Pesticide microcapsule
A technology of microcapsules and pesticides, applied in the fields of animal repellents, botanical equipment and methods, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult performance regulation, high price, restrictions, etc., and achieve long-term pesticide slow-release effect and shell material cost. Low, reducing the effect of decomposition and loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Dissolve 0.2 g of biodegradable polymer polybutylene succinate (PBS) in 10 ml of chloroform at room temperature, and then dissolve 0.8 g of pesticide chlorpyrifos.
[0036] 0.3 g of polyethylene oxide (20) sorbitan monostearate and 0.3 g of polyvinyl alcohol were dissolved in 100 ml of water.
[0037] Mix the above aqueous solution with chloroform solution dissolved in chlorpyrifos and polybutylene succinate, disperse and emulsify at high speed with a disperser, and emulsify at a stirring speed of 10000rpm for 5-10 minutes.
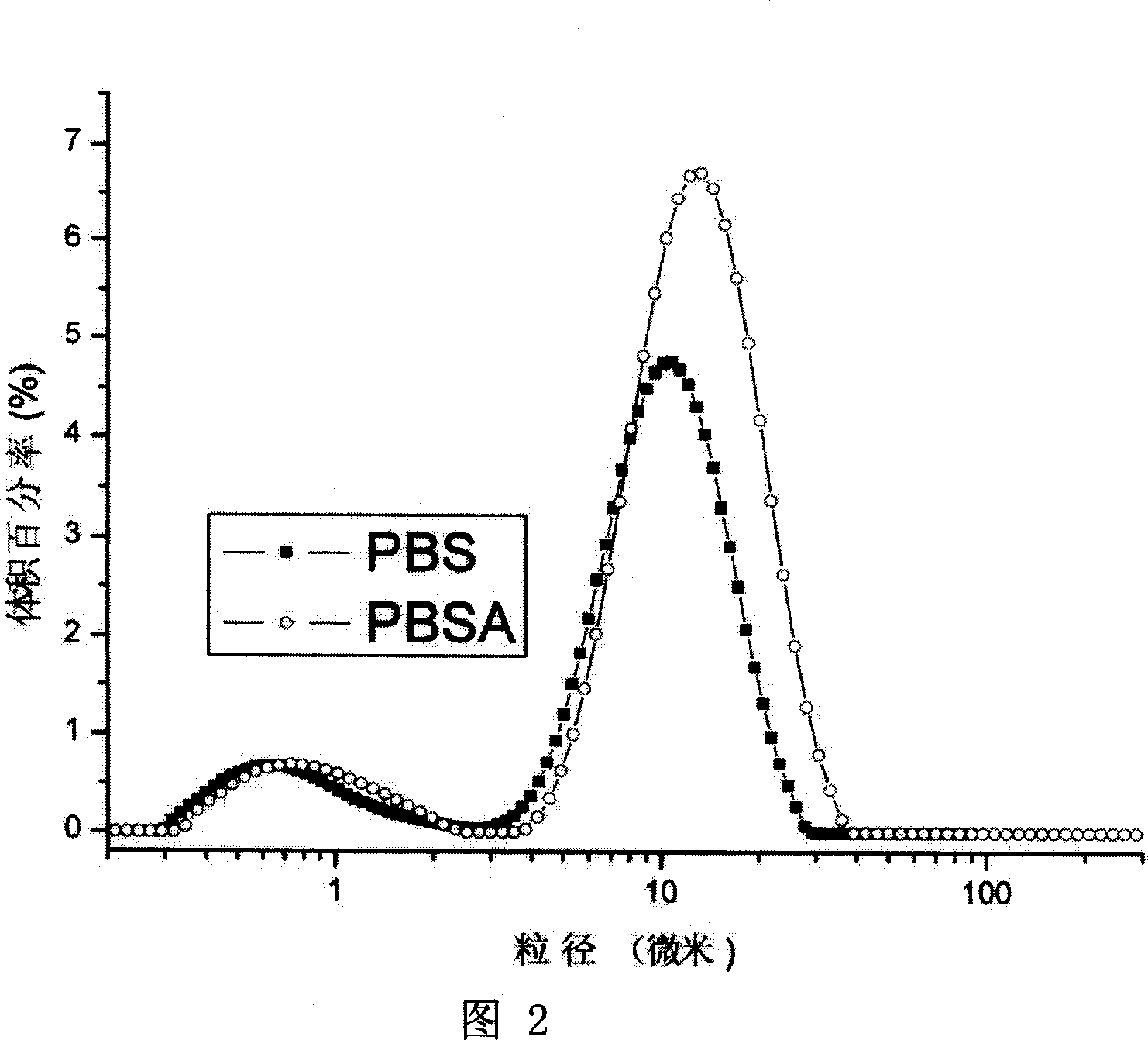
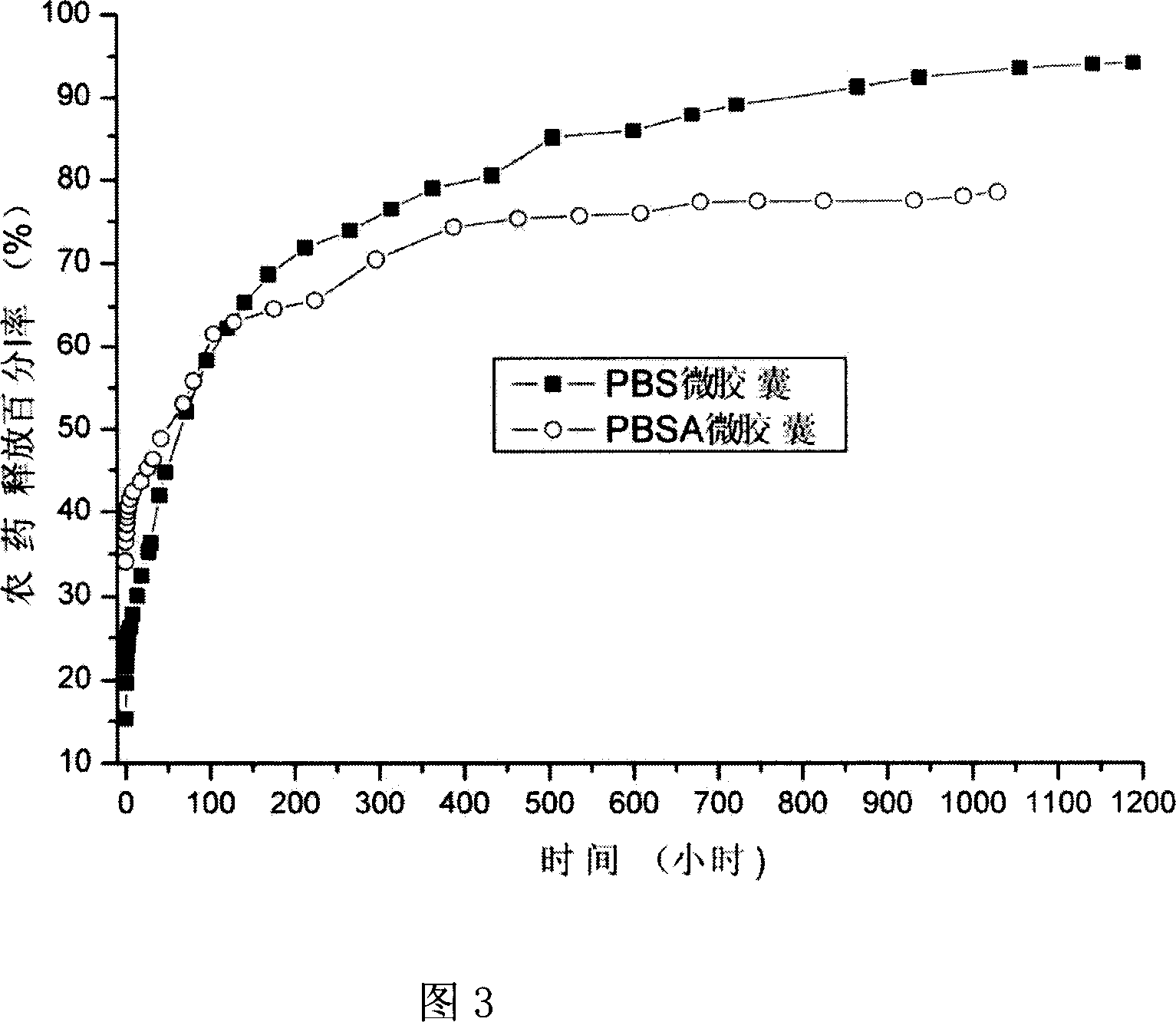
[0038] Heat the emulsified emulsion with a water bath to slowly raise the temperature, control the water temperature at 25-50°C and the stirring speed at 800rpm, and remove the chloroform. Finally, pesticide microcapsules with an average diameter of 0.3-40 μm are produced, and the diameter of the pores in the wall of the pesticide microcapsules is 0.01-3 μm. Figure 1, Figure 2.
Embodiment 2
[0040] In 20 ml of dichloromethane at room temperature, dissolve 0.6 g of butanediol succinate adipate copolyester (PBSA), and then dissolve 1.2 g of chlorpyrifos.
[0041] 0.1 g of sodium lauryl sulfate and 0.4 g of polyvinyl alcohol were dissolved in 150 ml of water. Among them, the degree of polymerization of polyvinyl alcohol is 1750, and the degree of alcoholysis is 88%.
[0042] The above aqueous solution is mixed with the dichloromethane solution dissolved in chlorpyrifos and butanediol succinate adipate copolyester, emulsified at high speed with a disperser, and emulsified at a stirring speed of 12000 rpm for 5-10 minutes.
[0043] The emulsified emulsion was slowly heated in a water bath from room temperature to 40° C., and dichloromethane was removed at 800 rpm. In the heating process, finally, pesticide microcapsules with an average diameter of 0.3-40 μm are produced, and the diameter of the pores in the wall of the pesticide microcapsules is 0.01-3 μm. Figure 1, ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In 20 ml of dichloromethane at room temperature, dissolve 0.6 g of butanediol succinate adipate copolyester (PBSA), and then dissolve 1.5 g of diazinon (Dianon).
[0046] 0.2g polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monooleate, 1.0g polyvinyl alcohol were dissolved in 150ml water. Wherein the degree of polymerization of polyvinyl alcohol is 1750, and the degree of alcoholysis is 88%.
[0047]The above aqueous solution is mixed with the dichloromethane solution dissolved in chlorpyrifos and butanediol succinate adipate copolyester, emulsified at high speed with a disperser, and emulsified at a stirring speed of 6000 rpm for 5-10 minutes.
[0048] The emulsified emulsion is slowly heated from room temperature to 40° C. in a water bath, and methylene chloride is removed at 800 rpm to manufacture pesticide microcapsules with an average diameter of 0.3 to 40 μm. The diameter of the capsule wall holes of the pesticide microcapsules is 0.01 to 3 microns.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com