Methoxypolyethylene glycol-modified arginine deiminase, preparation thereof and use thereof
A technology of arginine deiminase and methoxy polyethylene glycol, which is applied in the field of arginine deiminase and can solve the problems of increasing the enzyme, uncertain anti-tumor efficacy, and lack of it.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: the production of recombinant ADI
[0056] Many studies have shown that ADI from various mycoplasma sources has the same enzymatic properties although there are certain differences in sequence. Such as ADI derived from Mycoplasma arginini (ATCC23243) (SEQ ID NO: 1), Mycoplasma hominis (ATCC23114) (SEQ ID NO: 2), Mycoplasma arthritis (ATCC23192) (SEQ ID NO: 3), amino acid sequence homology More than 96%. Literature research (Clark, MikeA, U.S. Patent No.6183738) has proved that from specific activity, K m , V max , and pH optima prove that these enzymes are biochemically indistinguishable. ADI from these different sources are therefore suitable for use in the present invention. In the following examples of the present invention, ADI derived from Mycoplasma arginini (abbreviated as aADI) is used as an example for illustration.
[0057] The aADI gene is derived from arginine mycoplasma. Since some codons of mycoplasma cannot be effectively recognized and...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2.ADI enzyme activity assay
[0062] ADI uses arginine (Arg) as a substrate, and the product guanidine can react with blood and urine nitrogen reagent (BUN) at a high temperature of 100°C to appear red. Add the final concentration of 10mM Arg, 5μg ADI to the reaction system, add 20mM PB (pH 7.2) to 500ul, and react accurately at 37°C for 30min, take 50ul of the reaction solution and add it to the blood and urine nitrogen reagent (BUN), mix well, bathe in boiling water for 10min, and finally Measure OD 540 , with guanidine as the standard for the standard curve. The blank control was blood urine nitrogen reagent (BUN) without ADI. The content (μmol) of the reaction substrate guanidine was converted from the standard curve. Definition of enzyme activity unit: 1 enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the enzyme activity that catalyzes the complete conversion of 1 μmol of arginine into 1 μmol of guanidine within 1 minute at 37°C.
[0063] The protein content ...
Embodiment 3
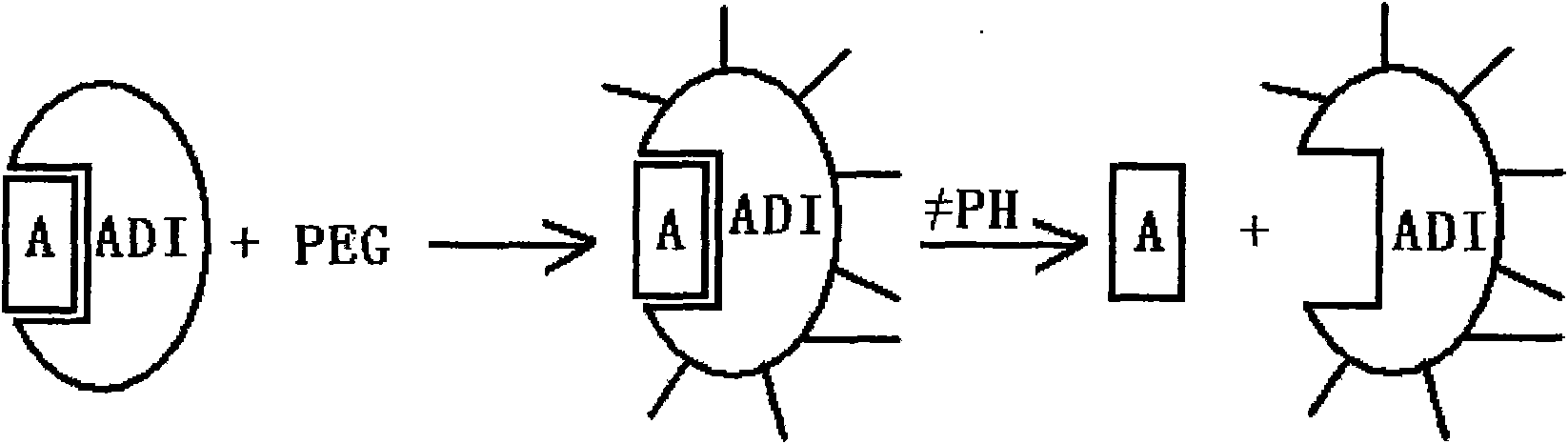
[0064] Example 3: PEG modification of raADI
[0065] Modification experiments were performed in two groups:
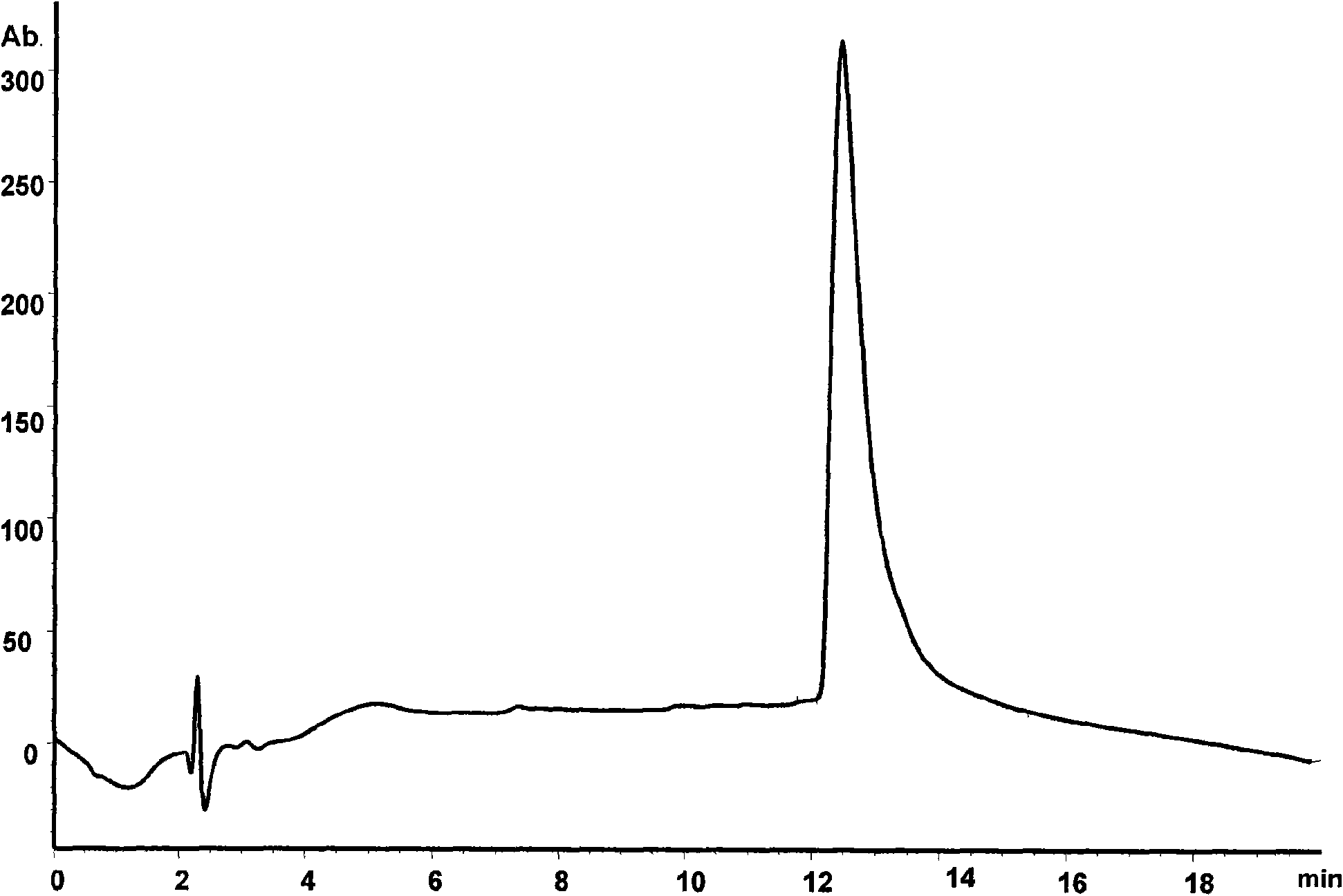
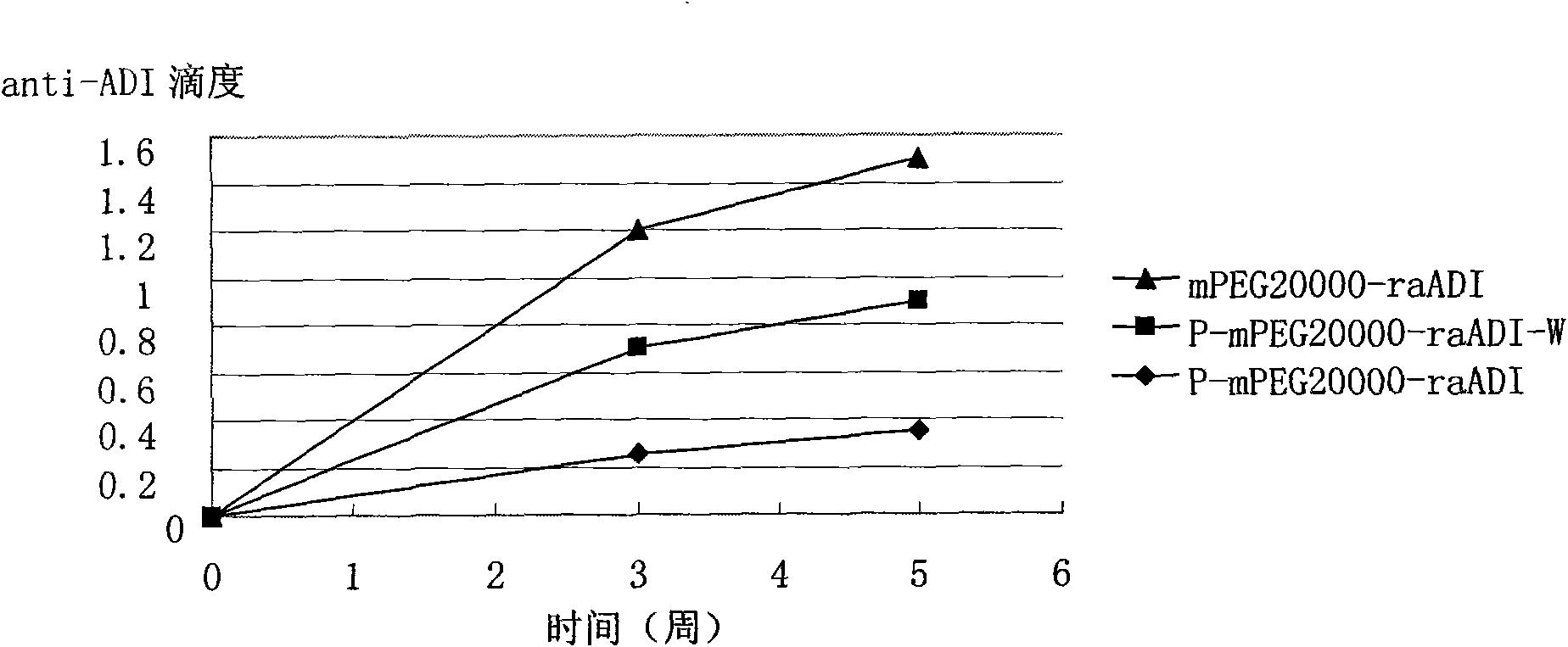
[0066] Reaction (1): in 100 milliliters of 1 mg / ml raADI solution (buffer system is 100mM Bicine, pH8.0), add PEG reagent (mPEG 20000 -SPA, Nektar). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. The modified product PEG-raADI was purified with Phenyl-Sepharose HP, and the corresponding target peak was collected, and finally removed with a G25 desalting column (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 . The final prepared product is named mPEG 20000 -raADI.
[0067] Reaction (2): In addition to adding 10 mg / ml of BOC-Arg to the raADI solution first (corresponding to a molar ratio of BOC-Arg:raADI of 5:1), the purified modified product can be appropriately increased in the equilibrium stage before elution. Time, using the reversible binding and dissociation characteristics between the placebo substrate and the enzyme, it can be easily removed, other conditions are completely con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com