Method for preparing dithiocarbamate-based modified porous starch
A technology of dithiocarbamic acid and porous starch, which is applied in the field of modified starch to achieve strong chelation, improved removal rate, and less dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
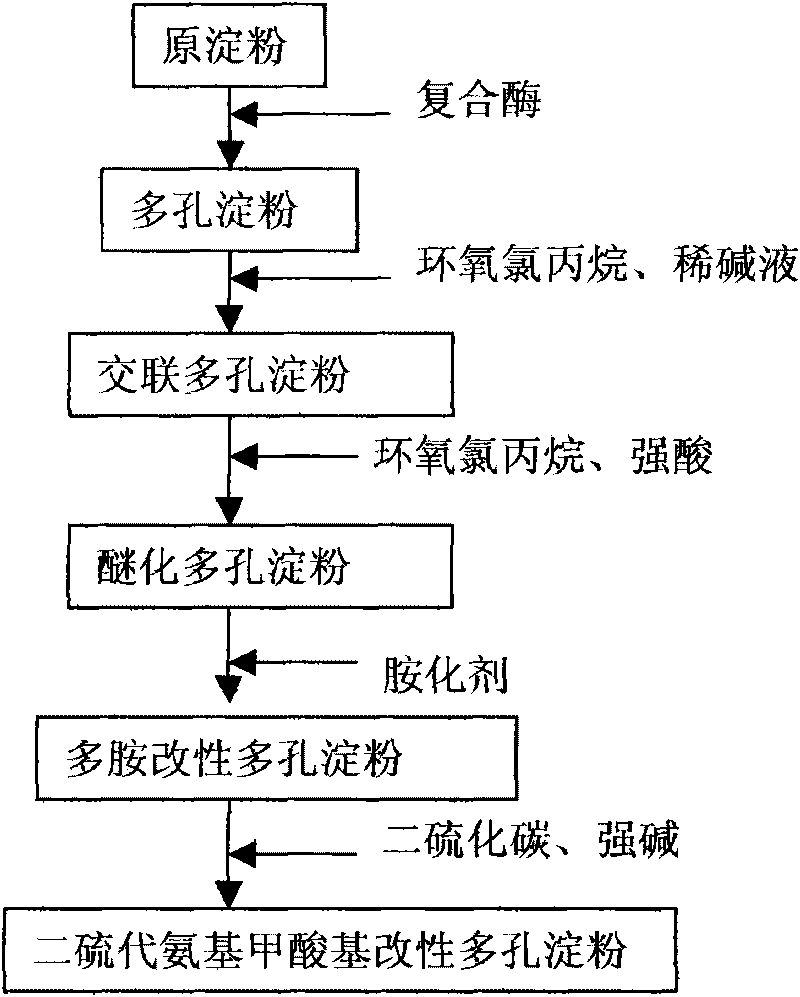
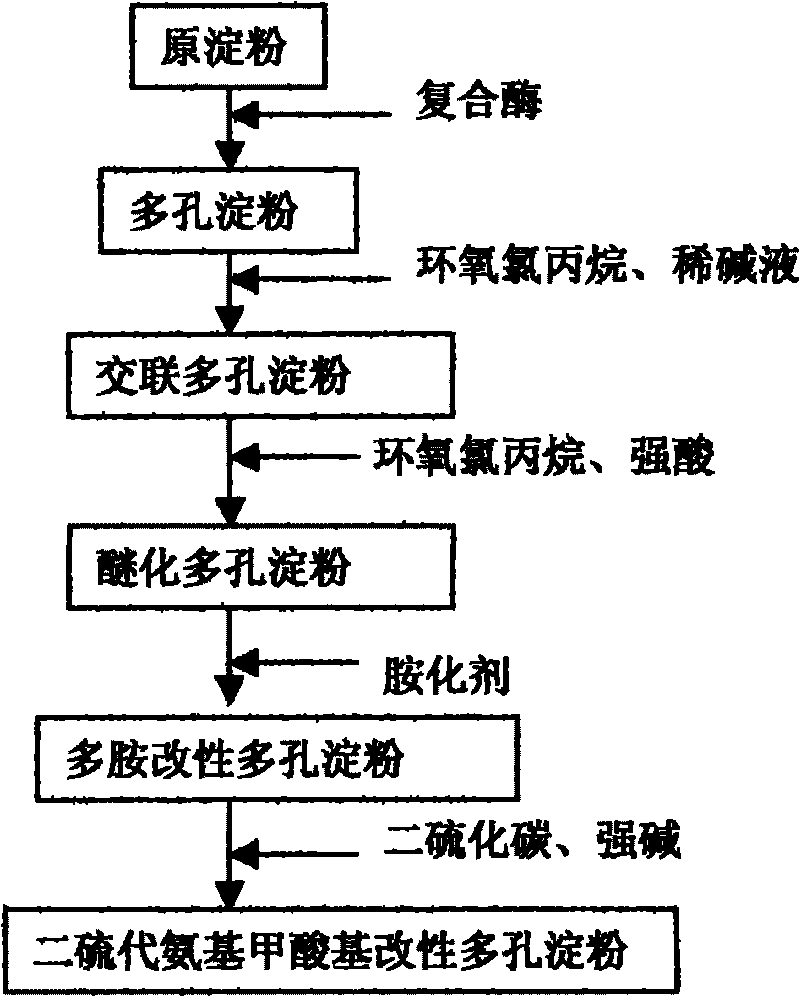
[0033] First, 30 g of commercially available potato starch was used as a raw material and dissolved in 200 mL of a buffer solution with a pH of 5 to obtain a starch slurry with a concentration of 15% by mass. The buffer solution is obtained by measuring commercially available analytically pure citric acid: disodium hydrogen phosphate = 1:2 mass ratio, then adding water and stirring until uniform. Then add the compound enzyme that is made up of the glucoamylase of 0.15g and 0.75g alpha-amylase in the starch slurry, the addition of compound enzyme is 3.0% of starch weight, then react at constant temperature under 45 ℃ of water bath shaking conditions for 8h, then from water bath Take it out, add 5mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass percentage concentration of 4%, stop the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, and then filter and separate the solid and supernatant, wash the solid with distilled water until the pH value is neutral, and finally at 45 ° C Dry under vacuum for 12 ho...
Embodiment 2
[0040] 30g potato starch was dissolved in the same 200mL pH as in Example 1 in the buffer solution of sodium citrate-disodium hydrogen phosphate of 5 to obtain a starch slurry with a concentration of 15% by mass. Add a compound enzyme consisting of 0.25 g of glucoamylase and 0.50 g of α-amylase to the starch slurry. The amount of the compound enzyme added is 2.5% of the weight of the starch, followed by a constant temperature reaction at 60 ° C and a water bath for 18 hours, then taken out and removed. Add 5mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 4% by mass to terminate the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, then filter and separate the solid and supernatant, wash the solid with distilled water until the pH value is neutral, and finally dry it in vacuum at 45°C After 12 hours, the white powder obtained is porous starch, and the water absorption rate of the porous starch is ≥1.80g / g.
[0041] Add 20mL of dilute lye and 2mL of epichlorohydrin to 5g of porous starch, ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Cornstarch was used as raw material, diethylenetriamine was used as amination agent, and the rest of the formula was the same as in Example 1 to obtain dithiodiethylenetriamine formic acid-based modified porous cornstarch.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com