Metal ceramic inert anode for molten salt electrolysis and preparation method thereof
A cermet, inert anode technology, applied in the direction of electrodes, electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of poor conductivity, inert anode structure and performance decay, difficult connection of metal guide rods, etc., to alleviate thermal expansion mismatch, solve Selective dissolution and the effect of facilitating high-temperature conductive connections
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
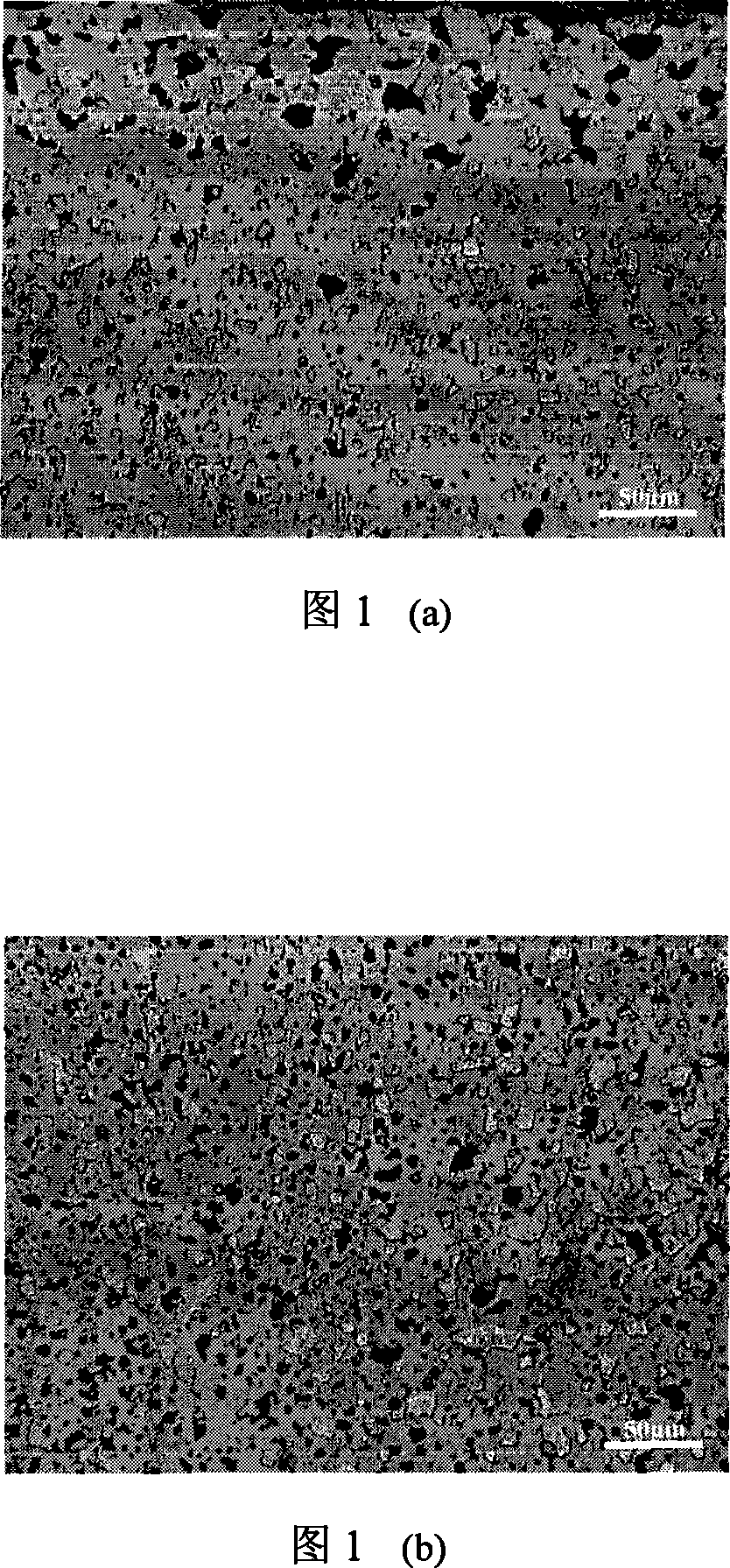
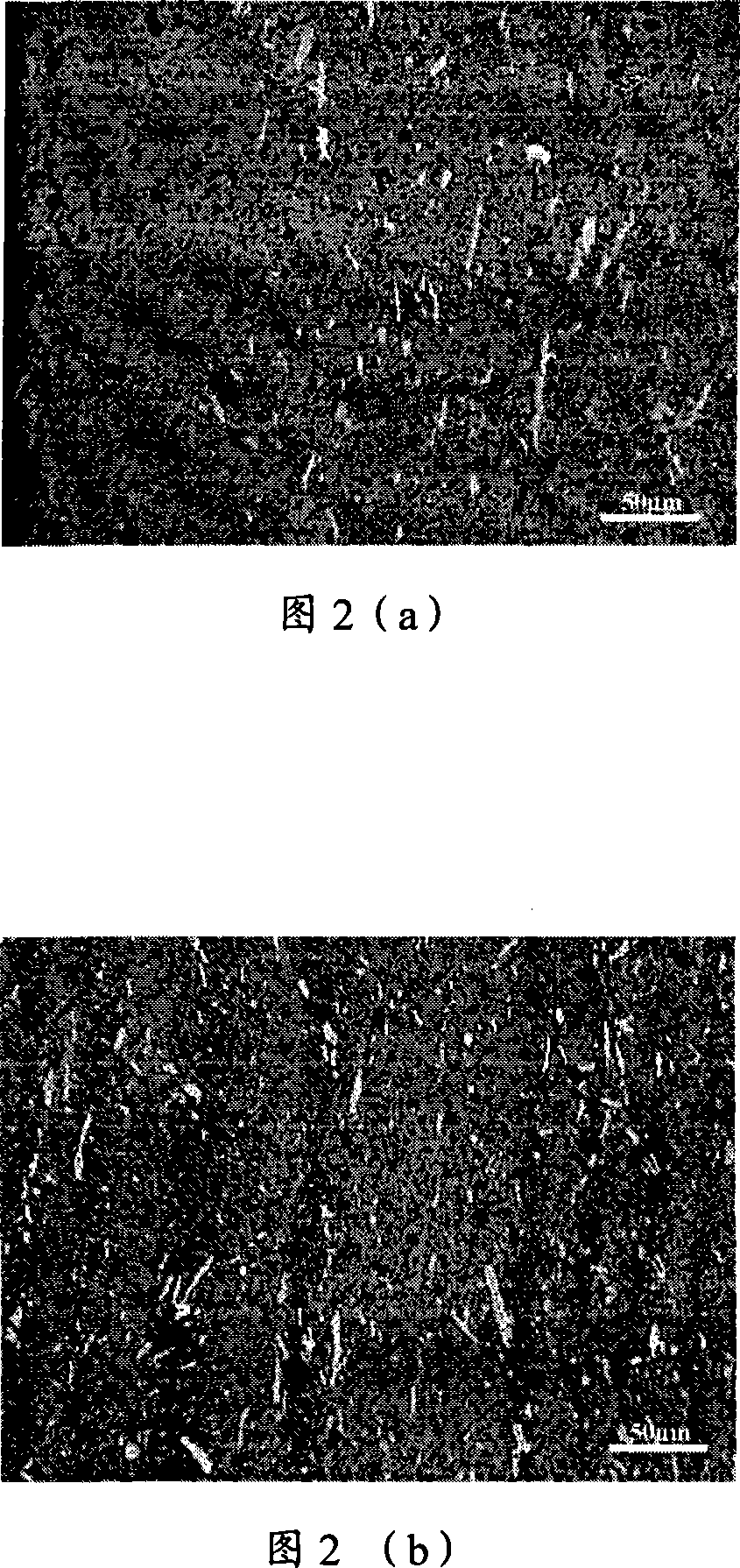
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: CaO-Cu-NiO-NiFe 2 o 4 Cermet inert anode
[0046] CaO-Cu-NiO-NiFe 2 o 4 The raw material formula of the cermet inert anode is shown in Table 1. First weigh NiO and Fe respectively according to 1.35:1 (molar ratio) 2 o 3 powder, where NiO powder particle size is 10μm, Fe 2 o 3 The particle size of the powder is 10 μm, and it is dispersed with at least one of industrial alcohol or water, phthalic acid, oleic acid, ammonia salt solution, polyacrylamide solution, fish oil, butyl phthalate, polyacrylate, and polyacrylamide agent, ball milled for 8h, dried at 80°C for 24h, then put into a corundum crucible, placed in an electric resistance furnace in an air atmosphere, and calcined at 1200°C for 6h to obtain a composite ceramic powder with an average particle size of about 10μm. X-ray diffraction phase analysis shows that the ceramic powder mainly contains NiO and NiFe 2 o 4 two phases. Then with pre-prepared NiO-NiFe 2 o 4 The powder is a ceramic phas...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: CaO-Ni-NiFe 2 o 4 Cermet inert anode
[0050] CaO-Ni-NiFe 2 o 4 The raw material formula of the cermet inert anode is shown in Table 2. First, weigh NiO and Fe respectively according to 1:1 (molar ratio). 2 o 3 powder, where NiO powder particle size is 20μm, Fe 2 o 3 The particle size of the powder is 20 μm, and it is dispersed with at least one of water or industrial alcohol, phthalic acid, oleic acid, ammonium salt solution, polyacrylamide solution, fish oil, butyl phthalate, polyacrylate, and polyacrylamide agent, ball milled for 8 hours, dried at 80°C for 24 hours, then put into a corundum crucible, placed in a resistance furnace in an air atmosphere, and calcined at 1200°C for 6 hours to obtain a composite ceramic powder with an average particle size of about 18 μm. X-ray diffraction phase analysis shows that the ceramic powder mainly contains NiFe 2 o 4 Mutually. Then with pre-prepared NiFe 2 o 4 The powder is a ceramic phase base material,...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: CaO-BaO-Ni-NiO-NiFe 2 o 4 Cermet inert anode
[0054] CaO-BaO-Ni-NiO-NiFe 2 o 4 The raw material formula of the cermet inert anode is shown in Table 3. First weigh NiO and Fe respectively according to 1.35:1 (molar ratio) 2 o 3 powder, where NiO powder particle size is 50μm, Fe 2 o 3 The particle size of the powder is 50 μm, and it is dispersed with at least one of phthalic acid or industrial alcohol, water, oleic acid, ammonia salt solution, polyacrylamide solution, fish oil, butyl phthalate, polyacrylate, and polyacrylamide agent, ball milled for 8 hours, dried at 80°C for 24 hours, then put into a corundum crucible, placed in a resistance furnace in an air atmosphere, and calcined at 1200°C for 6 hours to obtain a composite ceramic powder with an average particle size of about 32 μm. X-ray diffraction phase analysis shows that the ceramic powder mainly contains NiFe 2 o 4 Mutually. Then with pre-prepared NiFe 2 o 4 The powder is a ceramic p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com