Packing material for liquid chromatography and process for separation and purification of biopolymer by means of the packing material
A technology for liquid chromatography and packing materials, which is applied in the field of packing materials for liquid chromatography, can solve the problems of reduction, the protein adsorption capacity is not improved, and it is impossible to increase the adsorption capacity, so as to improve the binding capacity, effectively separate and purify or concentrate and recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
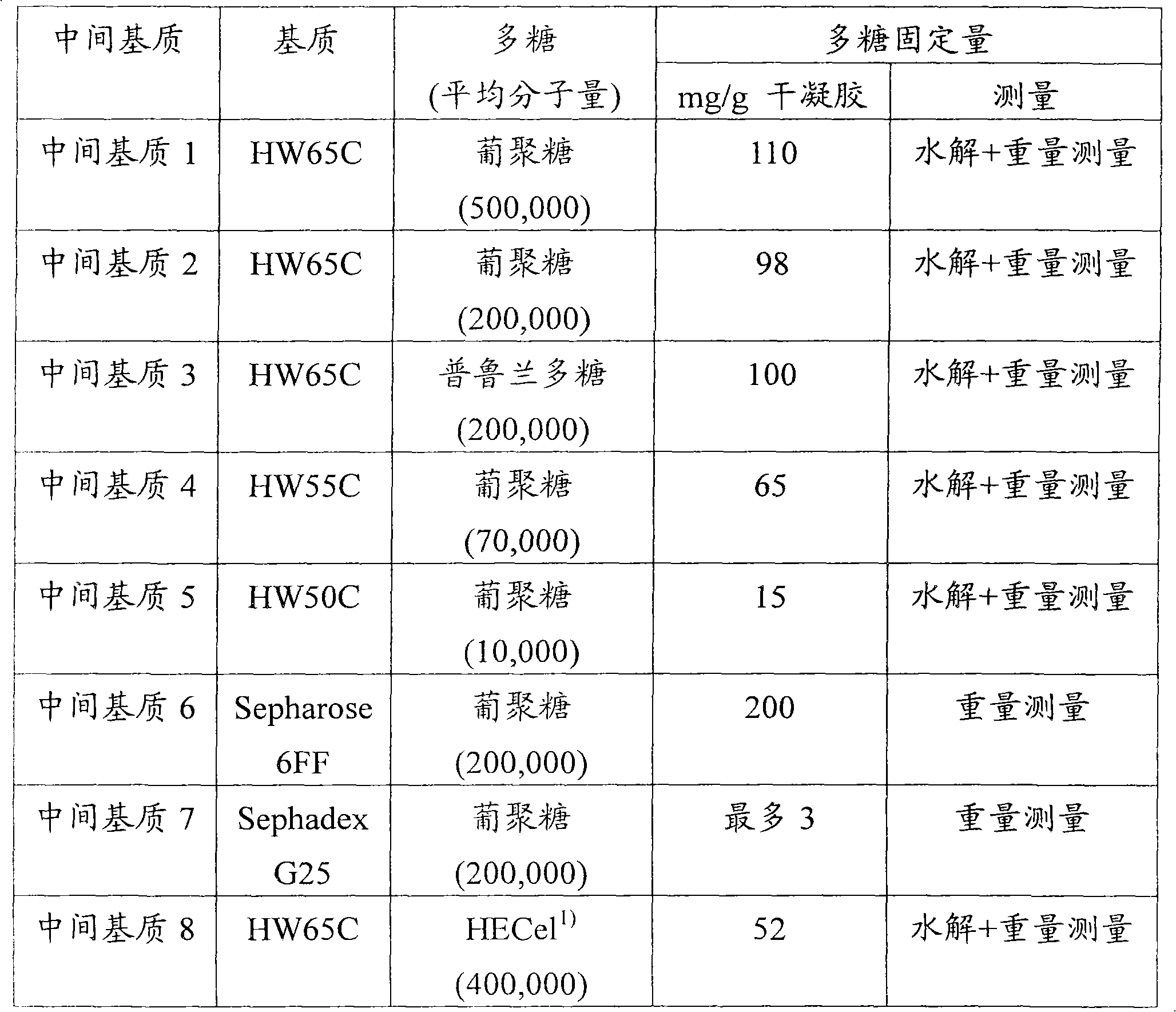
[0116] Now, the present invention will be described in further detail based on examples, but it should be construed that the present invention is by no means limited thereto. In addition, various substrates used in the following Examples and Comparative Examples are supports (hydrophilic substrates) having alcoholic hydroxyl groups on their surfaces. The performance of the matrix with respect to the porous structure under aqueous conditions was evaluated by exclusion limiting molecular weight and porosity. The measurement method is as follows.
[0117] Measurement of Exclusion Limit Molecular Weight and Porosity
[0118] By using an aqueous gel slurry solution of a hydrophilic matrix, the matrix was put into a stainless steel column with an inner diameter of 10.7 mm and a length of 150 mm at the highest packing density, and then, the packed column was installed on a RI-8020 detector (by TOSOH CORPORATION) HPLC system (manufactured by TOSOH CORPORATION).
[0119] Then, by us...
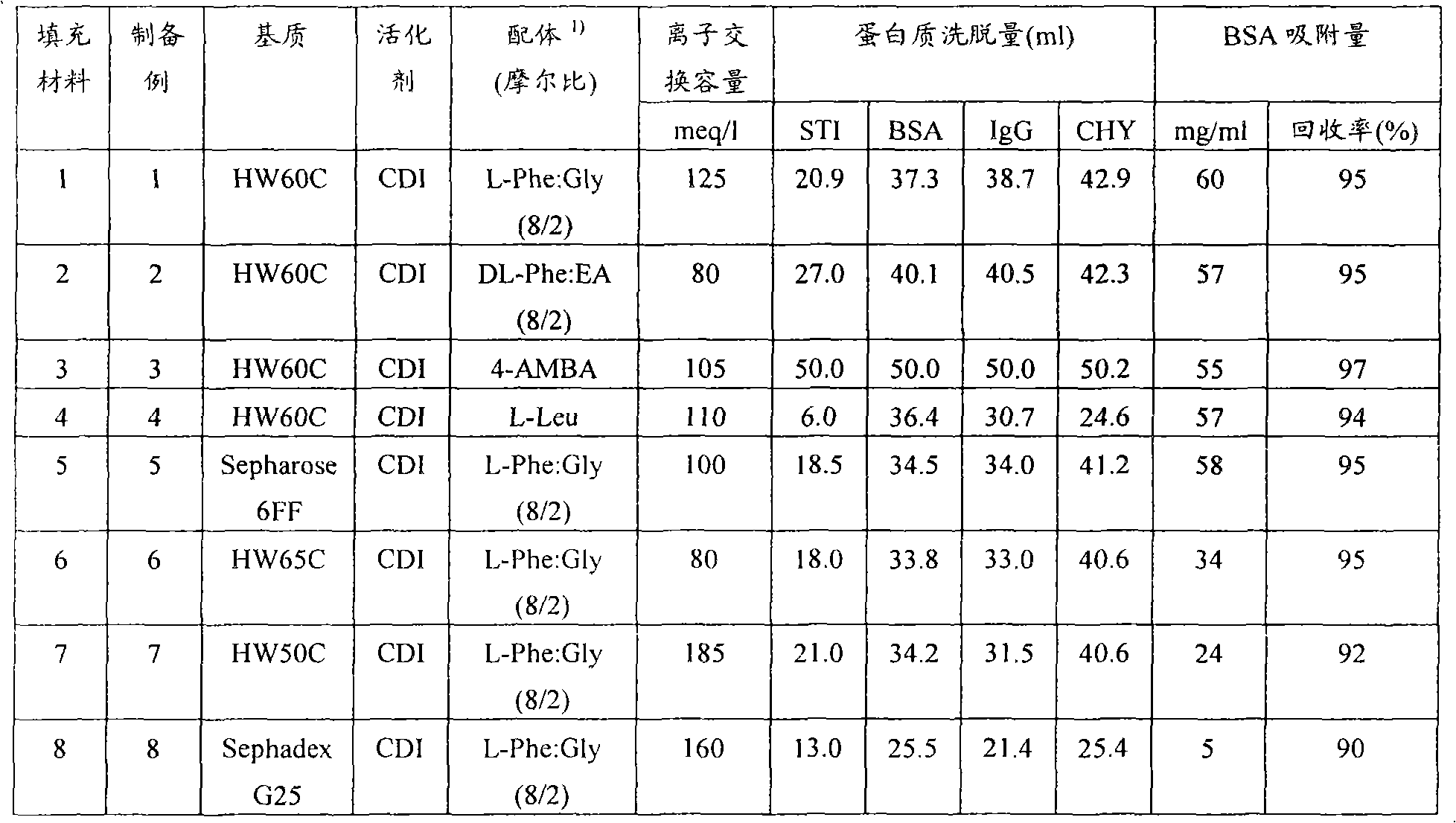
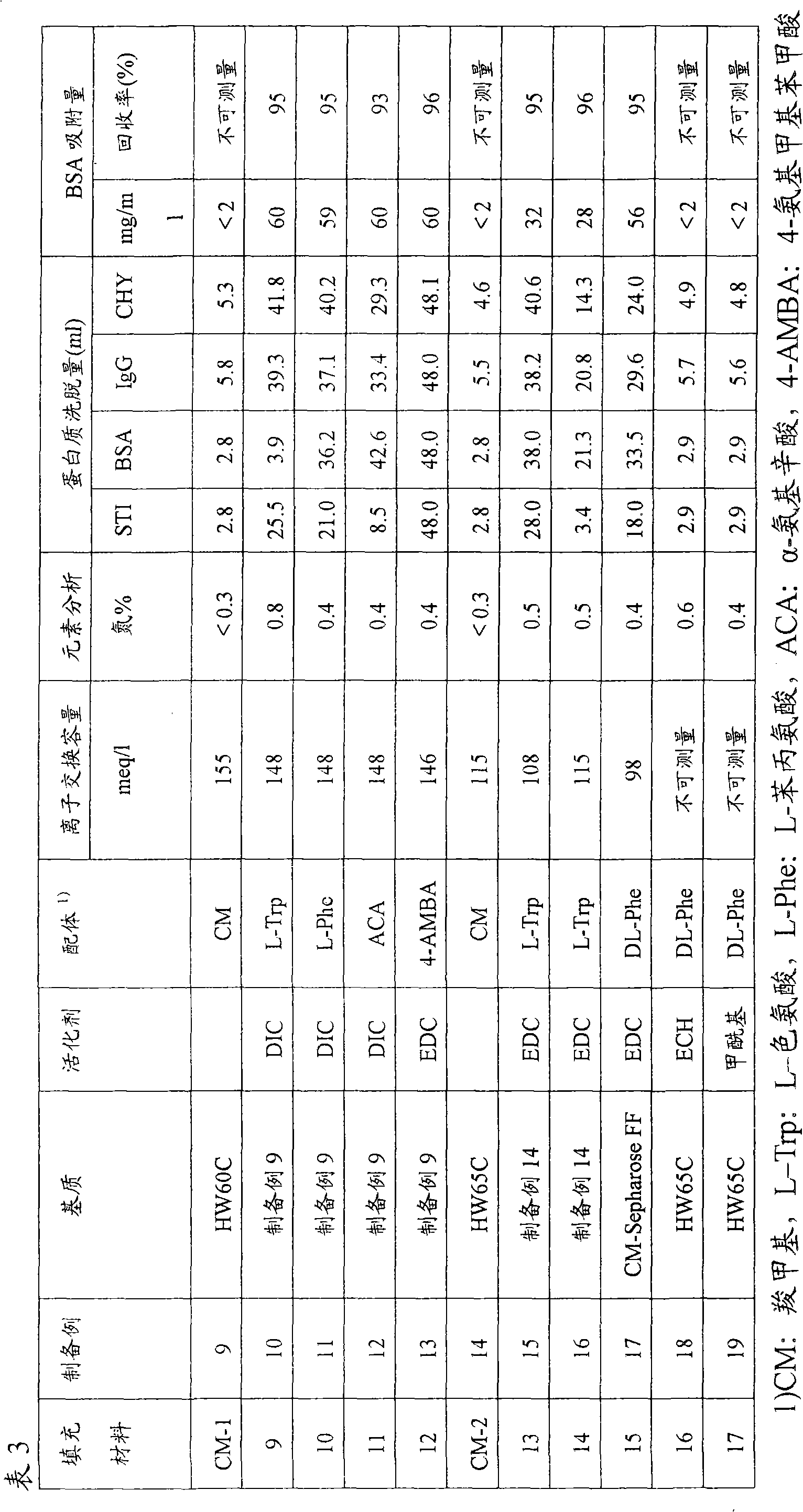
preparation example 1
[0125] A polymethacrylate porous filling material having alcoholic hydroxyl groups on the surface [by TOYOPEARL HW-60C (manufactured by TOSOH CORPORATION)] was repeatedly suspended with a dioxane solvent and filtered on a glass filter to remove moisture, and was filtered by suction The dispersion solvent in such filler material slurry is removed to prepare a drained gel mass.
[0126] 50 g of gel mass and 100 ml of dioxane were added to a 300 ml separatory bottle and stirred. 60 mmol of CDI was dissolved in 30 g of dioxane, and the CDI solution was added dropwise to the separatory bottle at a constant temperature of 30°C. After the dropwise addition, stirring was continued for 1 hour. Then, the slurry was filtered with a glass filter, and the gel was washed with dioxane solvent to remove unreacted CDI or by-products, thereby synthesizing a CDI-activated drained gel piece.
[0127] The entire amount of the resulting gel mass was added again to a 300 ml separating bottle and 1...
preparation example 2
[0132] The drained gel block activated by CDI was synthesized in the same manner as in Preparation Example 1. The entire amount of the resulting gel mass was added again to a 300 ml separating bottle, and 100 ml of DMF was added, followed by stirring. 24 mmol DL-phenylalanine and 6 mmol ethanolamine were dissolved in 25 ml of 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, 50 ml of DMF was added and mixed. This amino acid solution was put into a separatory bottle at one time and stirred to perform a reaction at room temperature for 16 hours.
[0133] After the reaction, the obtained gel was washed again in this order with DMF, 50% acetone, 0.1 mol / L sodium hydroxide and pure water on the glass filter. The gel obtained from this reaction is referred to as filling material 2. Its ion exchange capacity was measured in the same manner as in Preparation Example 1, and was found to be 80 meq / liter. The introduction amount of the phenylalanine ligand of the filling material 2 correspon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com