Self-repairing fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite and preparation method thereof
A fiber-reinforced material and fiber-reinforced technology, applied in the field of self-healing fiber-reinforced polymer-based composite materials and their preparation, can solve problems such as lack of self-healing ability, achieve good bonding repair effect, facilitate mutual diffusion, The effect of high reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
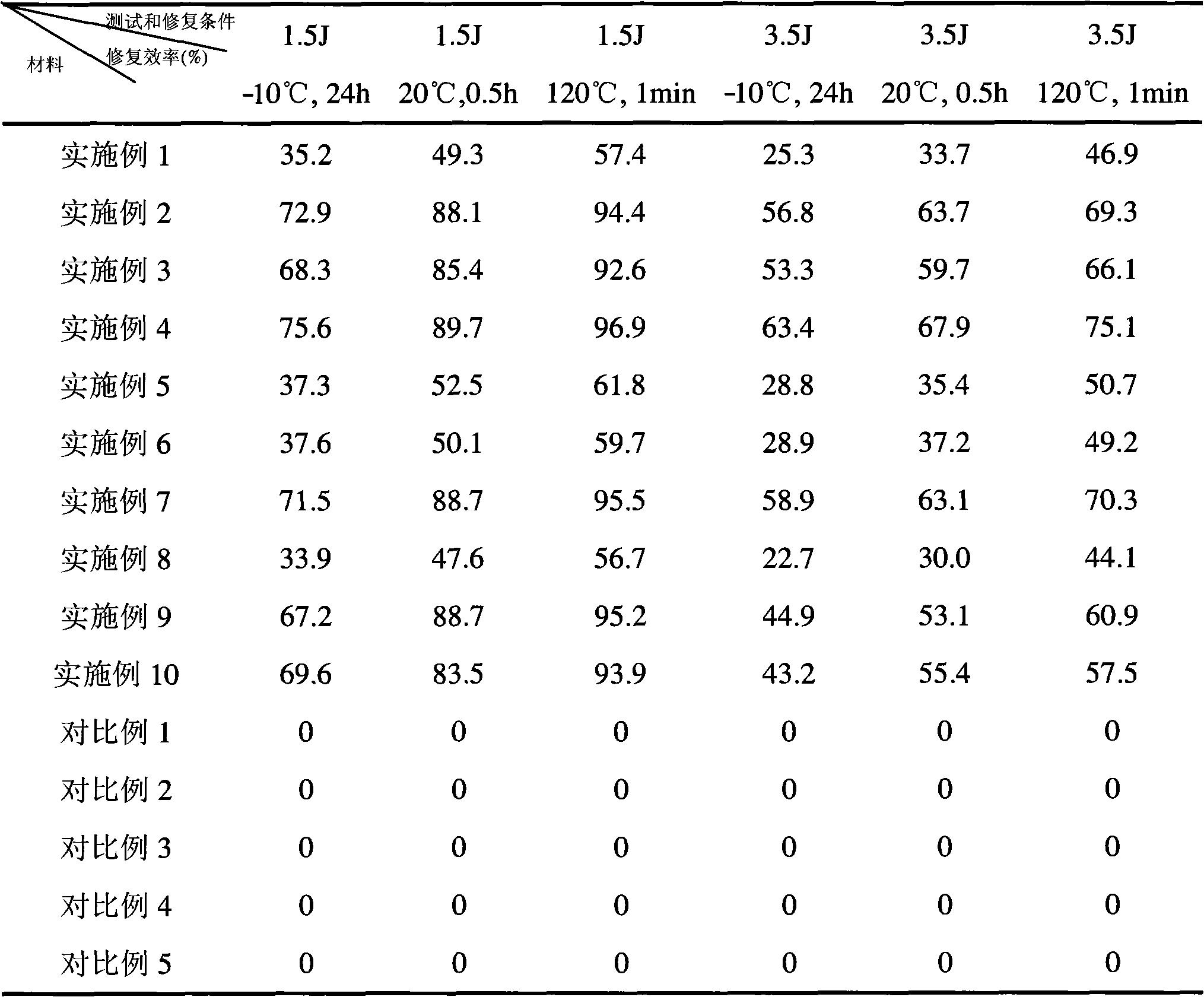
[0042] Take by weighing 10g epoxy resin capsule (capsule core is glycidyl tetrahydrophthalate, capsule core content is 81%, average particle diameter 7.2 μ m) and 10g polythiol capsule (pentaerythritol tetrakis (mercapto propionate), Content 78%, benzyl dimethylamine content 6%, (average particle size 6.9μm), uniformly dispersed in 100g EPON 828 epoxy resin at 40~50℃, add 2gKH-560, 12.5g diethylenetriamine Rapid mixing and degassing. Use the above mixture to impregnate 80g of fiber reinforced material (C-glass fiber grid cloth), lay up, cure and post-cure molding. The curing and post-curing process is: room temperature 24h, 40°C 24h.
[0043] Ultrasonic scanning (T-scan) was used to test the change of the damage area of the composite material after the impact of the falling hammer to evaluate the repair efficiency of the material: using two representative impact energies (1.5J, the matrix crack is the main damage form; 3.5 J, debonding of reinforcing fibers from the matrix, ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Take by weighing 15g epoxy resin capsule (capsule core is bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, capsule core content is 93%, average particle diameter 52 μ m) and 15g polythiol capsule (pentaerythritol tetrakis (mercapto propionate), content 86% , 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol, content 8%, average particle size 49μm)), uniformly dispersed in 100g EPON 828 epoxy resin under the condition of 40~50 ℃, add 1g KH - 570, 7g of the matrix was quickly mixed with a curing agent (2-ethyl-4-methyl-imidazole), degassed. Use the above mixture to impregnate 65g of fiber reinforced material (aramid fiber square cloth), lay up, cure and post-cure to form. Curing and post-curing process: 1h at 50°C, 1h at 80°C, 2h at 100°C.
[0046] The evaluation method is the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Take by weighing 10g epoxy resin capsules (capsule core is bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, capsule core content is 93%, average particle diameter 52 μ m) and 5g Lewis acid capsules (boron trifluoride glycerol complex, capsule core content 58 μ m) %, average particle size 12μm), uniformly dispersed in 100g EPON 828 epoxy resin at 40~50℃, add 1g KH-570, 20g matrix curing agent (adduct of tetraethylenepentamine and acrylonitrile) Rapid mixing, degassing. Use the above mixture to impregnate 40g of fiber reinforced material (E-glass fiber grid cloth), lay up, cure and post-cure to form. The curing and post-curing process is: 1h at 120°C, 1h at 160°C, and 1h at 180°C.
[0049] The evaluation method is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com