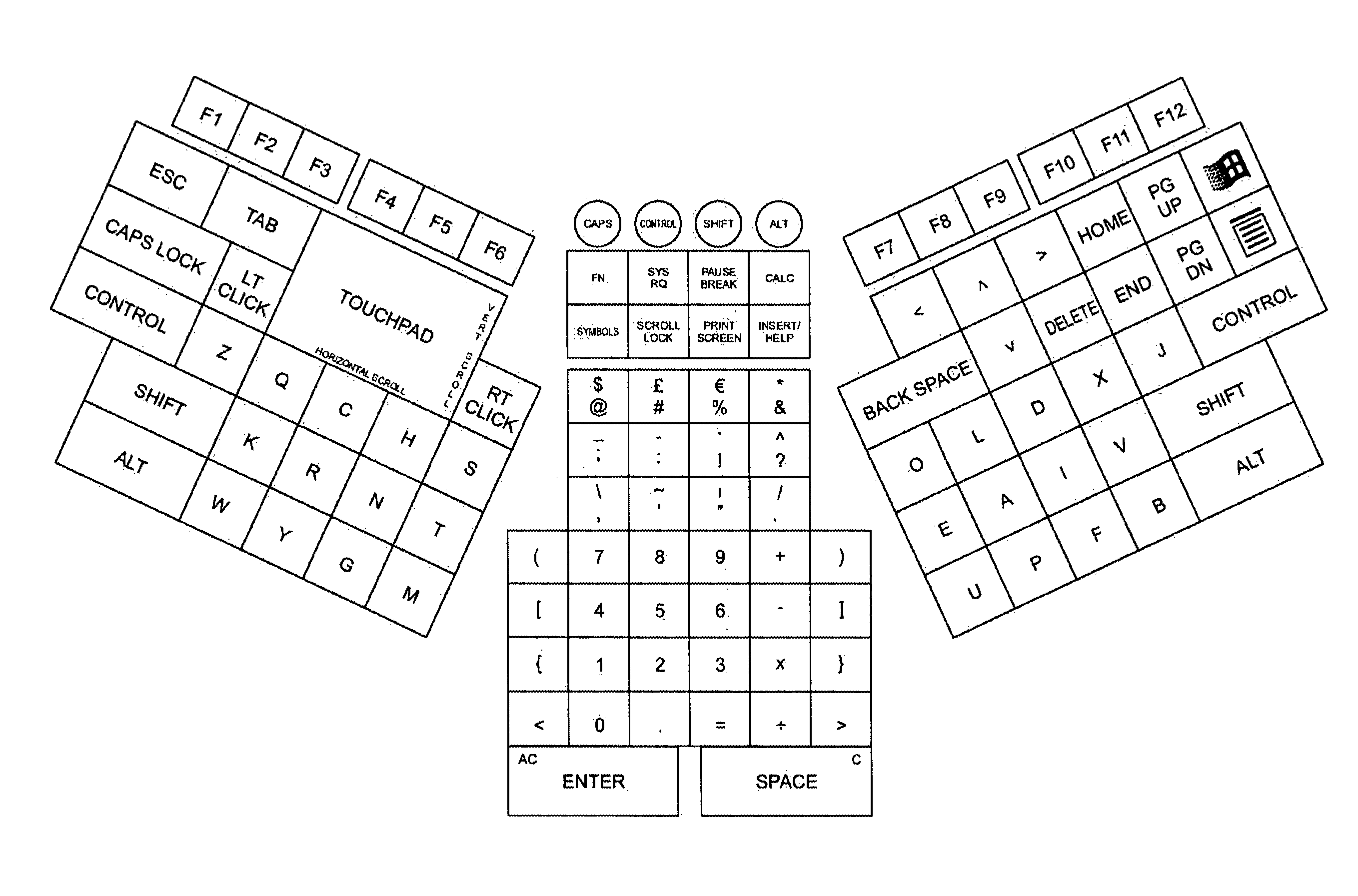
Data entry device (DED)
ActiveUS20120176310A1Easy to useInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsMathematical OperatorsUsability
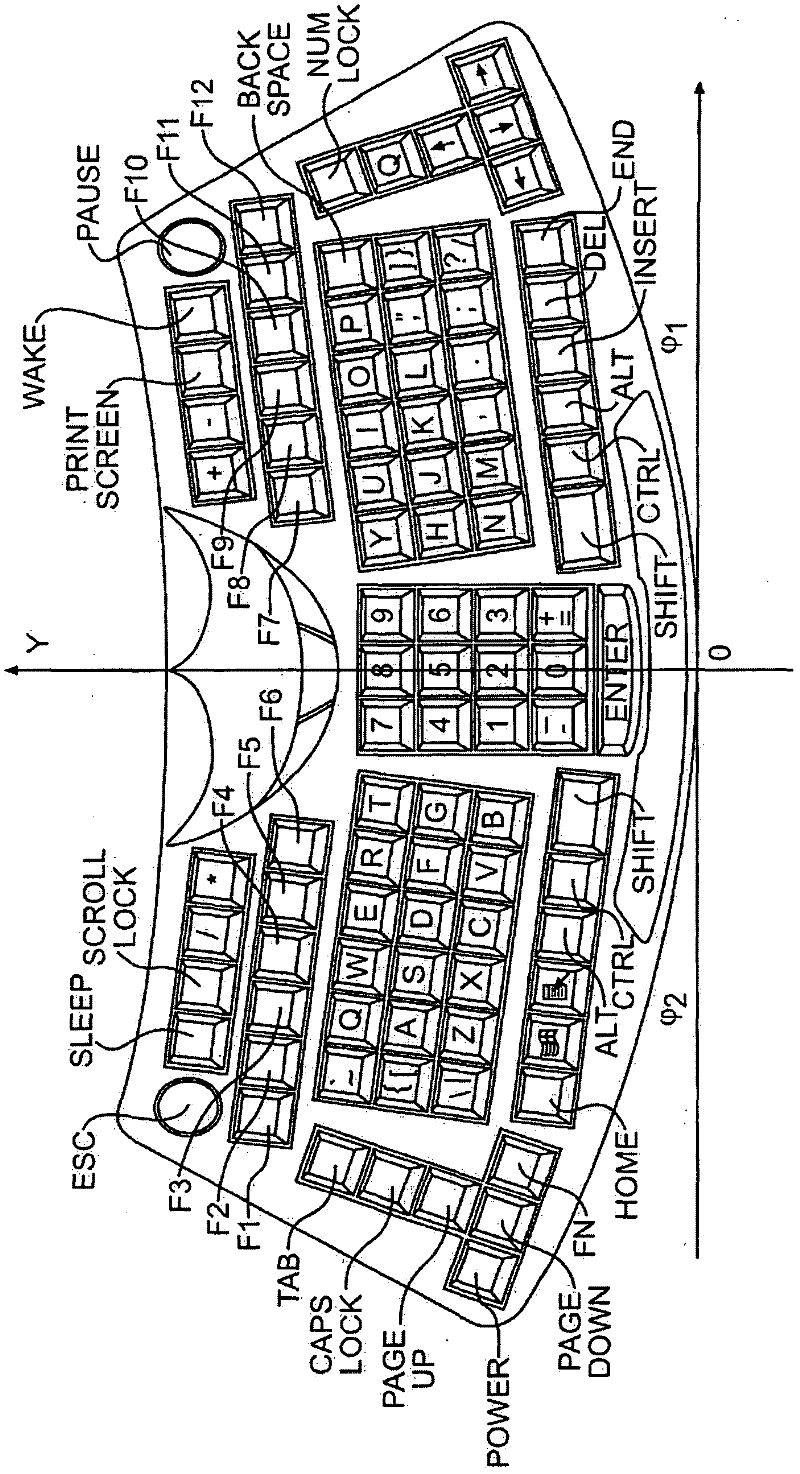
The present invention provides a Data Entry Device for computers and other devices. An embodiment of the present invention provides a Data Entry Device combining a keyboard and pointing device for computers and other devices; The Data Entry Device of the present invention introduces a completely new ergonomic construction for all keys. In the Data Entry Device of the present invention the keyboard and pointing device can both be used without shifting the hands from its initial resting position and where the shift key has to be used only for capitals and a few rarely used punctuations and symbols. The vowels are all on one side thus making them easy to access and use. All the letters are arranged so that on maximum occasions the letters are alternating between hands. The character keys are separated into alphabets, numerals, mathematical operators, punctuations and symbols. The placement of the characters on the DED is based on their frequency of occurrence in the environment, the ideal workload that should be allotted to each finger, the order of ease of use of keys, their pattern of use and similarity of type. In the present invention the concept of Home Row for fingers has been replaced by Home Keys for each finger being the keys on which the fingers tend to rest naturally and is not in one row. All this together makes the DED easy to comprehend, easy to learn, easy to use, more difficult to forget, increase the speed of typing, reduce errors and makes the user less prone to medical problems.
Owner:NAIR PREM KUMAR
Digital keyboard English and Chinese input method
InactiveCN101105718AStart fastEasy inputInput/output processes for data processingUpper Case LetterLatin script
The digit keyboard English and Chinese input method comprises the digit keyboard English letter input method and the Chinese character input method according to Pinyin; a digit keyboard in the invention has ten digit keys and at least two function key; twenty six Latin letters and Chinese Pinyin vowel ¿� are divided into six groups according to the font, pen type and structure character of uppercases; the single vowels of Chinese Pinyin A, O, E, I and U are taken as the first letters of each group and arrayed in order; the group number and the order number in a group of each letter constitute the double-number code of the letter. English letters or Chinese Pinyin characters can be directly input an electron equipment by the double-number code; in order to offer convenience for input operation, codes of different English big letters and different English small letters are equipped so that big letters and different English small letters can be directly input; codes of Chinese Pinyin double initial consonants and compound vowels are equipped so that Chinese characters and Chinese phases can be input swiftly; traditional Chinese characters and punctuation marks can be directly input. The digit keyboard English and Chinese input method has the advantages of quick access and convenient use; the user can input letters or characters into the electron equipment according to a screen only by remembering the first letters of six groups; the digit keyboard English and Chinese input method is suitable for the electron equipment equipped with digit keyboard.
Owner:桂林鑫鹰电子科技有限公司
Device for inputting English characters for a mobile communication terminal, and method for same
InactiveCN102474539AContinuous input operationQuick input operationInput/output for user-computer interactionAlphabetical characters enteringKey pressingComputer network
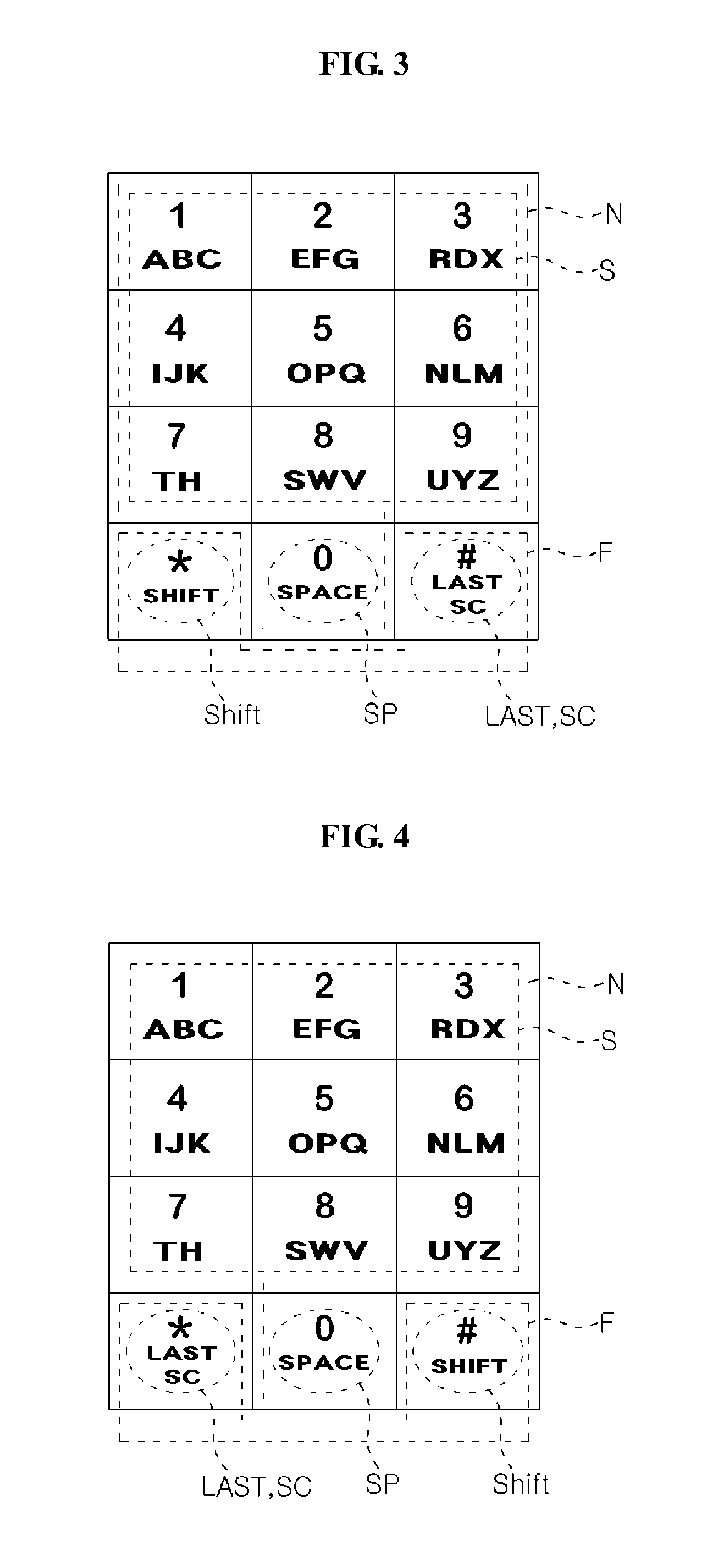
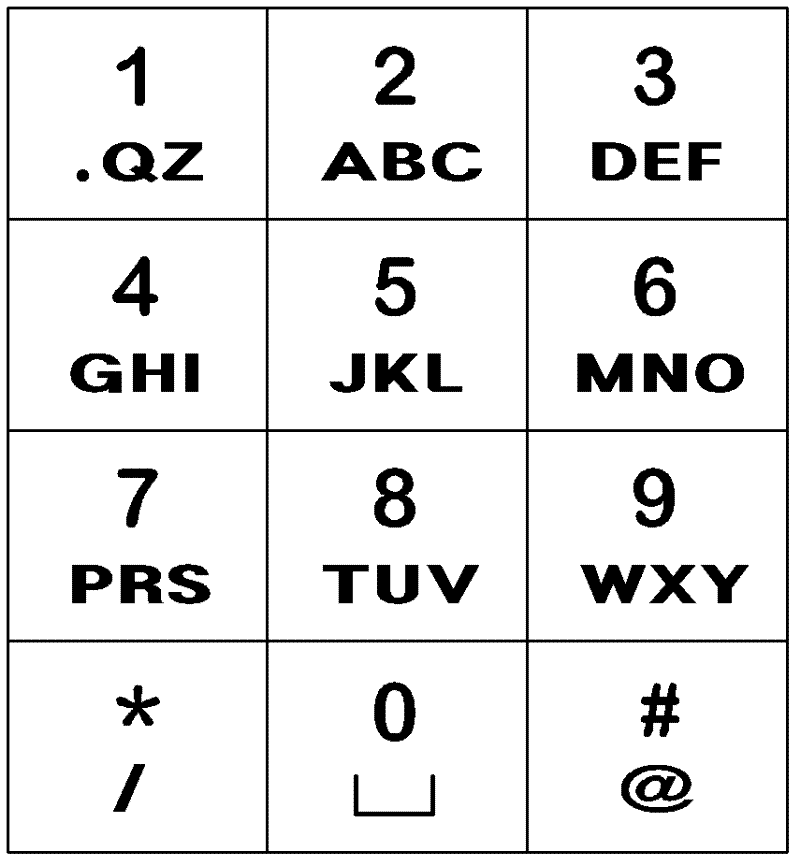
The present invention relates to a device for inputting English characters for a mobile communication terminal, comprising: a keypad input unit having a plurality of keys for inputting English characters; a display unit which outputs English characters in accordance with the input operation of the keypad input unit; an English character completion unit which reads English characters corresponding to the input from the keypad input unit from a database with pre-stored English characters, and provides the read English characters to the display unit; and a control unit connected to each unit to control the units. The keypad input unit has numeric keys with numerals '0' to '9' and function keys with '*' and '#' arranged into a 34 matrix.; The numeric keys with numerals '1' to '9' serve as a plurality of English character buttons for inputting English characters, and the numeric key with numeral '0' serves as a space button for spacing among characters. Either the '*' key or the '#' key of the function keys serves as a last button for the continuous input of English characters and a special character button for inputting special characters. The other of the function keys, which does not serve as the last button and the special character input button, serves as a shift button for performing a character input mode setting and word-converting function for setting a character input mode for inputting the upper / lower case of the English characters and converting the inputted words into upper / lower case, and performing a character-converting function for converting inputted English characters into upper / lower case one by one.
Owner:尹淇燮
Storage method for inputting Chinese word into computer by calculation functional encoding phoneme of word
InactiveCN101004640AIntuitive lockPerfect lockInput/output processes for data processingChinese charactersUpper Case Letter
A method for inputting Chinese character by computer in storage mode includes using fixed four positions of line, column, longitudinal and order English capital letters as unique corresponding identification of Chinese character; enabling to use 26 English capital letters and two ASCII code symbols to directly spell out modern Chinese characters and phrase in reciprocal-corresponding way as per standard stroke attribute and pronunciation attributes of initial consonant and vowel as well as four tones.
Owner:北京汉码魔方科技有限公司
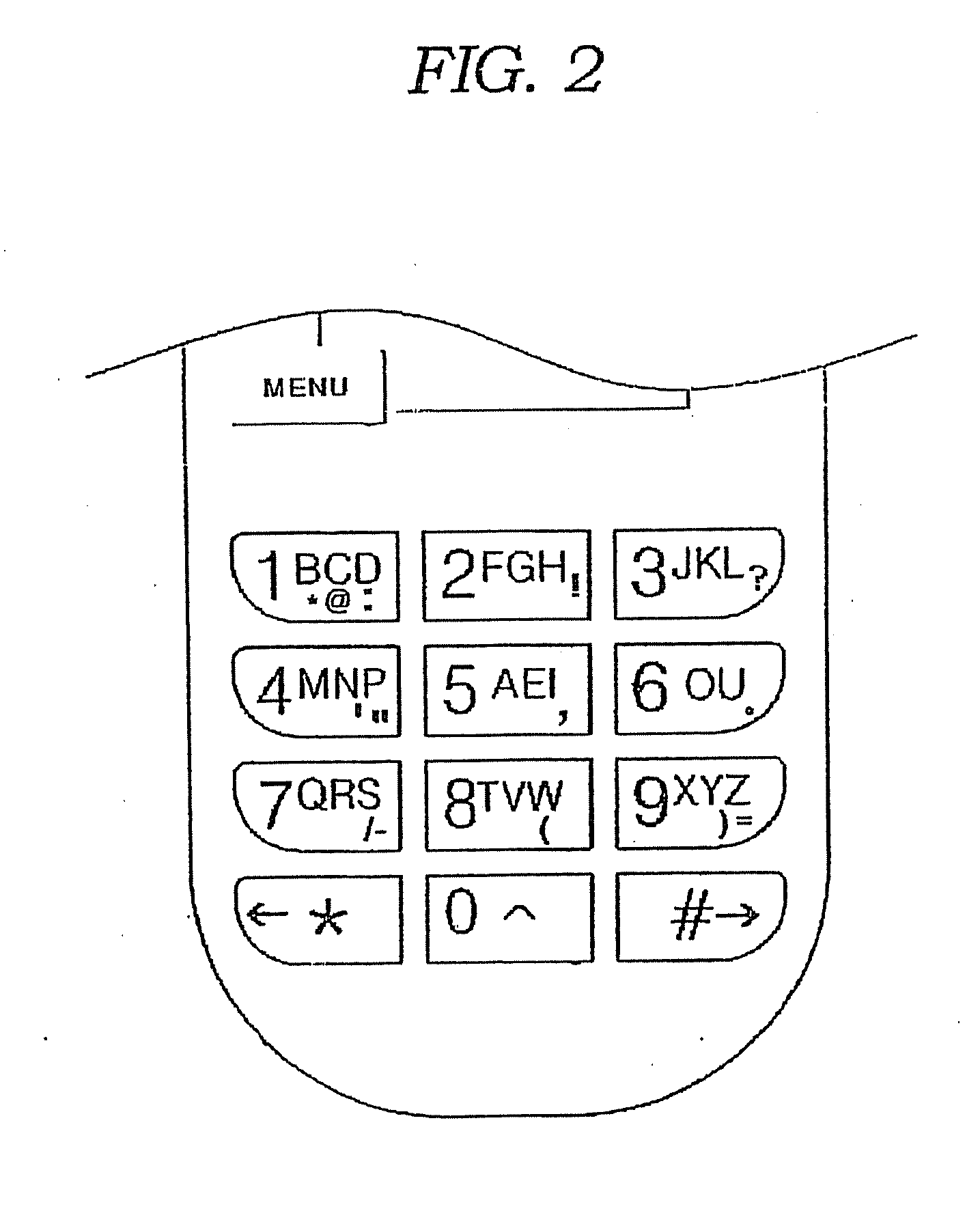
Function button and method of inputting letter using the same
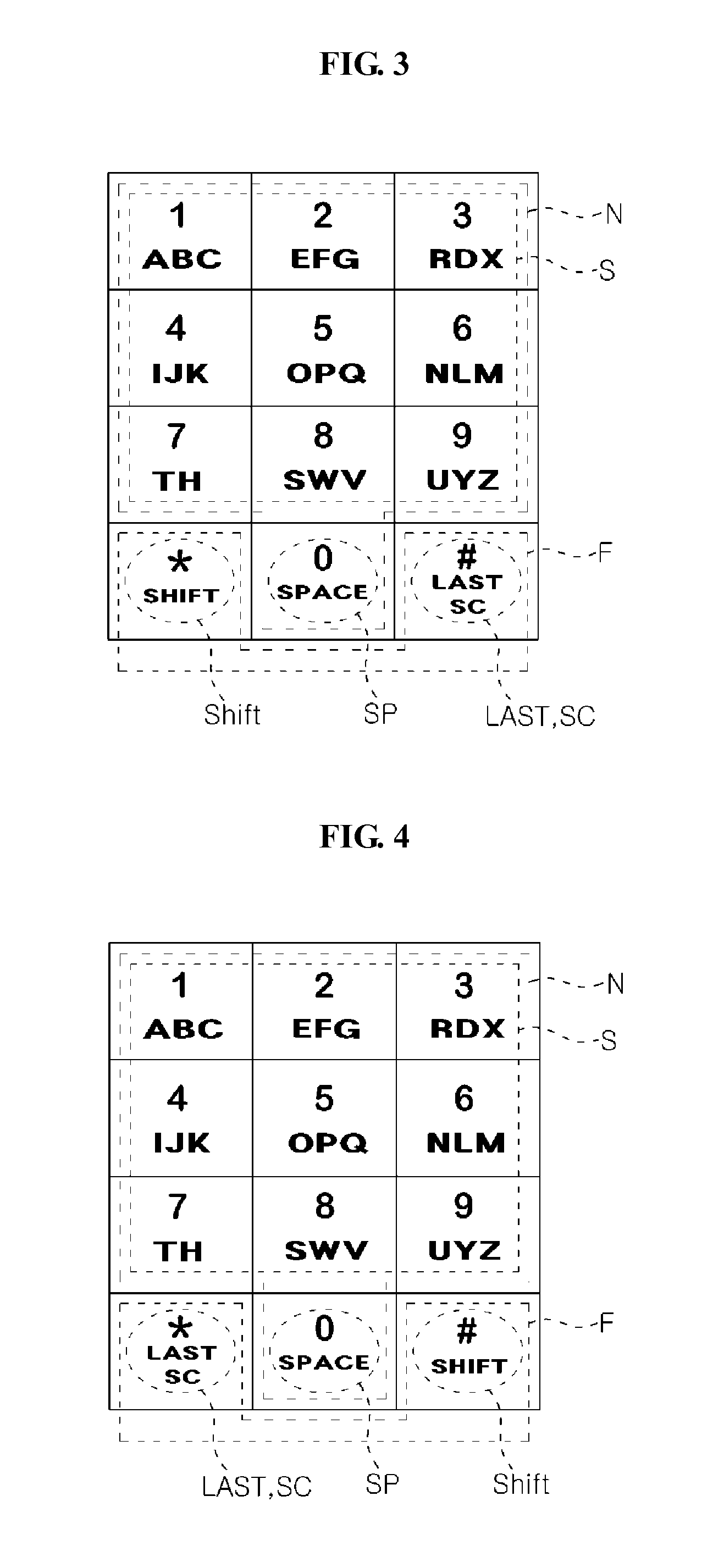
InactiveUS7800588B2Easily and mutually changingEasy inputInput/output for user-computer interactionAlphabetical characters enteringUpper Case LetterHuman–computer interaction
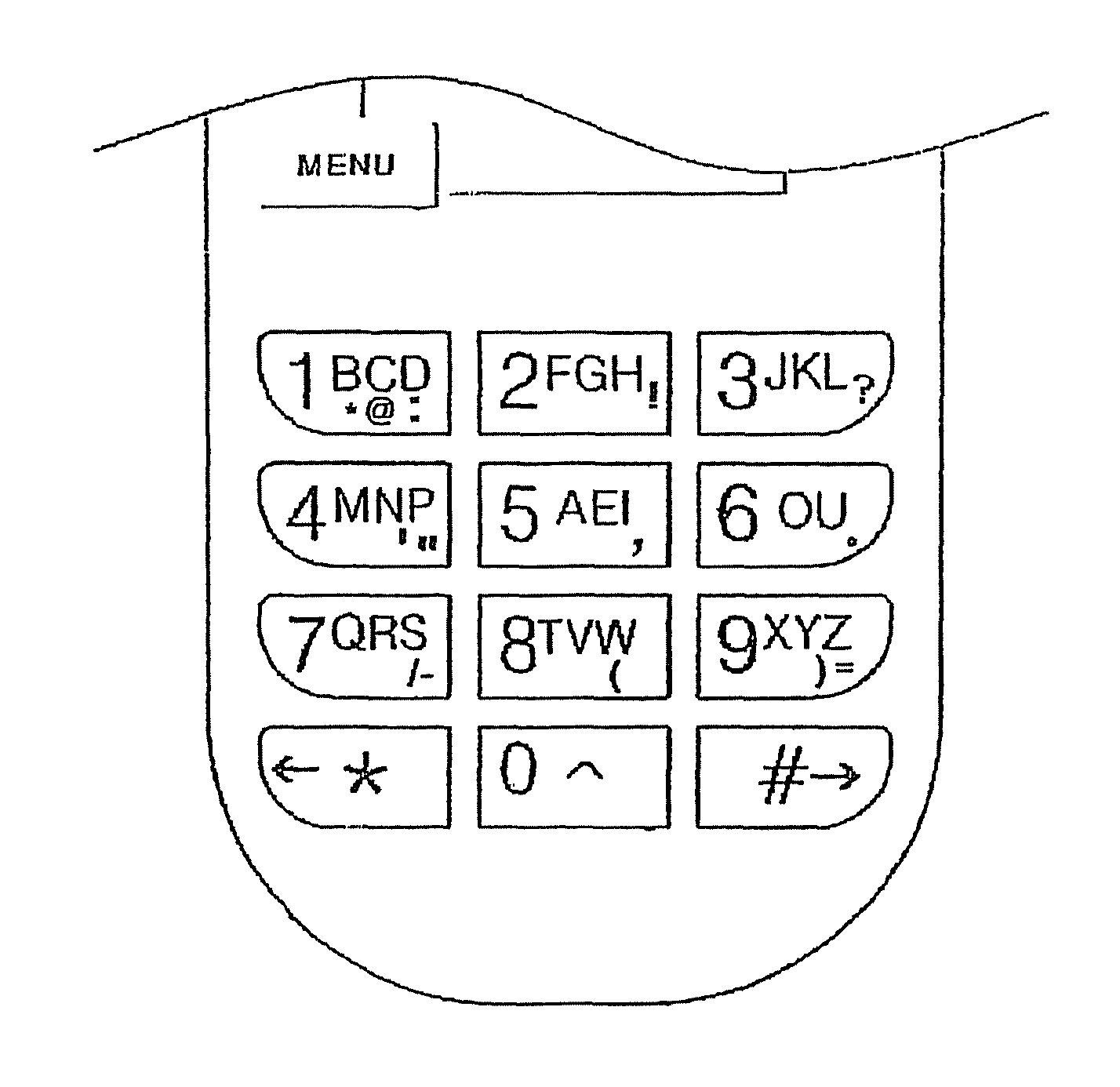
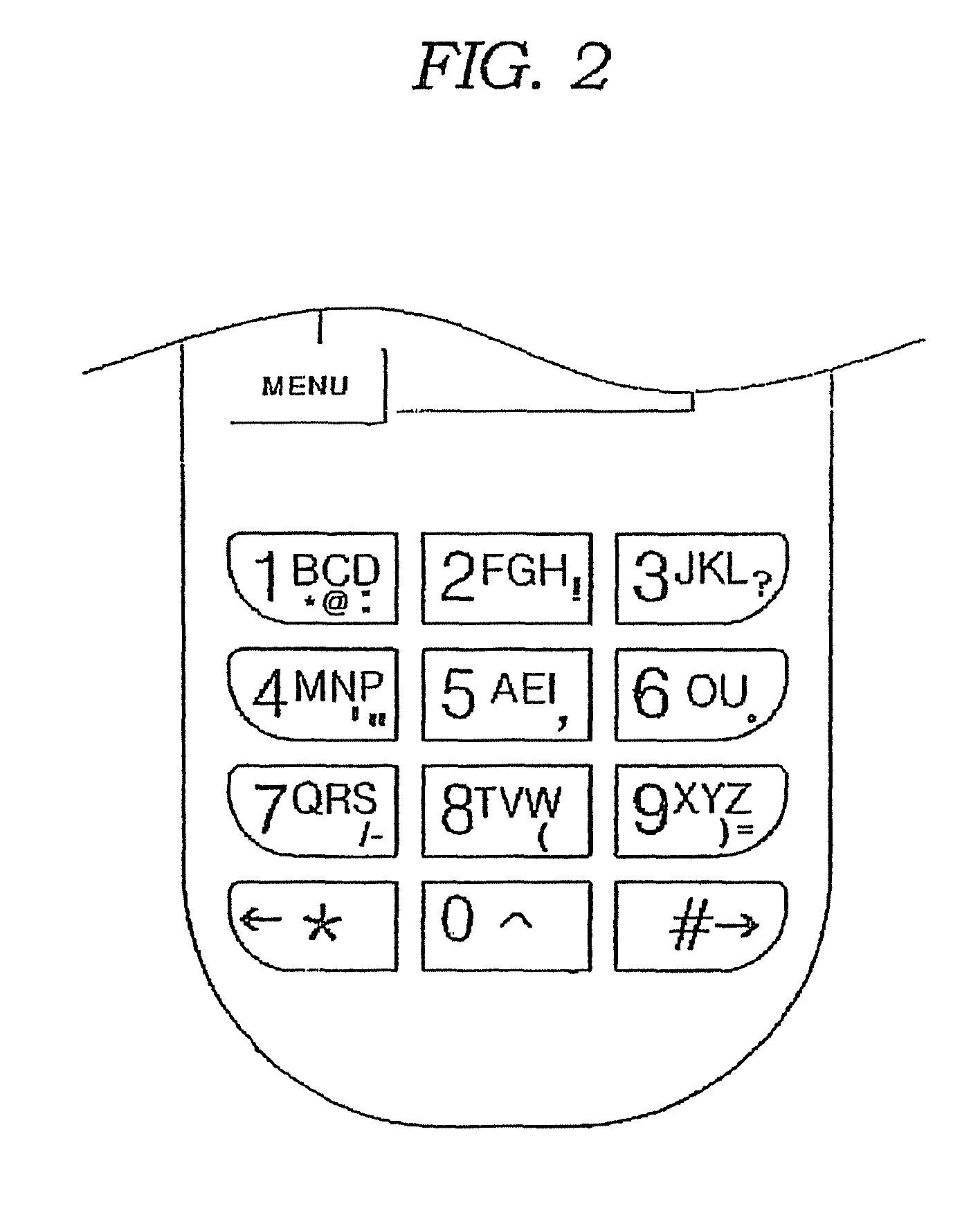
Disclosed herein are a keypad having a function button used to easily input characters in cellular phones and other character input devices and a method of easily inputting various languages and letters using the function button. The function button is set independently of a menu button. Whenever the function button is pushed in a default character input mode, the default character input mode is changed to an upper-case letter input mode, a lower-case letter input mode, a sentence mark input mode, a numeral input mode, a special character input mode and other language input modes. After a desired character has been inputted in a corresponding changed input mode, the function button is pushed to rapidly return to the initial character input mode. Various sentence marks can be effectively inputted using the function button.
Owner:KIM MIN HO
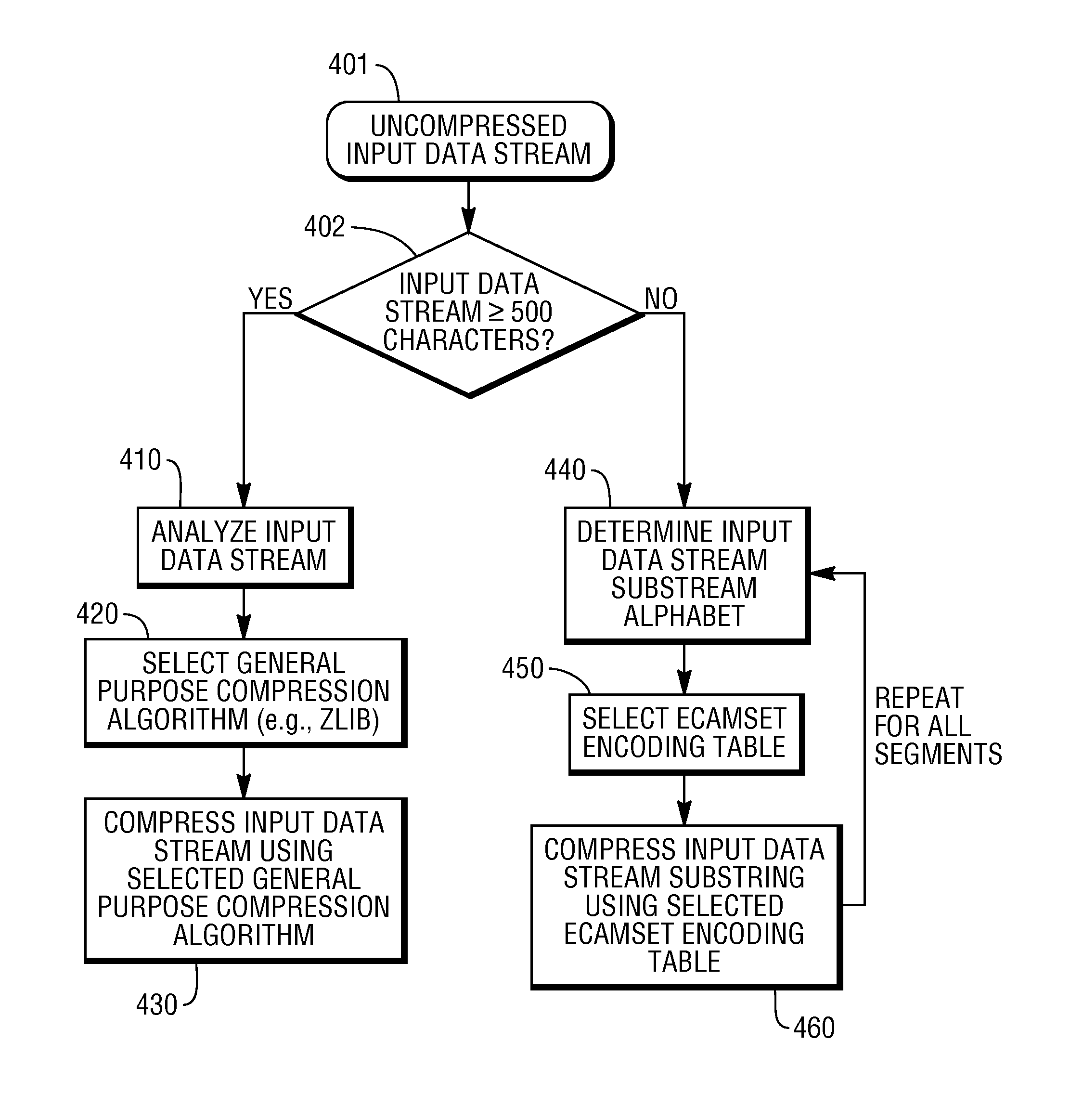
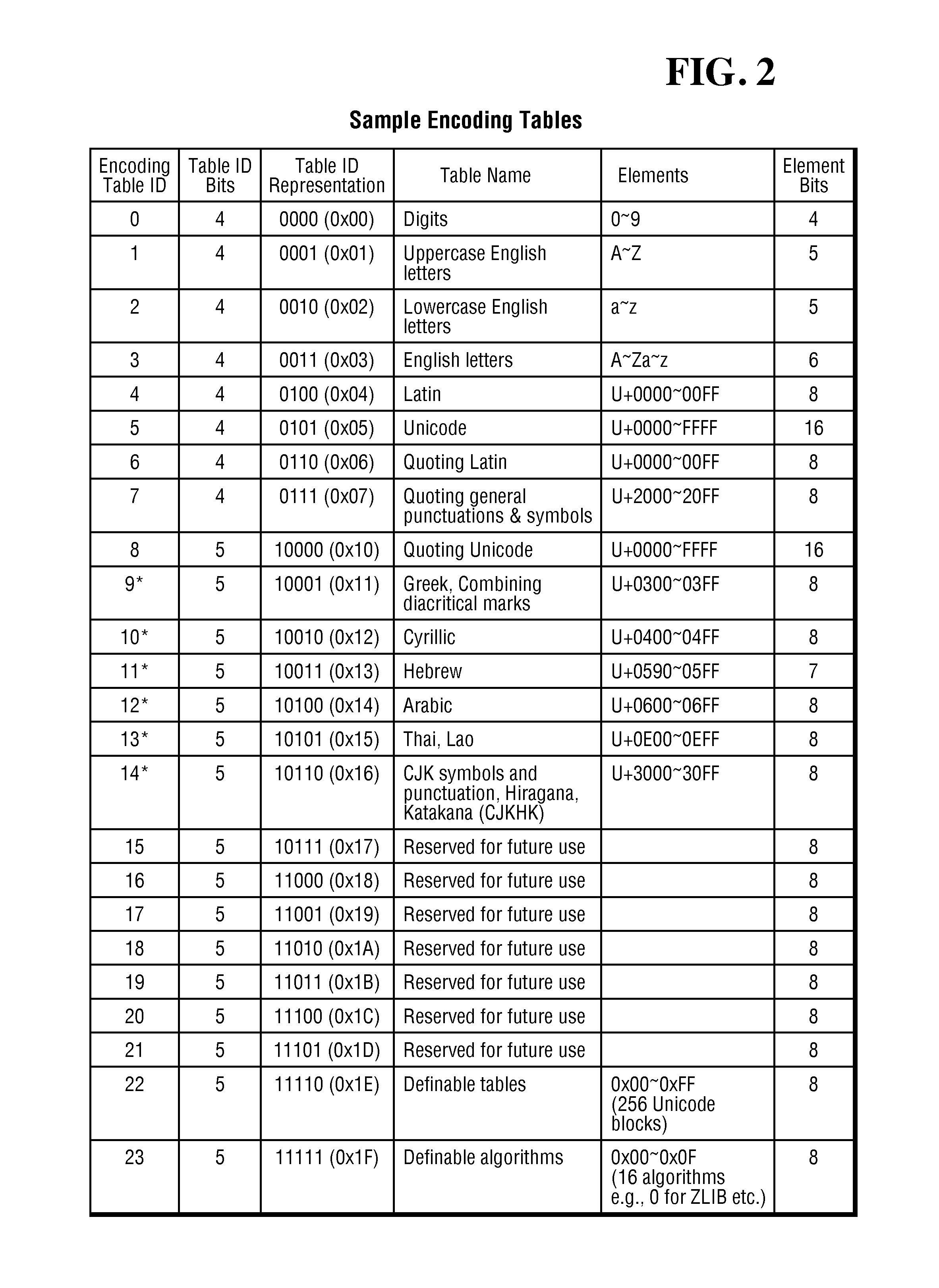
System and method for data compression using multiple small encoding tables
A system and method for compressing and decompressing multiple types of character data. The system and method employ multiple encoding tables, each designed for encoding a subset of character data, such as numeric data, uppercase letters, lowercase letters, Latin, or UNICODE data, to perform compressions and decompression of character data, and. The compression solution also provides for the creation of new encoding tables on the fly, and accommodates the compression of lengthy character streams using multiple different general compression algorithms, automatically choosing a suitable general compression algorithm for specific input data.
Owner:TERADATA
Device for inputting english characters for a mobile communication terminal, and method for same
InactiveUS8547337B2Input/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingKey assignmentDisplay device
According to the present invention, an alphabet input device of a mobile communication comprises a keypad input including a plurality of keys for inputting alphabets; a display for displaying alphabets inputted by said keypad input; an alphabet combiner for reading the alphabet corresponding to the input of the keypad input from pre-stored database and providing the display with said alphabet from said database; and, a controller coupled to said keypad input, said display and said alphabet combiner so as to control thereof, wherein said keypad input has a 3×4 matrix which includes numeric keys distinguished by the numbers ‘0’ to ‘9’ and function keys distinguished by the characters ‘*’ and ‘#’, and said numeric keys for ‘1 ’ to ‘9’ are assigned with a plurality of alphabet buttons for inputting alphabets, wherein said numeric key for ‘0’ is assigned with a space button for inputting a blank, wherein one of said function keys for ‘*’ and ‘#’ is assigned with a last button for successive inputting of the alphabet and a special character button for inputting a special character, wherein the other of said function keys that does not assigned with said last button and said special character button is assigned with a shift button, which performs a function of character input mode-setting and word-shifting for setting a character input mode so as to allow inputting of the capital / small letter of alphabet and for shifting a word inputted beforehand between the capital letter and the small letter, and a function of character-shifting for shifting characters inputted beforehand one at a time.
Owner:YOON KI SUP
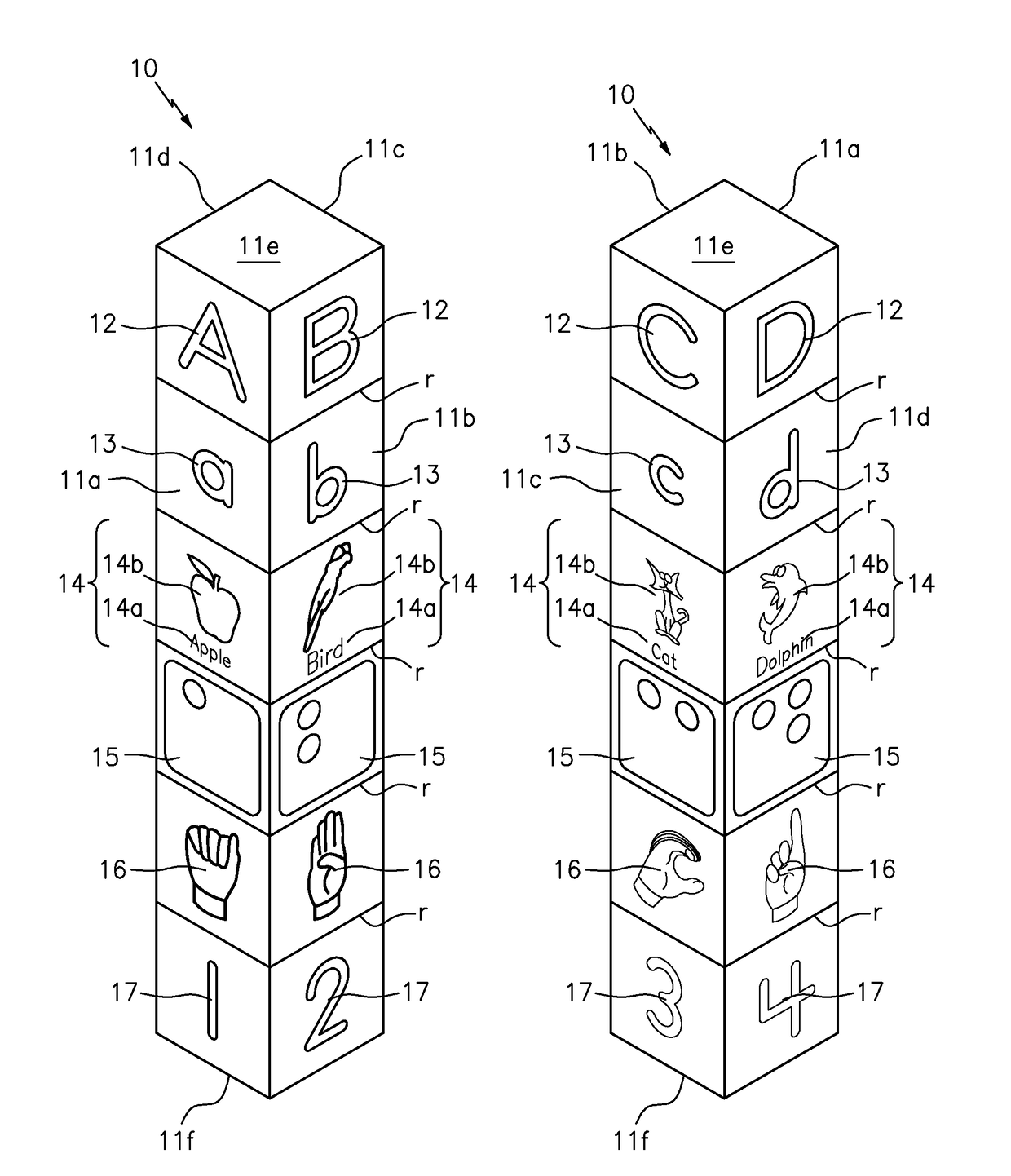
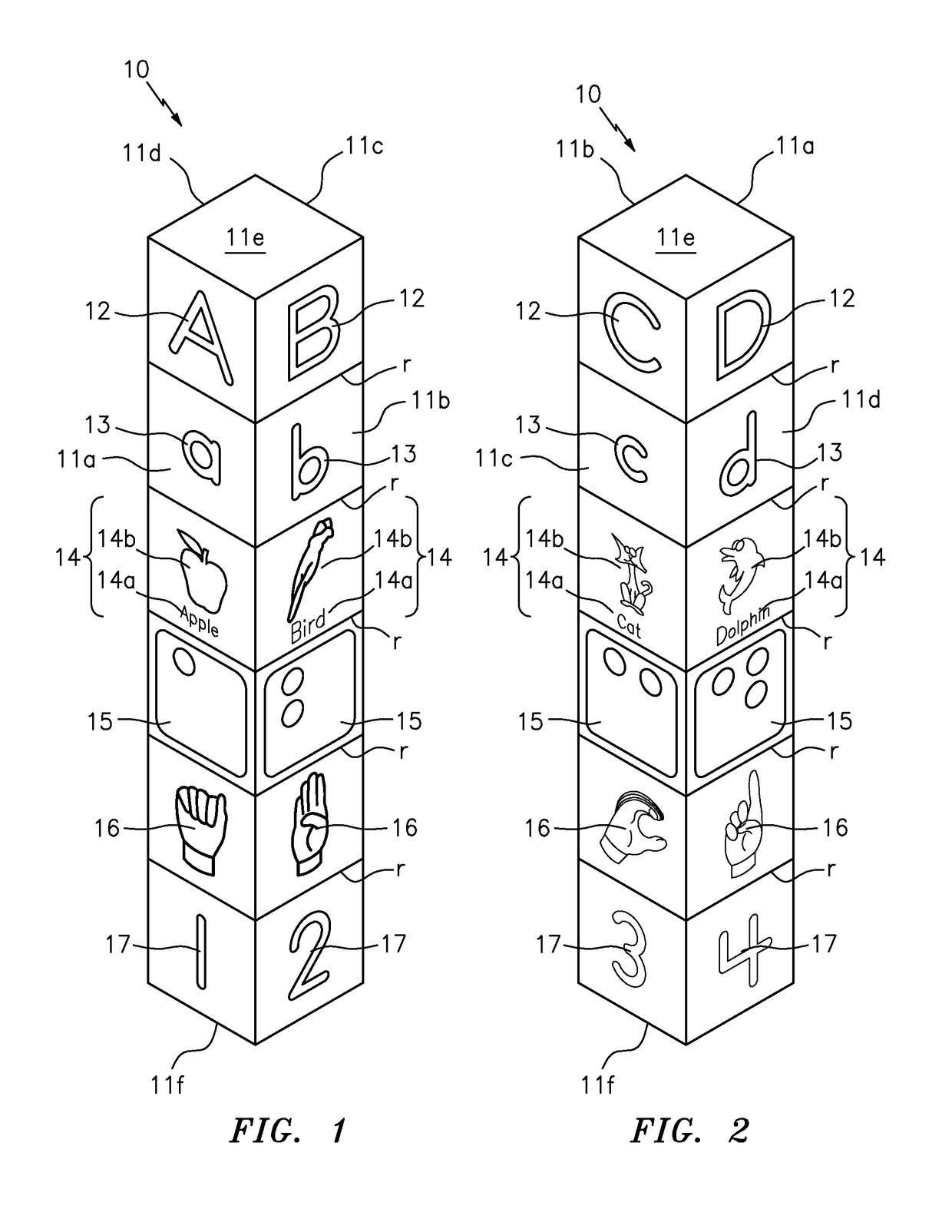
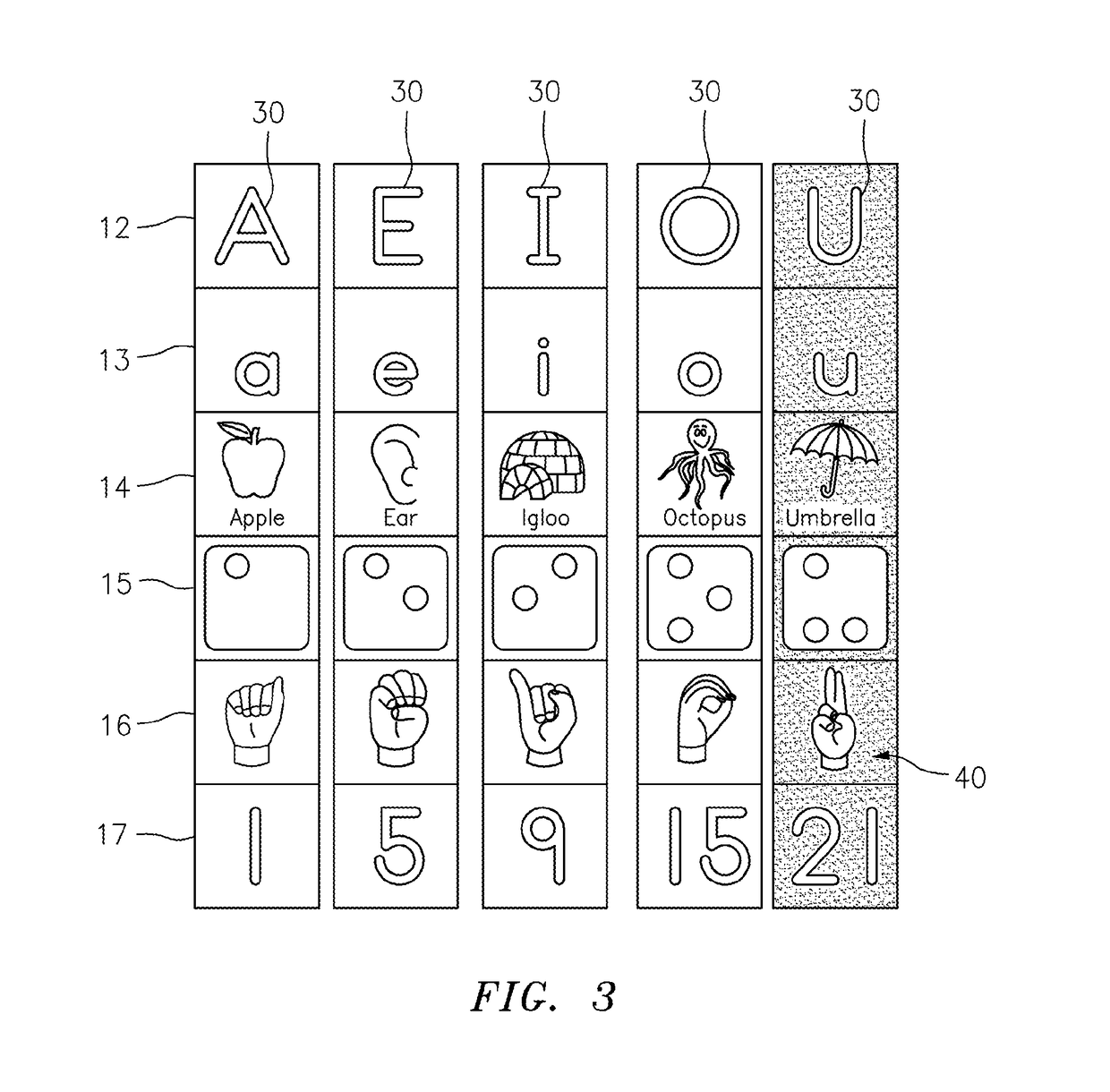
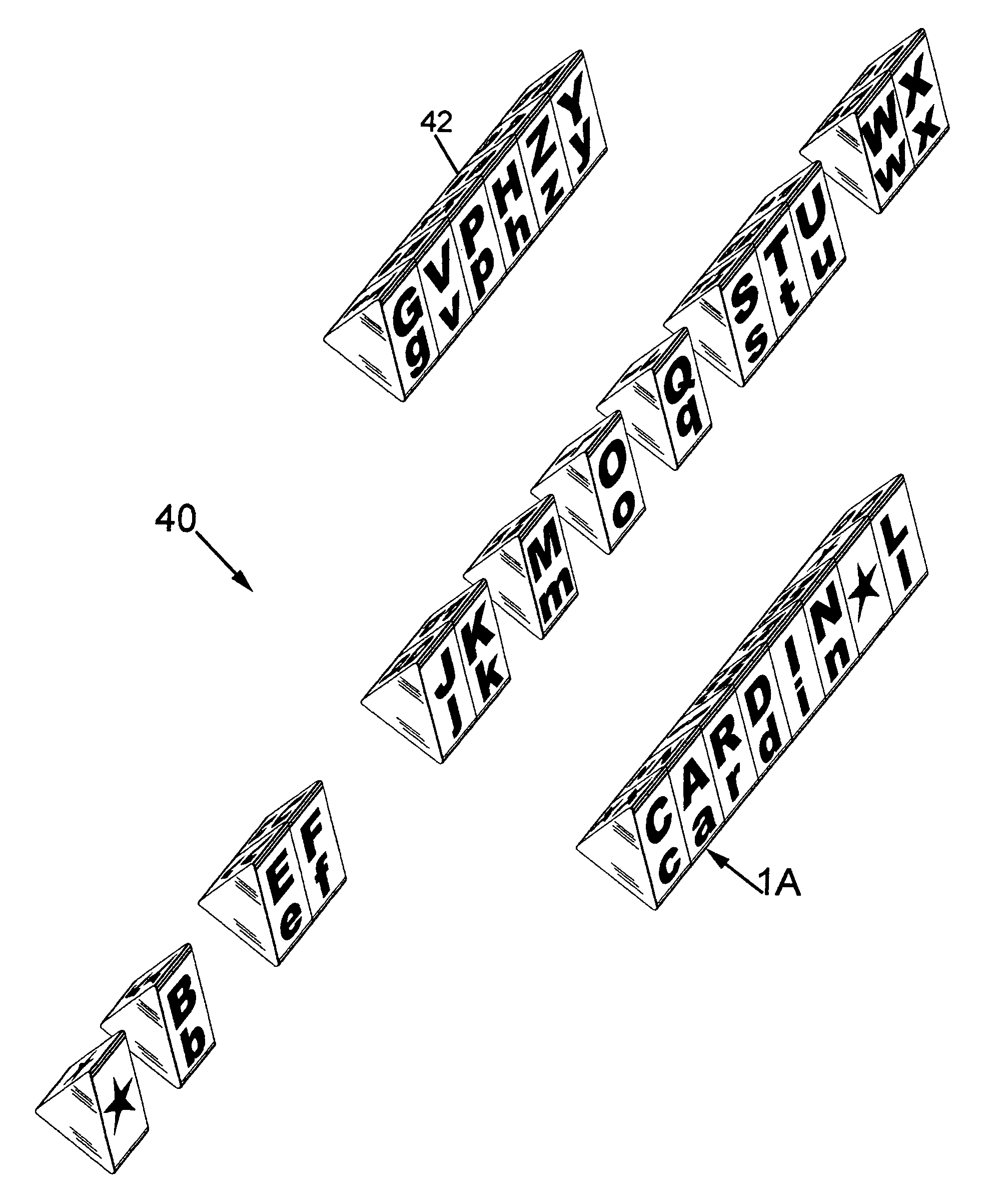
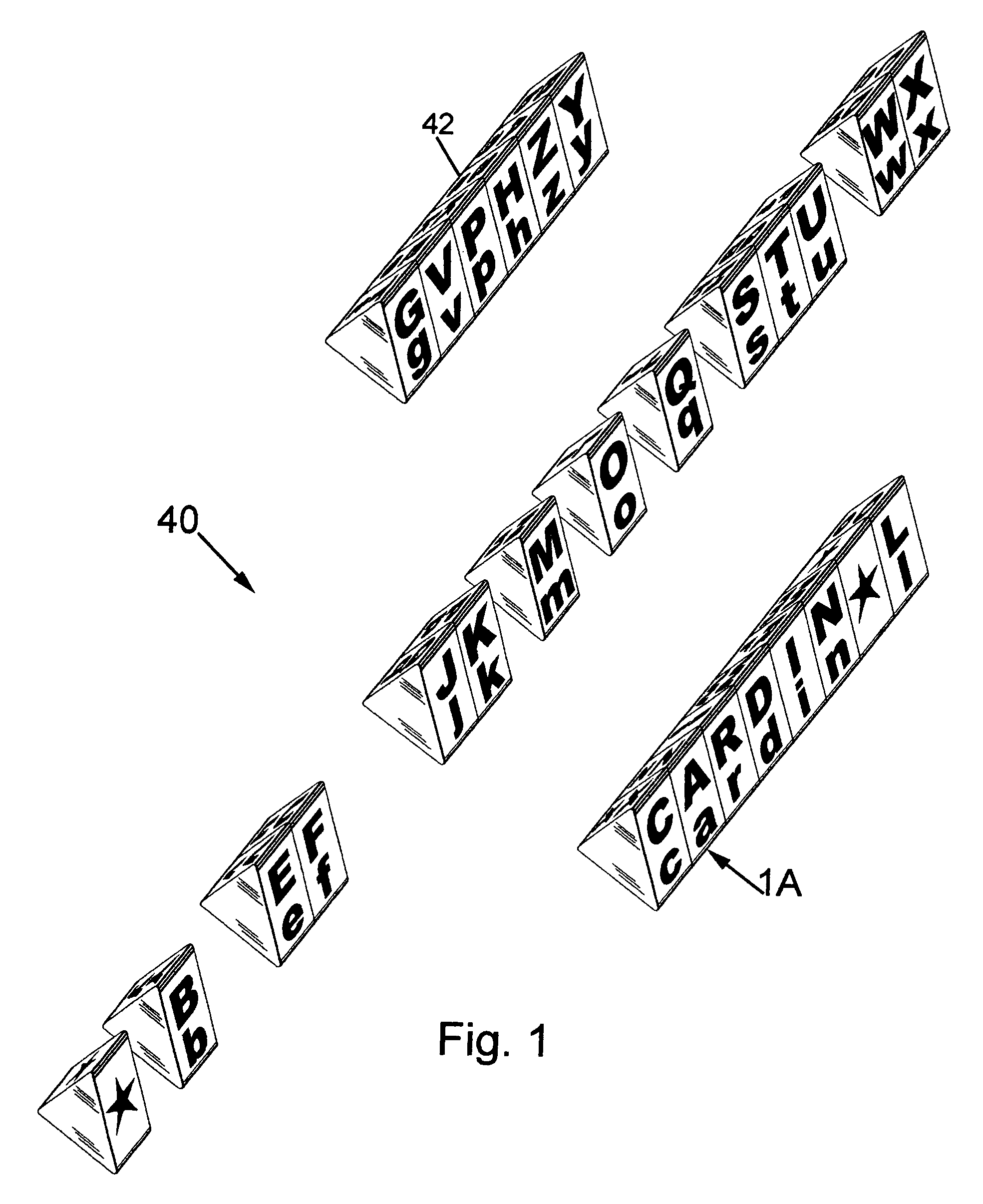
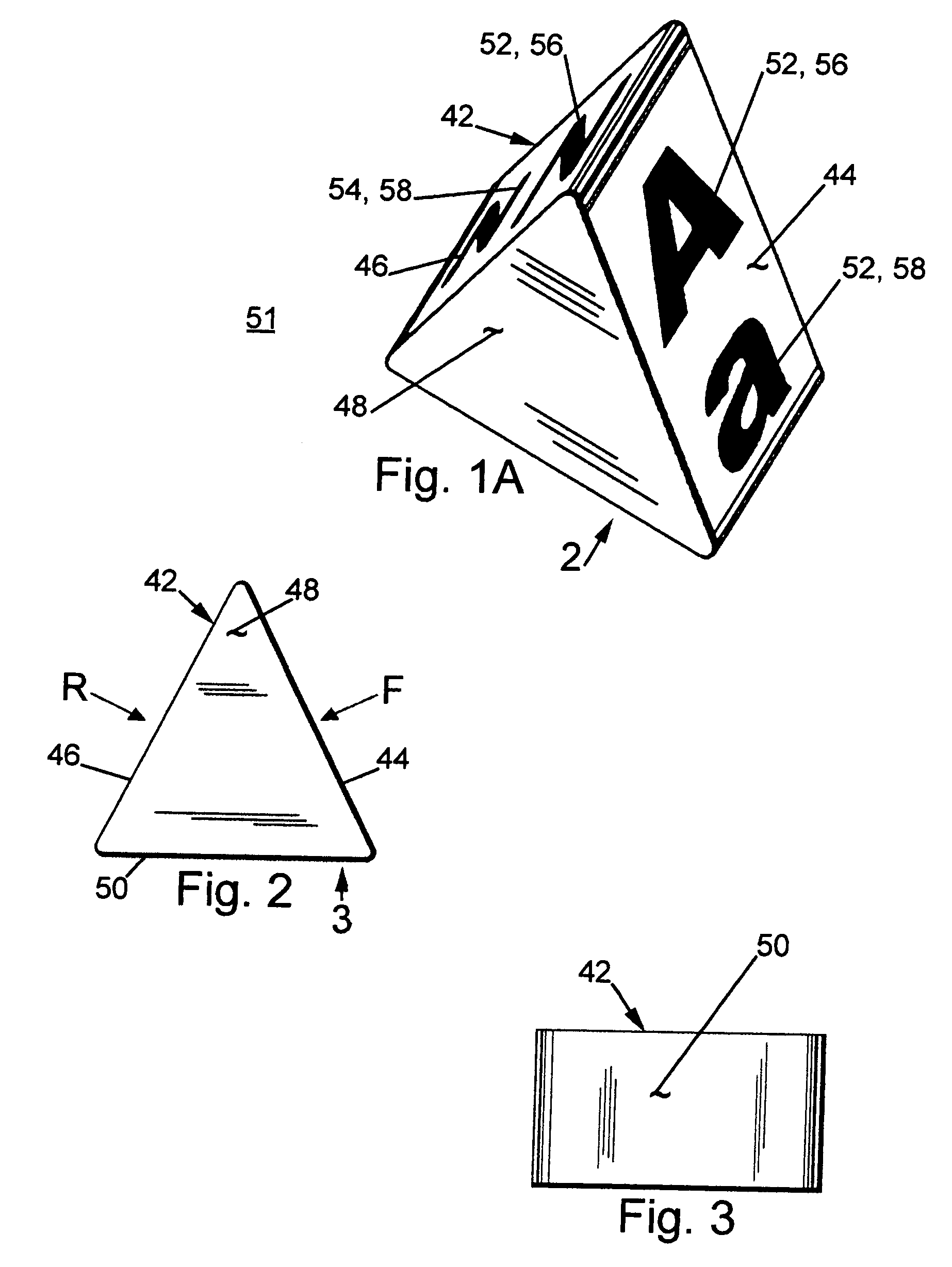
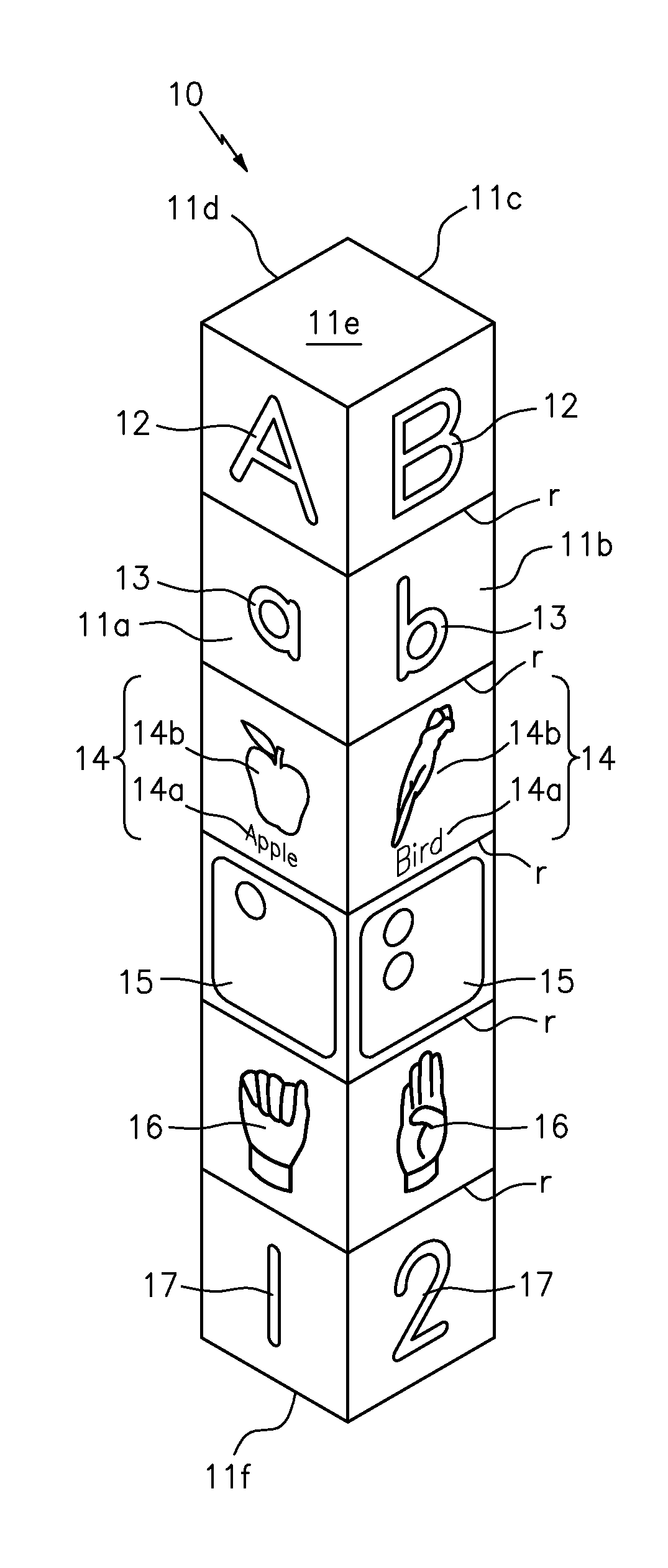
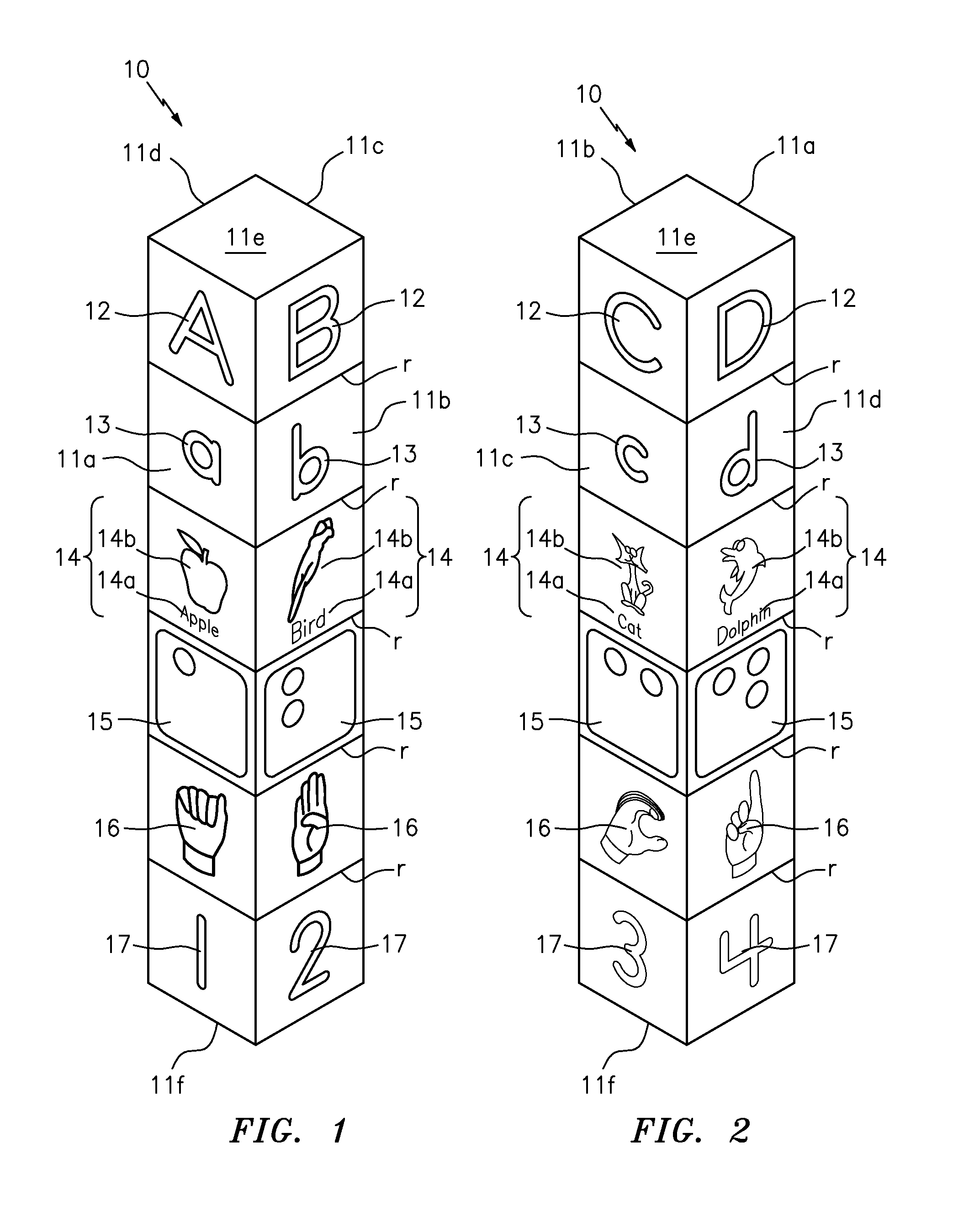
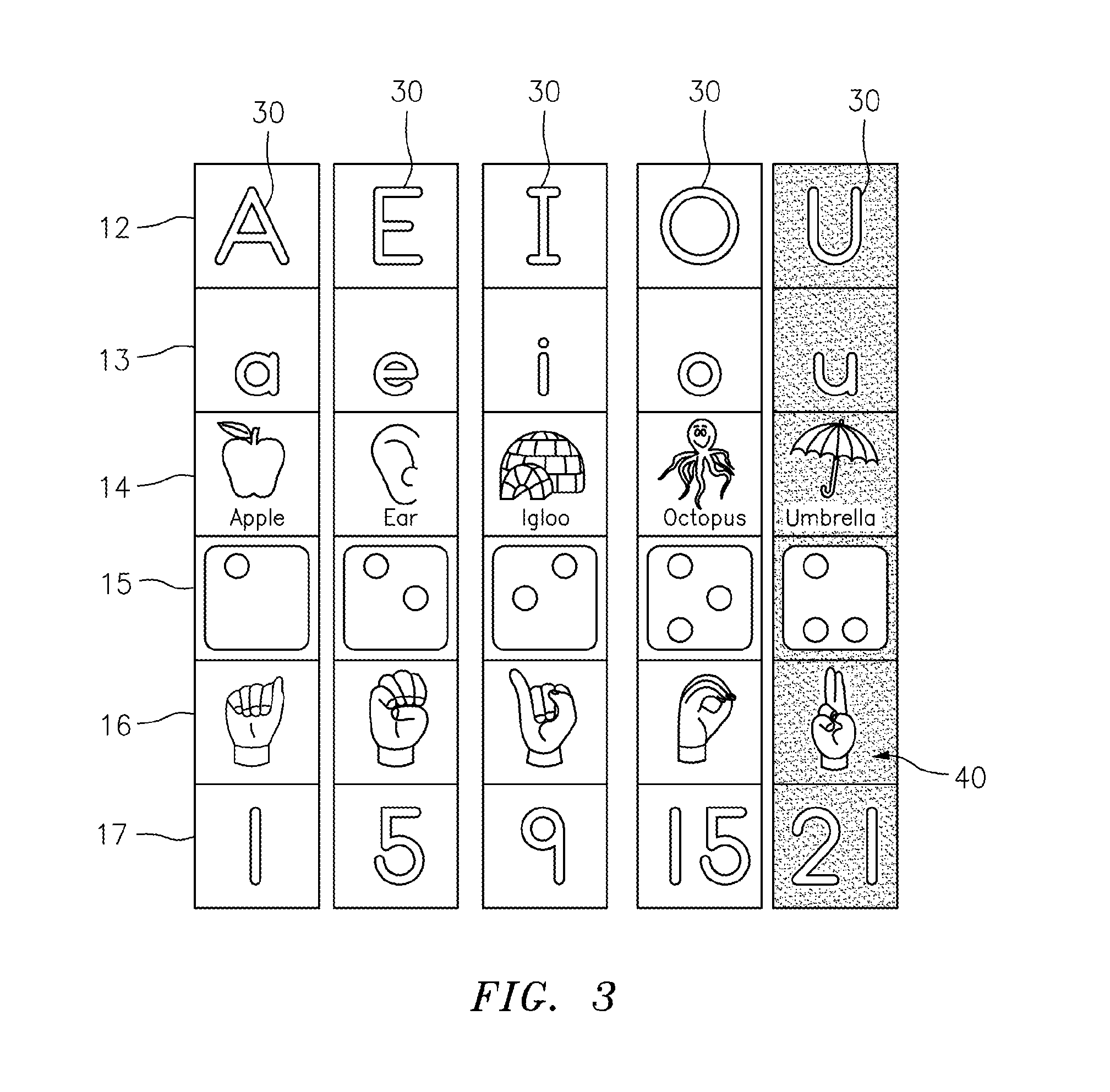
Tactile spelling totems
A spelling totem includes a generally rectangular box-shaped member having a plurality of side surfaces. Each of the side surfaces are directed towards a different letter of the alphabet and further include various implementations of the letter. The implementations can include any combination of an upper case letter, a lower case letter, a word that begins with the letter, an image of the word, the braille representation of the letter, the sign language representation of the letter, and a number showing where the particular letter falls in the alphabet. A set of individual spelling totems includes each letter of the alphabet, and each totem is designed to be aligned so as to spell various words.
Owner:TAPIA LARESA
Word-forming game for at least two players and apparatus therefore
InactiveUS7021629B1Avoid disadvantagesSimple and inexpensive to manufactureBoard gamesCard gamesEngineeringUpper Case Letter
Owner:WHITE HELEN E +1
Tactile spelling totems
A spelling totem includes a generally rectangular box-shaped member having a plurality of side surfaces. Each of the side surfaces are directed towards a different letter of the alphabet and further include various implementations of the letter. The implementations can include any combination of an upper case letter, a lower case letter, a word that begins with the letter, an image of the word, the braille representation of the letter, the sign language representation of the letter, and a number showing where the particular letter falls in the alphabet. A set of individual spelling totems includes each letter of the alphabet, and each totem is designed to be aligned so as to spell various words.
Owner:TAPIA LARESA
Function Button and Method of Inputting Letter Using the Same
InactiveUS20070242049A1Easily and mutually changingEasy inputInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingUpper Case LetterHuman–computer interaction
Disclosed herein are a keypad havng a function button used to easily input characters in cellular phones and other character input devices and a method of easily inputting various languages and letters using the function button. The function button is set independently of a menu button. Whenever the function button is pushed in a default character input mode, the default character input mode is changed to an upper-case letter input mode, a lower-case letter input mode, a sentence mark input mode, a numeral input mode, a special character input mode and other language input modes. After a desired character has been inputted in a corresponding changed input mode, the function button is pushed to rapidly return to the initial character input mode. Various sentence marks can be effectively inputted using the function button.
Owner:KIM MIN HO
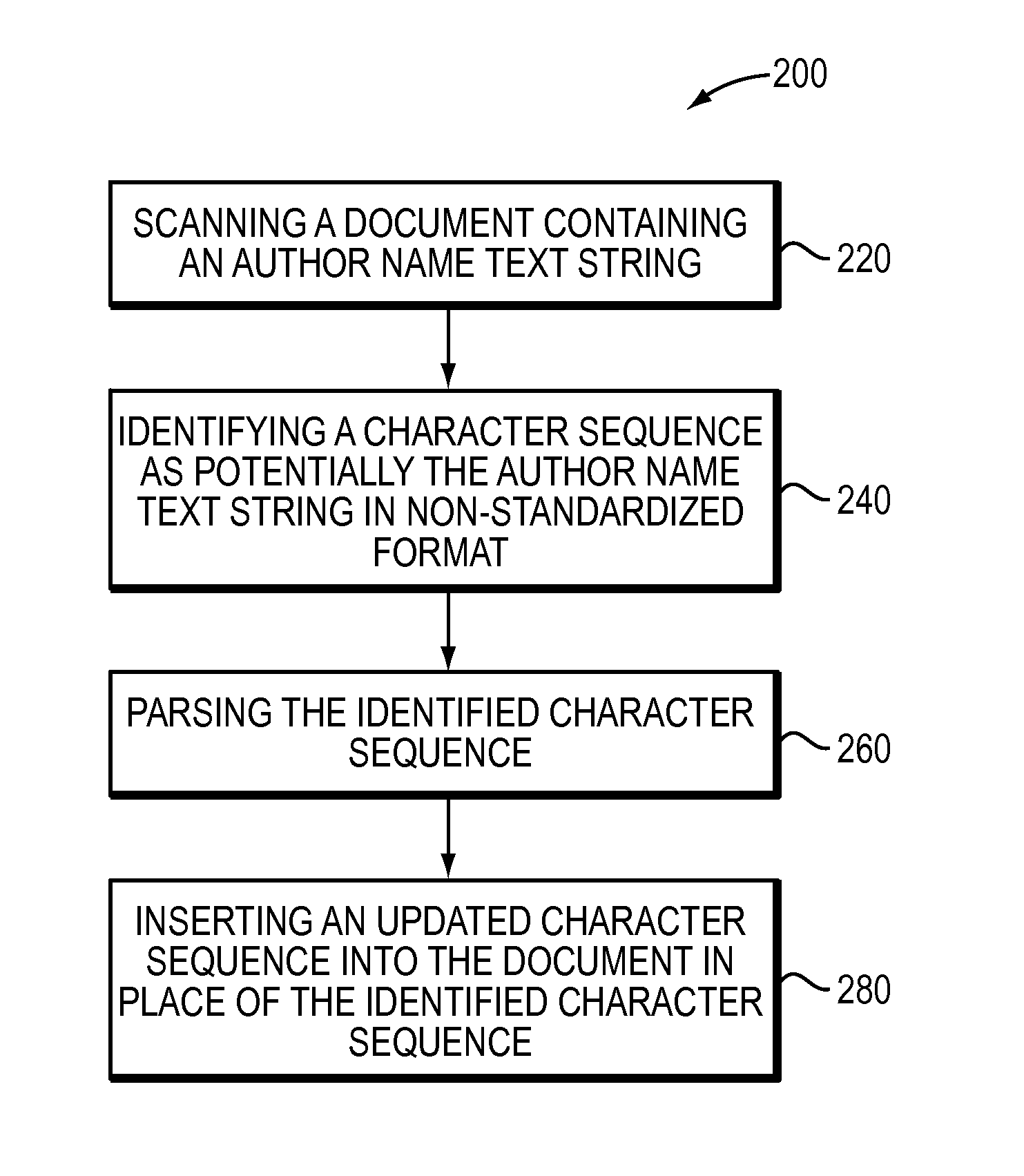
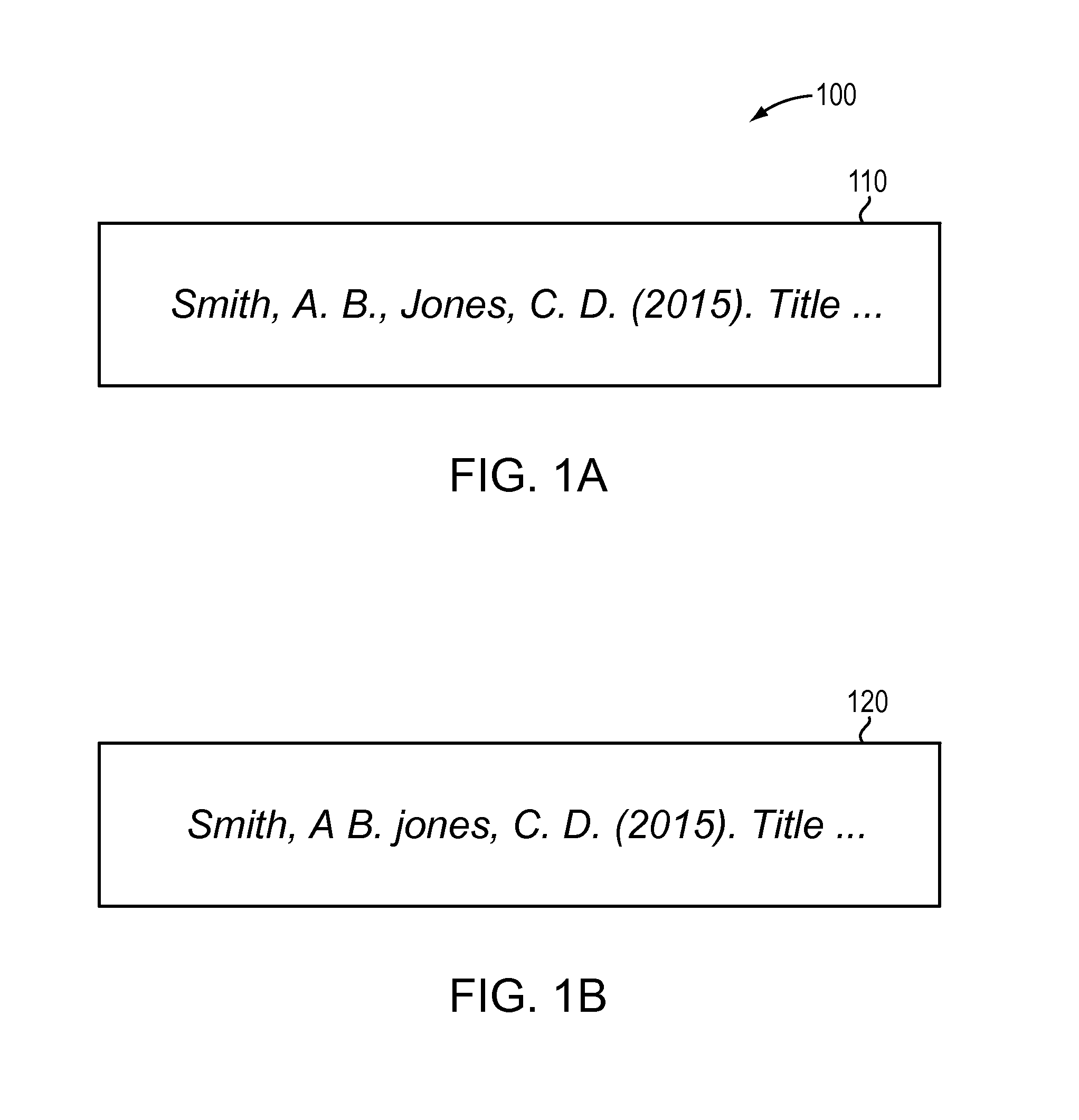
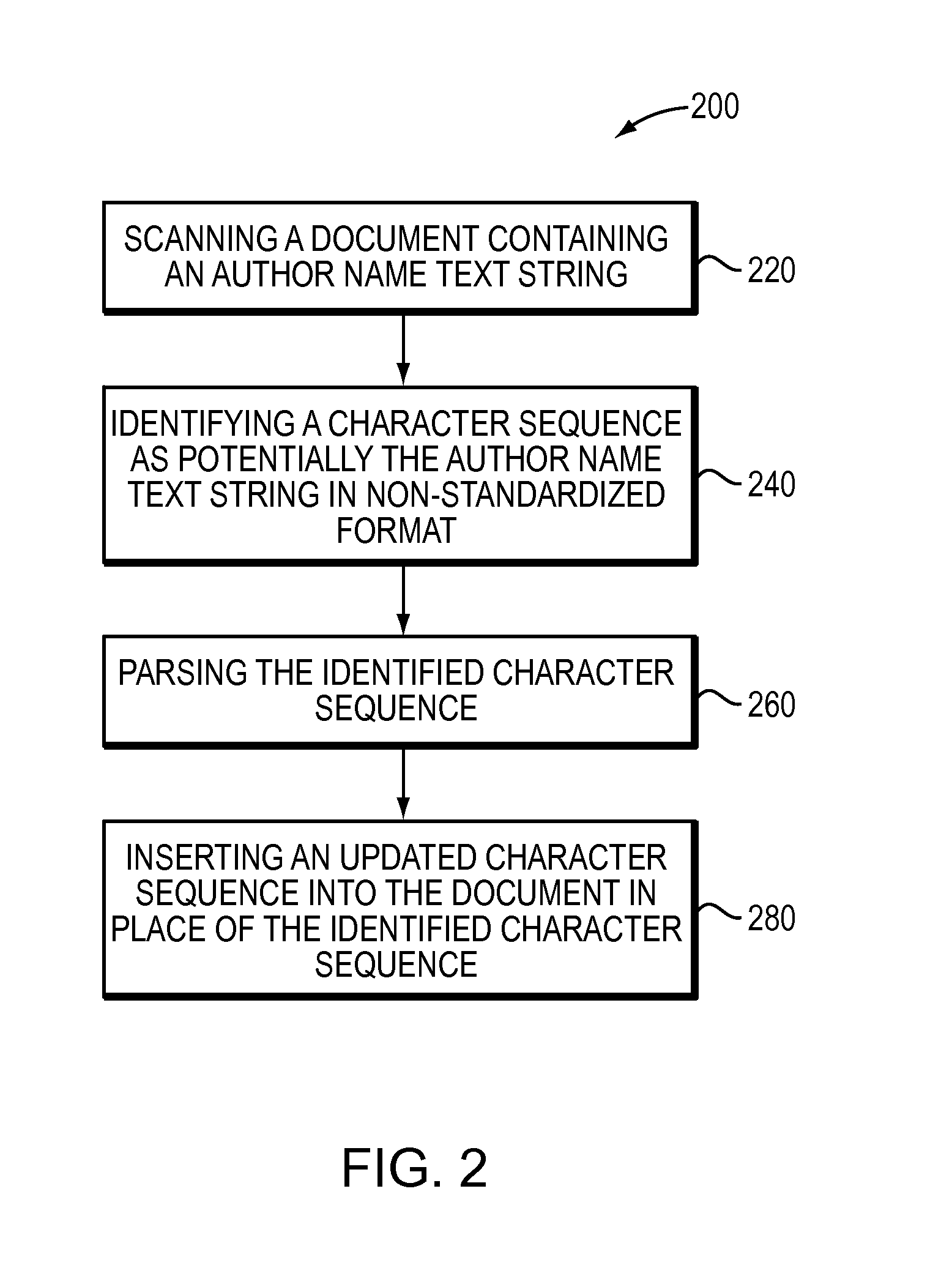
Parsing author name groups in non-standardized format
ActiveUS9430451B1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsAuthor nameTest string
The present invention is directed to a method and corresponding system for parsing author name text strings in documents. The method and system may electronically scan a document that contains an author name text string comprising a set of initials, one or more author surnames, and punctuation. The author name text string may be in non-standardized format. The method and system may identify a character sequence in the document as potentially being the author name test string based on (i) a sequence of title-case words, capital letter, and punctuation, and (ii) the character sequence ending with a recognized indicator. The method and system may parse the identified character sequence by converting any punctuation and whitespace between terms in the character sequence to a single space character, identifying a pattern of surname and set of initials comprising each author name contained in the character sequence, and marking up the components of surname and set of initials comprising each author name. The method and system may use the marked up character sequence to identify and correct errors in punctuation and capitalization in the character sequence, and output an updated character sequence in standardized format.
Owner:ATYPON SYST LLC
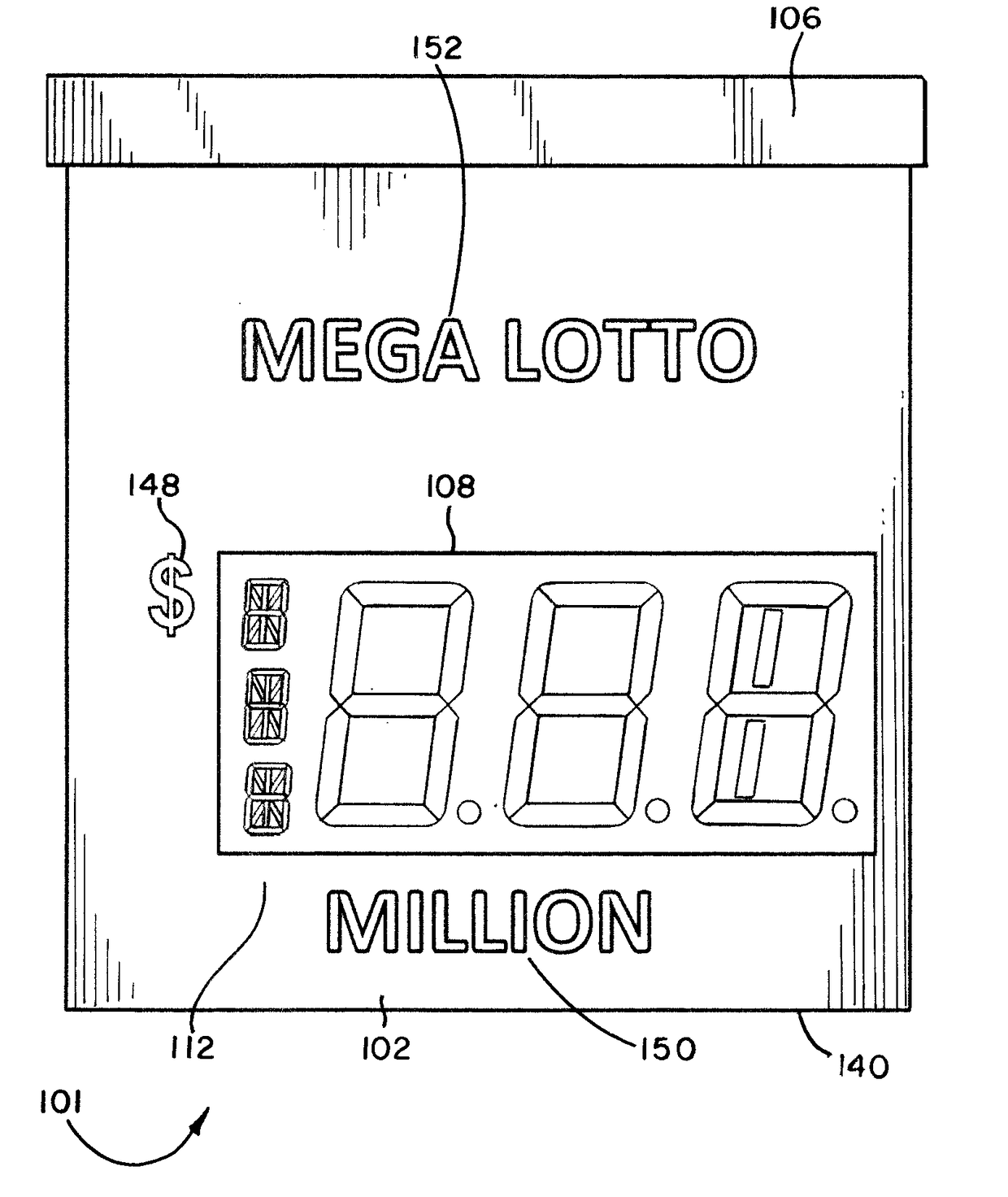
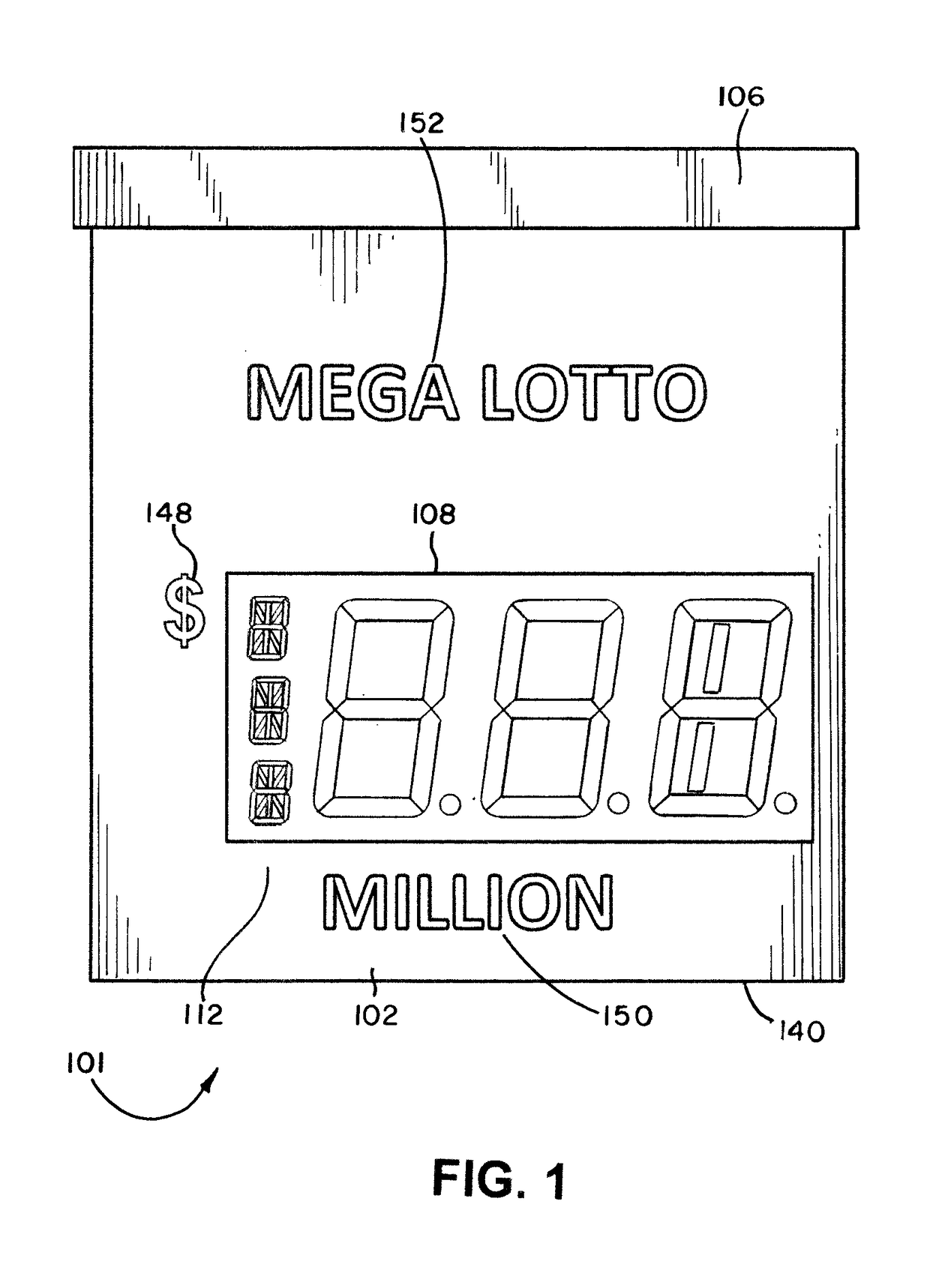
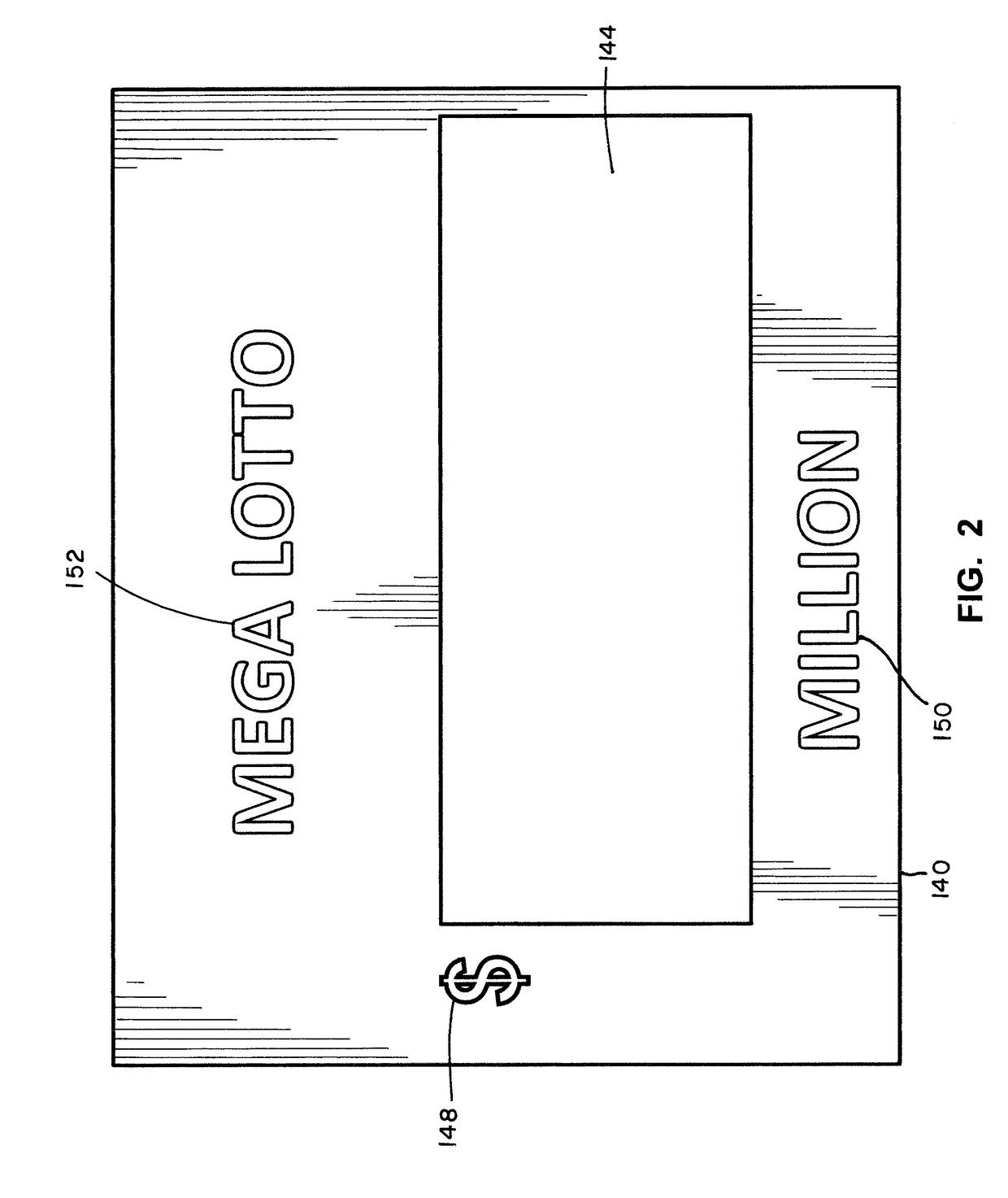
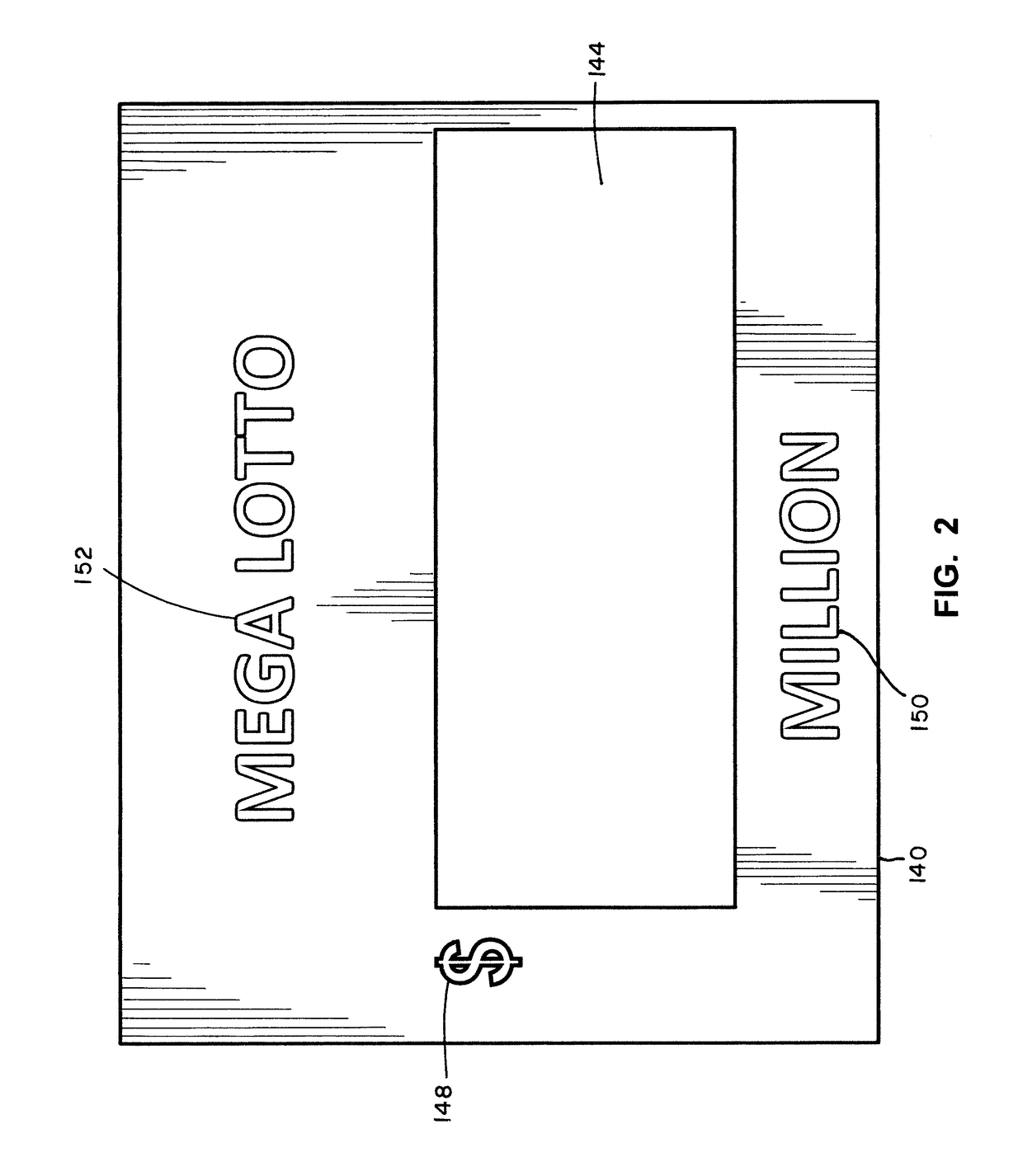
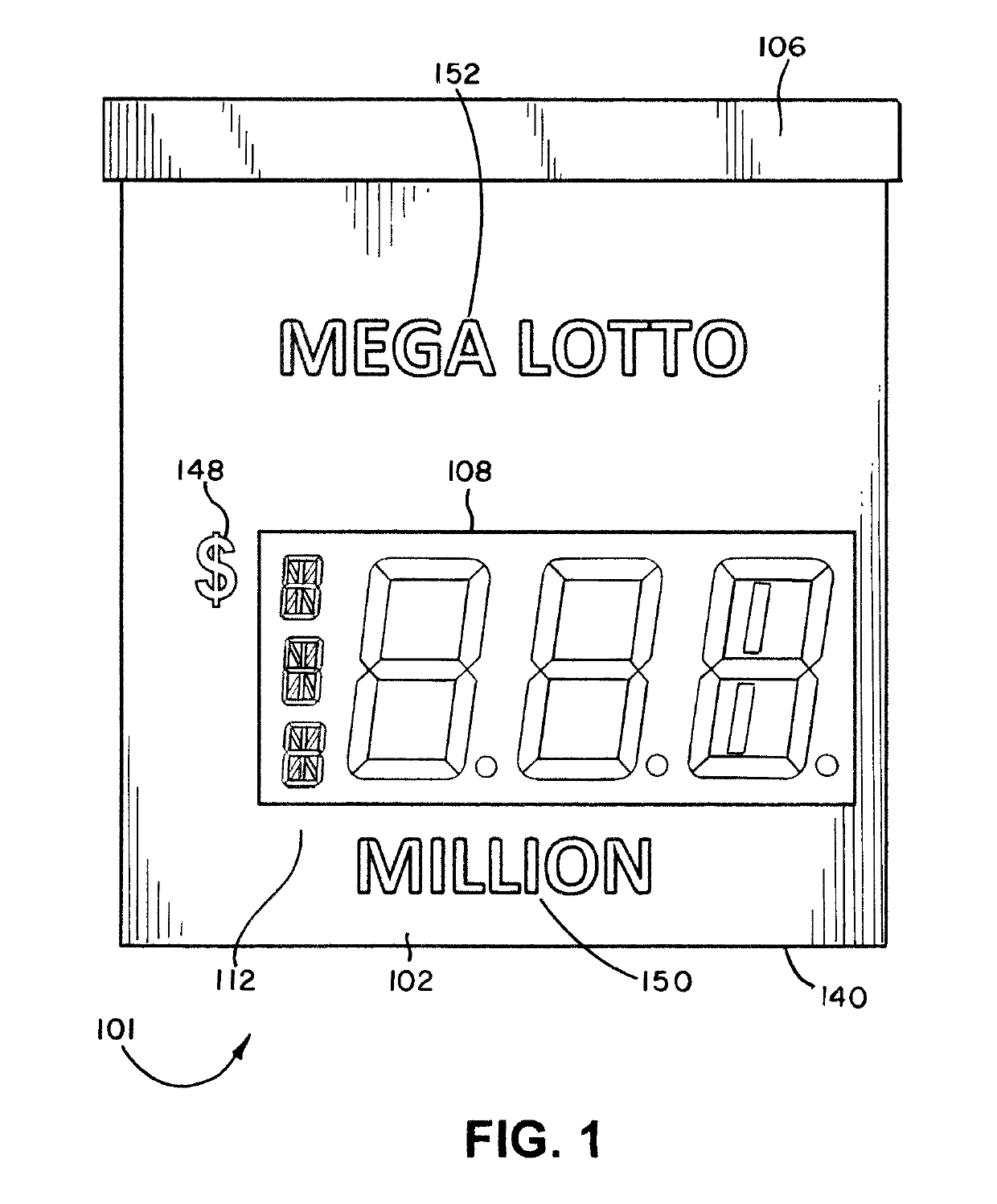
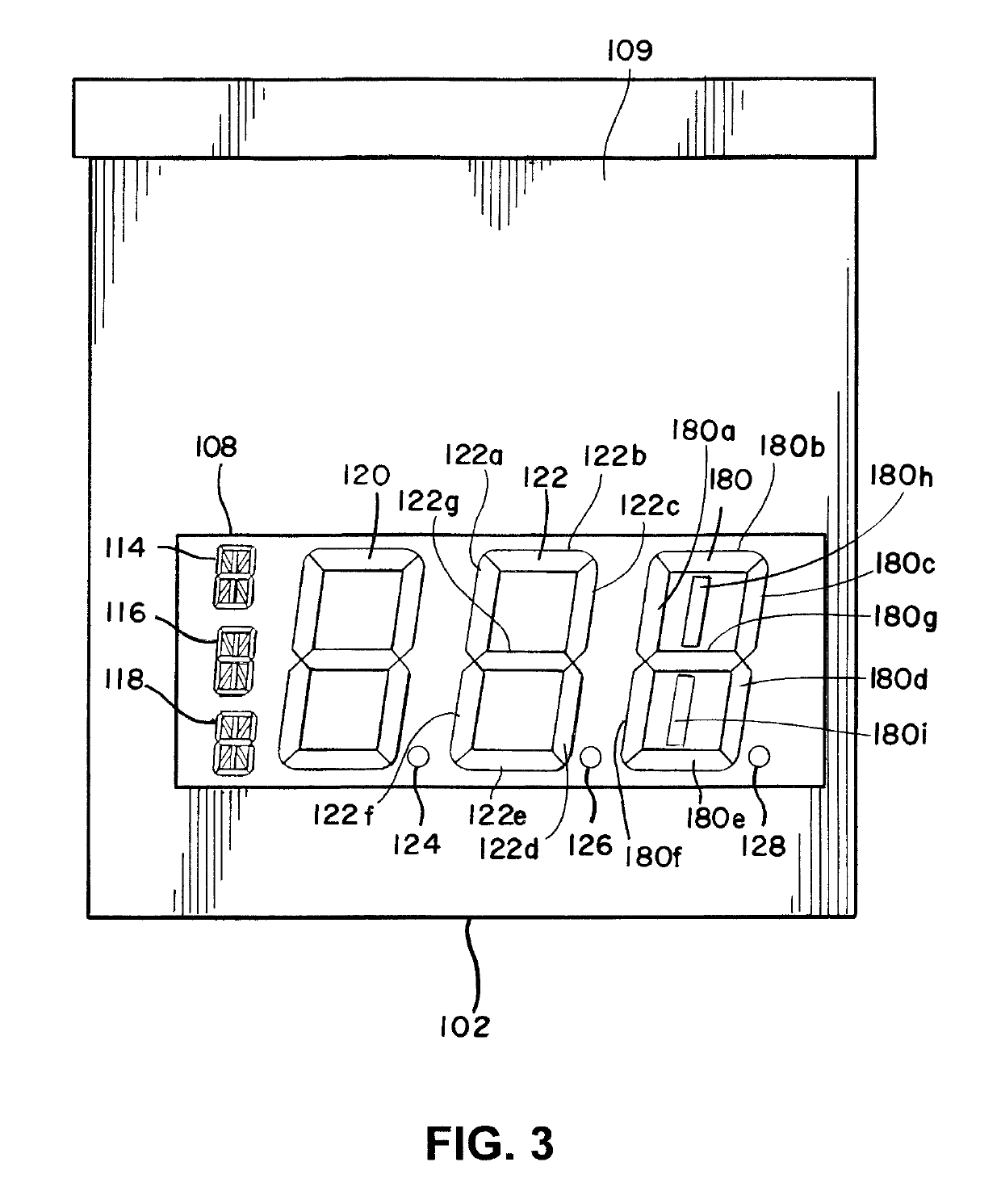
Lottery Signs For Displaying Lottery Jackpots Of Millions And Billions Of Dollars
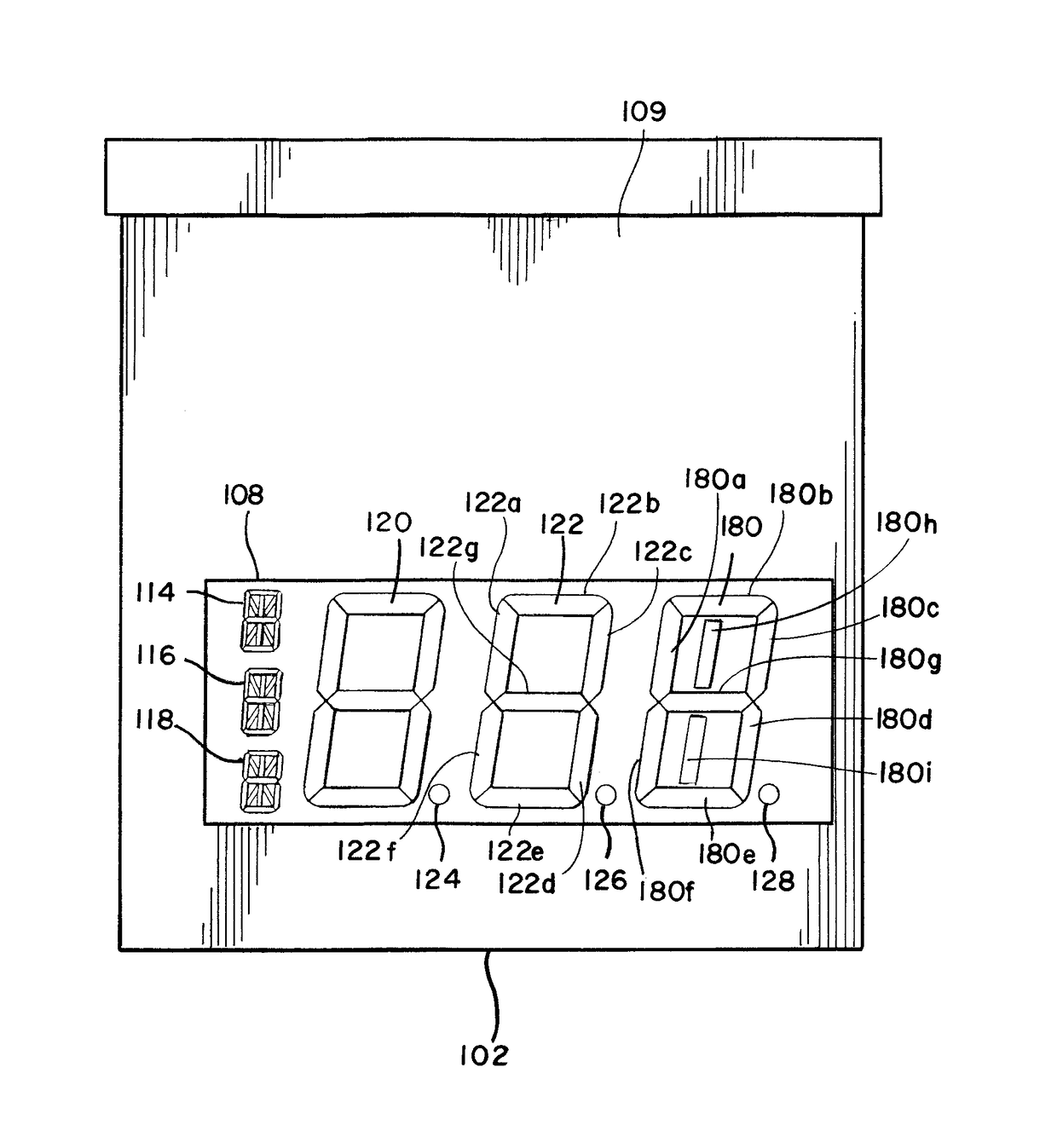
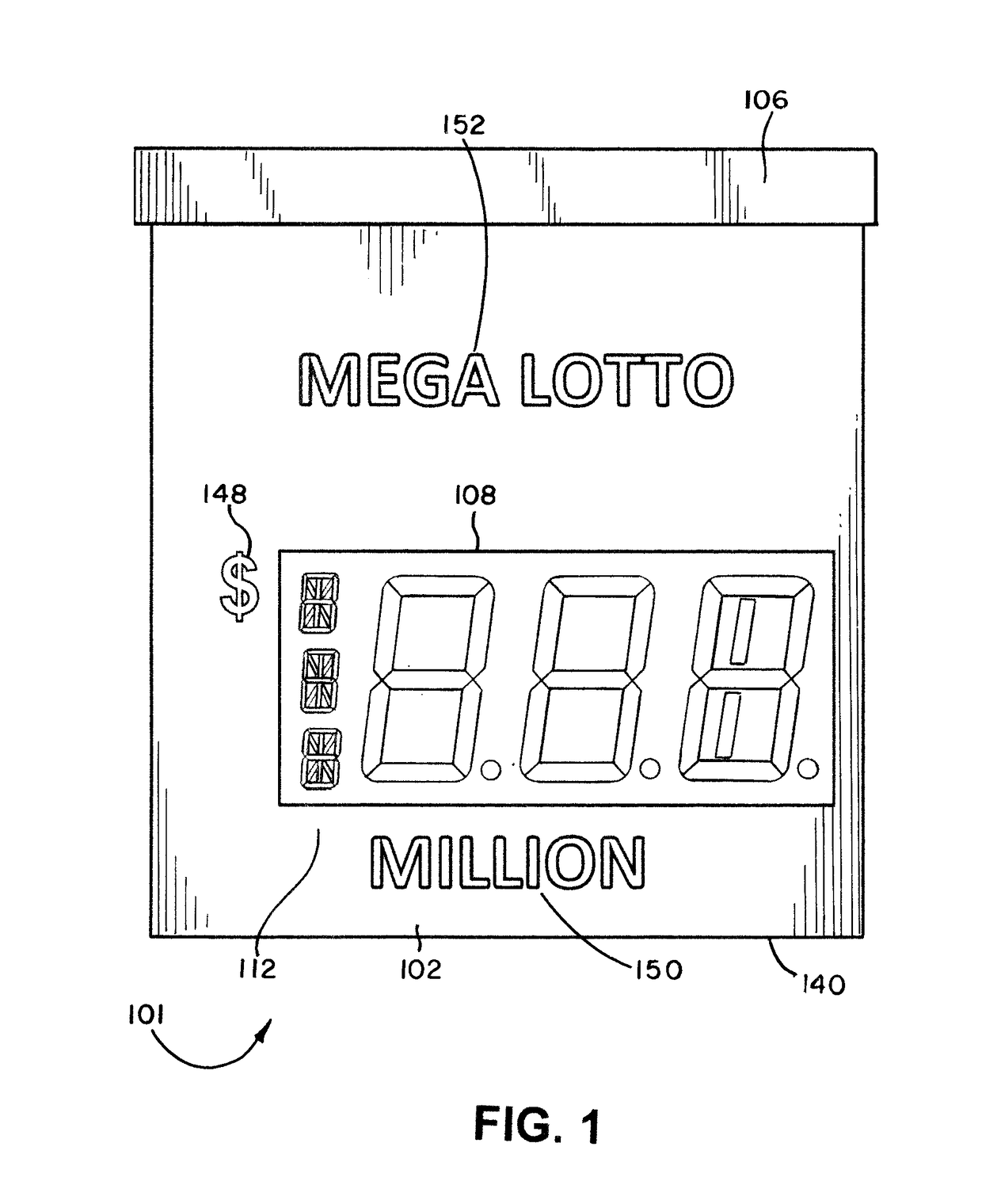
An illuminated display for displaying a lottery jackpot values in the range of millions and billions of dollars is disclosed. The lottery display has an LED array for selectively displaying either “MILLION” or “BILLION.” A special LED module for representing an uppercase letter “M” or uppercase letter “B” is positioned next to a series of LED elements configured to display “ILLION.” A special LED module having nine segments may be employed for the indicia of units, where the LED module may be illuminated to form the numerals 0 through 9, as well as an upper case letter “B.” The illuminated display may also display indicia for currency and the day of the week for the jackpot draw.
Owner:KAOH ANDY K F
Data entry device (DED)
ActiveUS9176591B2Easy to useInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsMathematical OperatorsUsability
The present invention provides a Data Entry Device for computers and other devices. An embodiment of the present invention provides a Data Entry Device combining a keyboard and pointing device for computers and other devices; The Data Entry Device of the present invention introduces a completely new ergonomic construction for all keys. In the Data Entry Device of the present invention the keyboard and pointing device can both be used without shifting the hands from its initial resting position and where the shift key has to be used only for capitals and a few rarely used punctuations and symbols. The vowels are all on one side thus making them easy to access and use. All the letters are arranged so that on maximum occasions the letters are alternating between hands. The character keys are separated into alphabets, numerals, mathematical operators, punctuations and symbols. The placement of the characters on the DED is based on their frequency of occurrence in the environment, the ideal workload that should be allotted to each finger, the order of ease of use of keys, their pattern of use and similarity of type. In the present invention the concept of Home Row for fingers has been replaced by Home Keys for each finger being the keys on which the fingers tend to rest naturally and is not in one row. All this together makes the DED easy to comprehend, easy to learn, easy to use, more difficult to forget, increase the speed of typing, reduce errors and makes the user less prone to medical problems.
Owner:NAIR PREM KUMAR
A data entry device (DED)
ActiveCN102576254ASmall sizeReduce errorsInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsMathematical OperatorsError reduction
The present invention provides a Data Entry Device for computers and other devices. An embodiment of the present invention provides a Data Entry Device combining a keyboard and pointing device for computers and other devices; The Data Entry Device of the present invention introduces a completely new ergonomic construction for all keys. In the Data Entry Device of the present invention the keyboard and pointing device can both be used without shifting the hands from its initial resting position and where the shift key has to be used only for capitals and a few rarely used punctuations and symbols. The vowels are all on one side thus making them easy to access and use. All the letters are arranged so that on maximum occasions the letters are alternating between hands. The character keys are separated into alphabets, numerals, mathematical operators, punctuations and symbols; The placement of the characters on the DED is based on their frequency of occurrence in the environment, the ideal workload that should be allotted to each finger, the order of ease of use of keys, their pattern of use and similarity of type. In the present invention the concept of Home Row for fingers has been replaced by Home Keys for each finger being the keys on which the fingers tend to rest naturally and is not in one row. All this together makes the DED easy to comprehend, easy to learn, easy to use, more difficult to forget, increase the speed of typing, reduce errors and makes the user less prone to medical problems.
Owner:普雷姆・库马・奈尔
Loading device for static strength test of end wall of car body
ActiveCN108918280AImplementation of static strength compression testSimple structureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRailway vehicle testingVertical planeActive force
The invention provides a loading device for a static strength test of the end wall of a car body, belonging to the field of active force loading devices for static strength tests of the end walls of railway vehicles. The loading device of the invention comprises a loading crossbeam, two crossbeam hanging seats with shapes resembling the upper-case letter of Pi, two flanged clamping seats and two force applying cylinders, wherein the front end of each crossbeam hanging seat is fixedly connected with one corresponding flanged clamping seat and with one corresponding force applying cylinder; eachcrossbeam hanging seat, the corresponding flanged clamping seat and the corresponding force applying cylinder compose one positioning and loading unit; each positioning and loading unit is fixedly connected with one end of the loading crossbeam via the corresponding crossbeam hanging seat; and two positioning and loading units are arranged in mirror symmetry about the mid vertical plane of the long edge of the loading crossbeam. According to the invention, a lifting rope is connected with a lifting sling so as to lift the loading device to an appropriate test height; and the force applying cylinders respectively in fixed connection with the rear parts of the flanged clamping seats are utilized for applying force to the end wall, so the static strength compression test of the end wall of the car body can be implemented.
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD +1
Numeral input method
InactiveUS20080297378A1Electronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingChinese charactersUpper Case Letter
A numeral input method simply uses the keys of a mobile phone or some of a computer keyboard and the beginning point and the ending point of each English letter manually written by hand on the keys to achieve a numeral code system for the English alphabet. So, under the mode, Chinese characters and English alphabets (small and capital letters), numerals and simple symbols can be retrieved, even available for other languages. It can lessen the knocking times on the keys and make input operated easily and conveniently like writing on a mobile phone or a keyboard, an people all over the world speaking diverse languages can key in sentences, information, etc. more easily and quickly.
Owner:SU WEI CHOU
Hiragana and katakana conversion method
InactiveCN101458569ASpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingHiraganaKatakana
The invention relate to the keypad input field. The invention provides a transferring method for hiragana and katakana which has characteristics that one of the hiragana and katakana is used as capital letter, another is used as small letter, long-short time is judged by using delaying method for judging whether being capital letter or small letter, hiragana or katakana is distributed on a digital keyboard, each digital keyboard has many hiragana and katakana, kana kind on one digital keyboard is transferred by using delaying technique and judges whether being hiragana or katakana letter by various long-short delaying time.
Owner:BEIJING SHANGXING WEISHI INFORMATION +1
Greece words conversion method
InactiveCN101241402ASpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingSoftware engineeringUpper Case Letter
The invention relates to a small keyboard input field for alphabetic writing, and provides a conversion method for a Greek letters. One of the Greek letter is regarded as an uppercase and another is regarded as a lowercase. The uppercase and lowercase are judged by judging time length by using a time-delay method.
Owner:BEIJING SHANGXING WEISHI INFORMATION +1
Lottery signs for displaying lottery jackpots of millions and billions of dollars
An illuminated display for displaying a lottery jackpot values in the range of millions and billions of dollars is disclosed. The lottery display has an LED array for selectively displaying either "MILLION" or "BILLION." A special LED module for representing an uppercase letter "M" or uppercase letter "B" is positioned next to a series of LED elements configured to display "ILLION." A special LED module having nine segments may be employed for the indicia of units, where the LED module may be illuminated to form the numerals 0 through 9, as well as an upper case letter "B." The illuminated display may also display indicia for currency and the day of the week for the jackpot draw.
Owner:KAOH ANDY K F
Method and system for representing capitalization of letters while preserving their category similarity to lowercase letters
InactiveUS20140129928A1Increase in sizeHigh strengthNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmUpper Case Letter
A computer-implemented method is proposed for representing capitalization in written text by quantitative differences in font size, font, color, boldness, and italics or some combination of these characteristics of lowercase letters rather than by the currently accepted use of uppercase letters. Shape differences between upper and lowercase letters impede learning to read. The proposed method of capitalization doesn't change the shape of the lowercase letter but only changes a property that leaves the basic shape of the letter intact. This design change makes text easier to read and allows children and illiterate adults to learn the alphabet more easily. It also transforms text to be readable by individuals who have learned the lowercase but not the uppercase letters. The proposed method of representing capitalization can also be used to signal capitalization in texts with unicase scripts.
Owner:PSYENTIFIC MIND
Cyril or Russion letter conversion method
InactiveCN101261538ASpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingUpper Case LetterComputer science
The invention relates to the input field of a small keyboard of pinyin characters, which provides a conversion method of Cyrillic letters or Russian letters, one of the Russian letters and the Cyrillic letters is taken as capital letters, the other is taken as lowercase letters, and the capital letters or the lowercase letters are judged by utilizing a delay method for carrying out the judgment of long time and short time.
Owner:BEIJING SHANGXING WEISHI INFORMATION +1
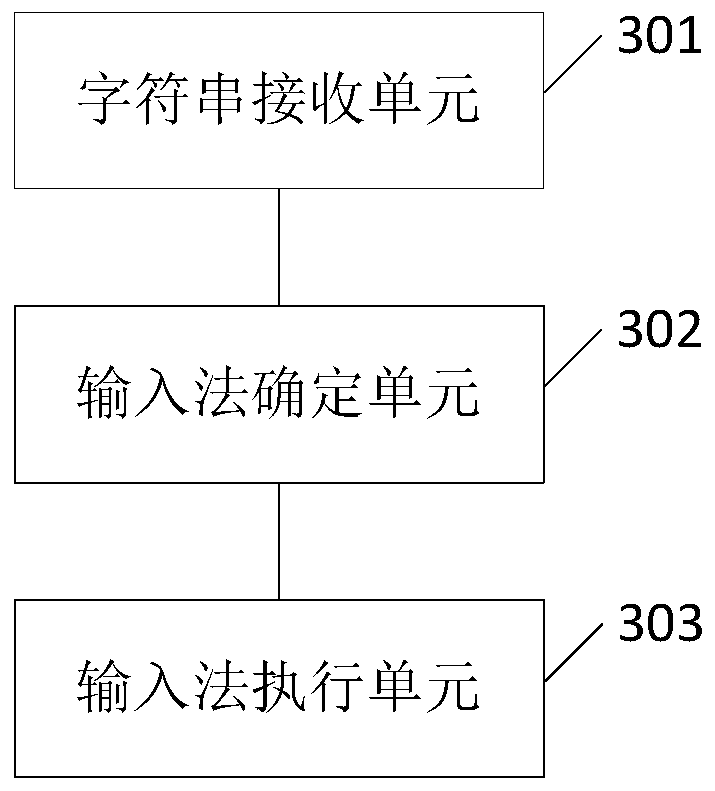
Input method for generating character string and executing instruction and electronic device
PendingCN114647322AInput/output processes for data processingProgramming languageSoftware engineering
The invention provides an input method for a disabled person to generate a character string on an electronic device, comprising: presenting an instruction on a display screen of the electronic device, the instruction comprising one or more language instructions, one or more digital instructions and one or more system instructions; the instruction is selected to generate the character string. In addition, the language instruction comprises an English language instruction and a Chinese language instruction; wherein the English language instructions comprise one or more English letter instructions, a punctuation instruction, an input / back key instruction and a first switching button instruction; the English letter instruction comprises an English capital letter and an English lowercase letter; the digital instructions comprise one or more digital character instructions, a decimal point instruction and a second switching button instruction; wherein the system instruction comprises a computer control instruction; the computer control instructions comprise one or more control instructions and a third switching button instruction, wherein the control instructions comprise functions of shutdown, logout, restart, internet, file opening and the like.
Owner:张世豪
Storage method for inputting Chinese word into computer by calculation functional encoding phoneme of word
InactiveCN100474219CIntuitive lockPerfect lockInput/output processes for data processingChinese charactersUpper Case Letter
A method for inputting Chinese character by computer in storage mode includes using fixed four positions of line, column, longitudinal and order English capital letters as unique corresponding identification of Chinese character; enabling to use 26 English capital letters and two ASCII code symbols to directly spell out modern Chinese characters and phrase in reciprocal-corresponding way as per standard stroke attribute and pronunciation attributes of initial consonant and vowel as well as four tones.
Owner:北京汉码魔方科技有限公司
Mongolian input method and input method system
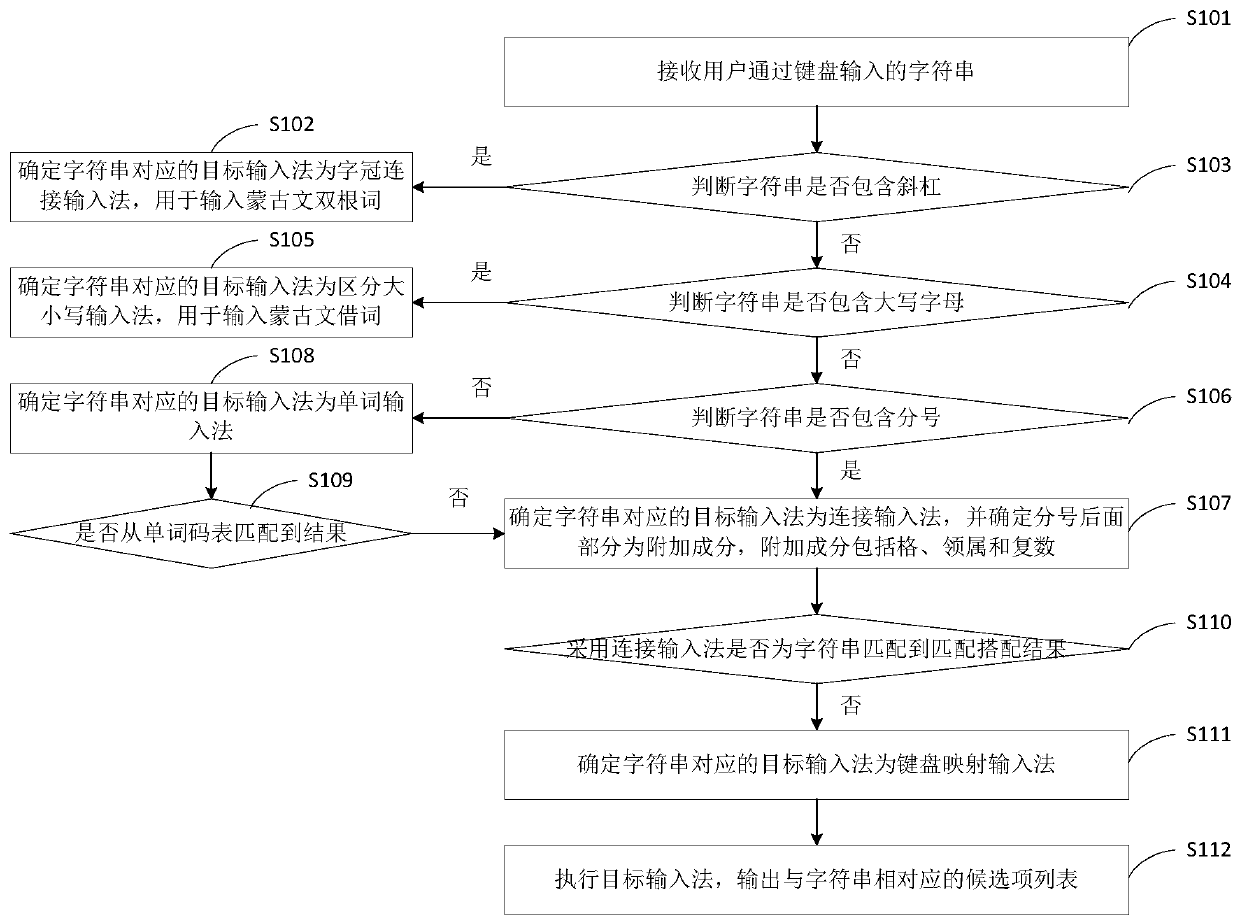
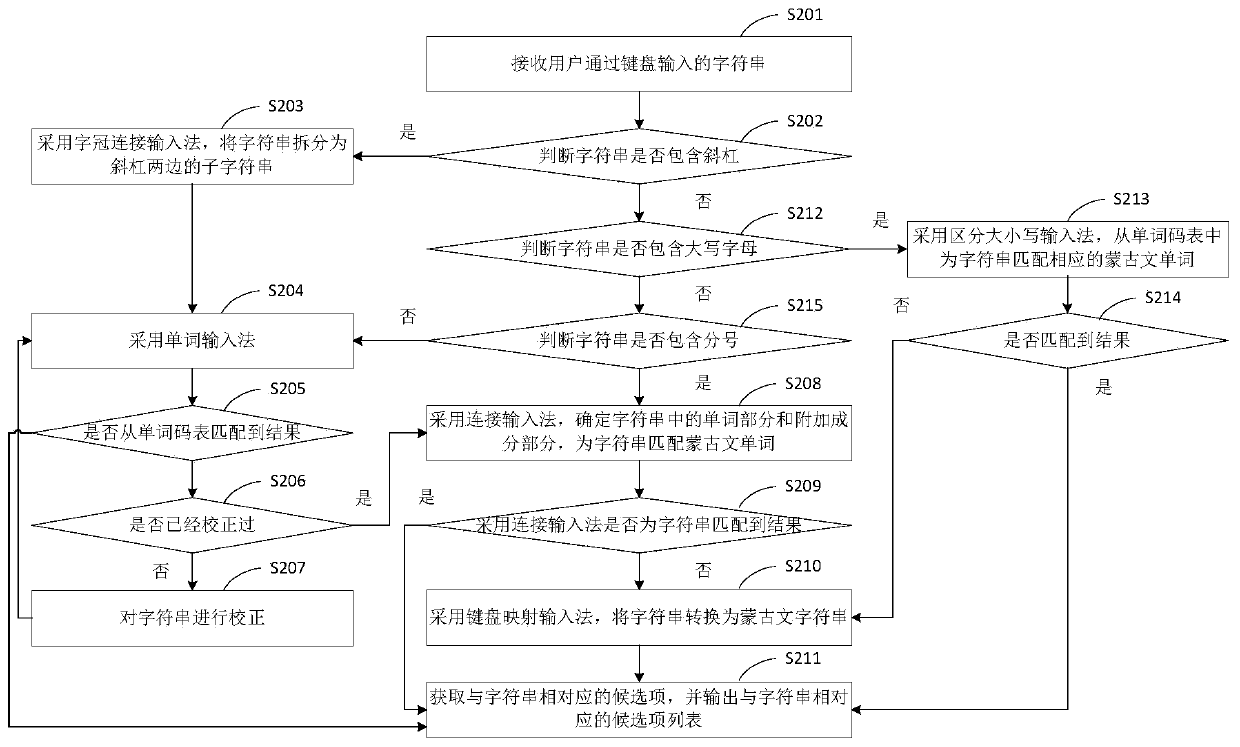
ActiveCN111580685AEnter exactlyEfficient outputEnergy efficient computingInput/output processes for data processingProgramming languageAlgorithm
The invention provides a Mongolian input method and an input method system, after a character string input by a user is received, a proper input method is automatically matched by analyzing the characteristics of the character string, and when the character string contains an oblique bar, double Mongolian words are input by adopting a prefix connection input method; when the character string contains capital letters, Mongolian borrowing words are input by adopting a capital and small letter distinguishing input method; Mongolian words consisting of words and additional components are input byadopting a connection input method when the character string contains the divisor; under the condition that the character strings do not contain inclined bars, capital letters and divisional numbers,a word input method is adopted, and when appropriate Mongolian words cannot be matched in the input methods, a keyboard mapping input method is adopted. Therefore, no matter which type of Mongolian word is input by the user, the Mongolian word can be accurately and efficiently output by adopting the corresponding input method, and the method is not limited by borrowing words and pronunciation of users in different regions.
Owner:马福泉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com