Astaxanthin-producing strain, mutagenesis and screening method and application thereof
A technology for the production of bacterial strains and astaxanthin, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle, pollution, low astaxanthin content, etc., achieve stable output and large application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
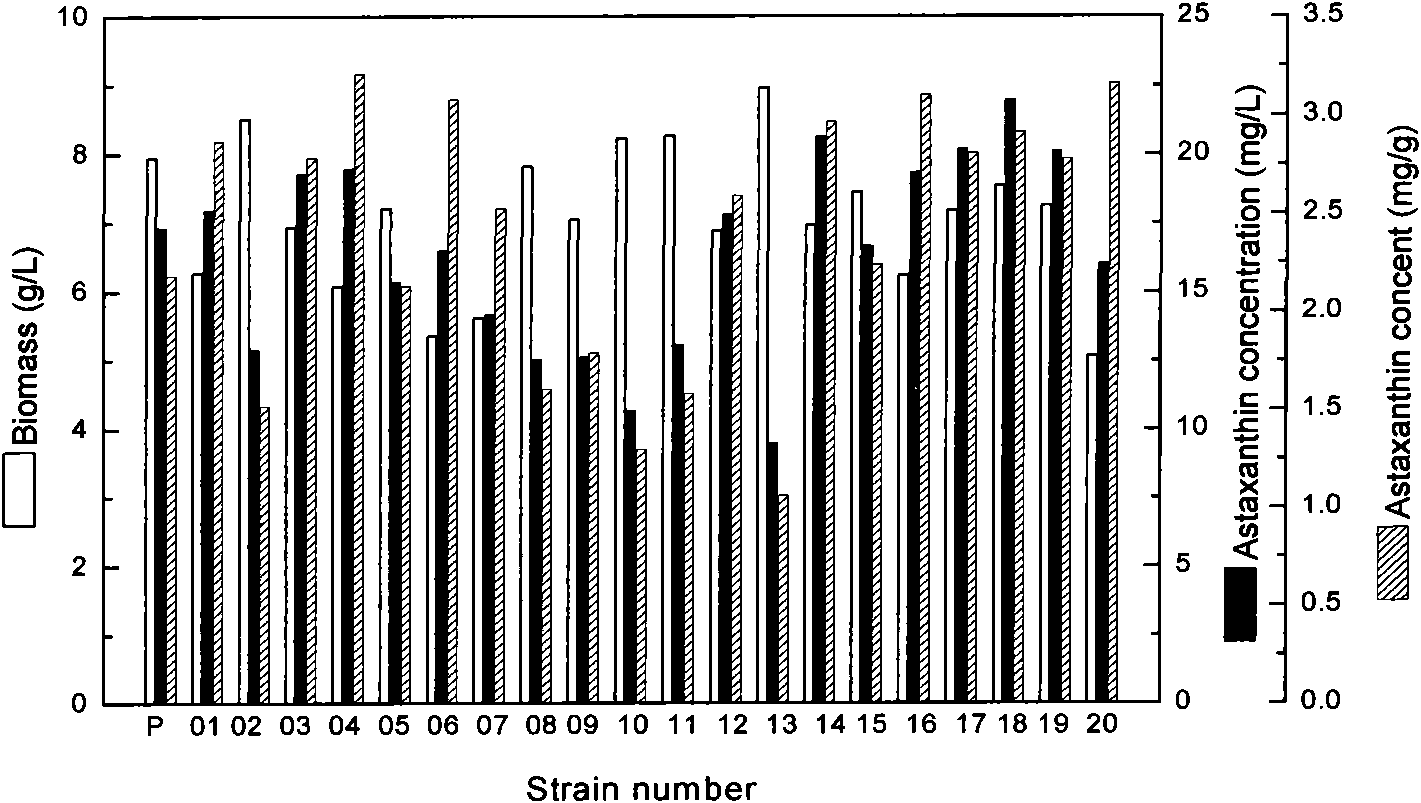
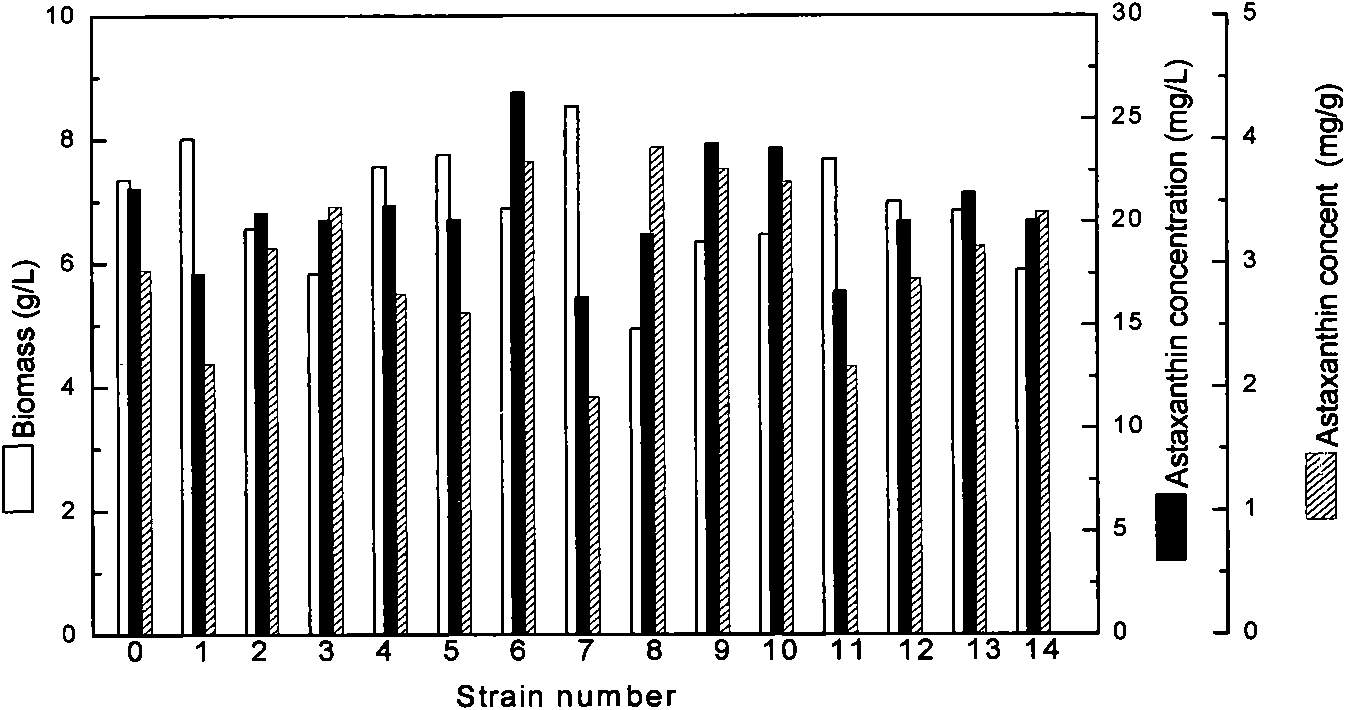
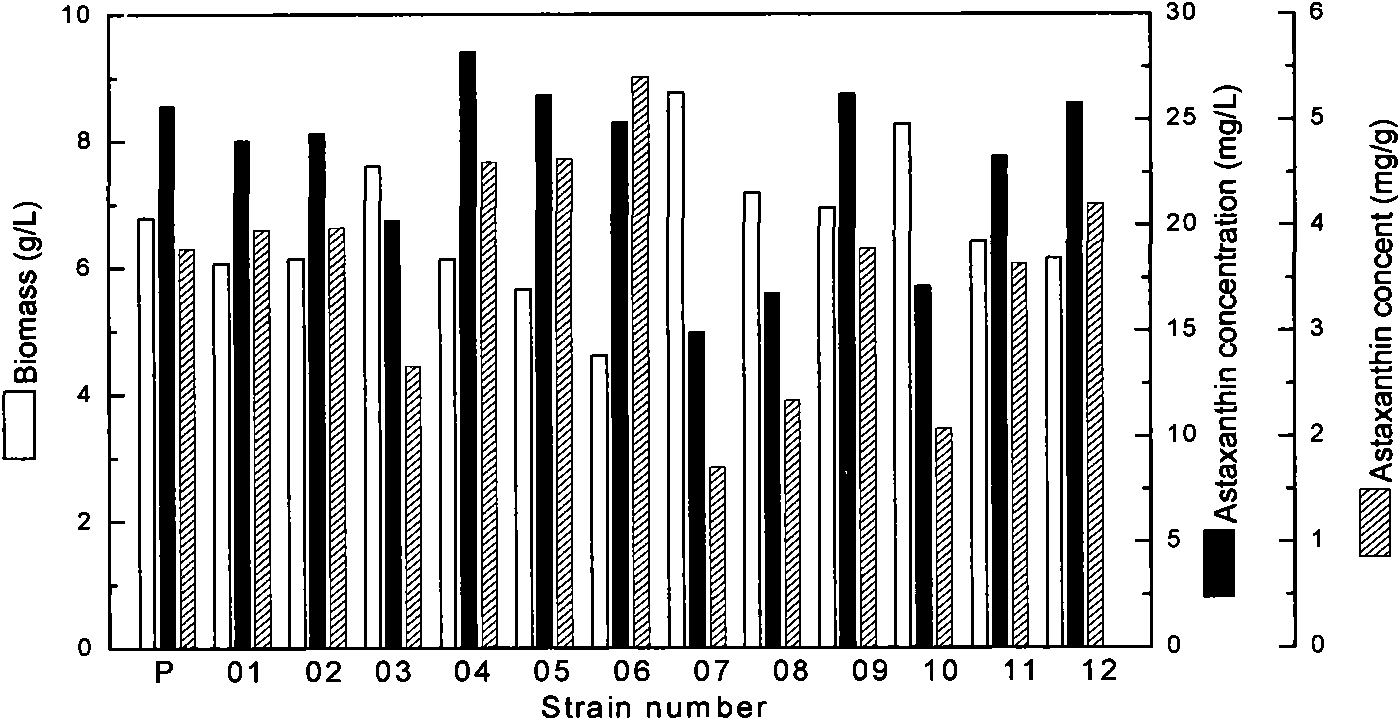
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034](1) The starting strain of Phaffia rhodozyma was inoculated into the slant of YM agar medium, and cultured at 22° C. for 3 days. YM agar medium (g / L) is glucose 10, peptone 5, yeast powder 3, wort juice 3, pH 5.0.
[0035] (2) Pick a loop of bacteria from the activated slant and inoculate it into a shake flask, culture at 22° C. and 200 rpm for 36 hours, wherein the culture medium of the shake flask is YEPD. YEPD medium (g / L) is glucose 20, peptone 20, yeast powder 10; natural pH.
[0036] (3) Protoplast preparation: the above-mentioned cultivated bacterial liquid was collected by centrifugation to collect the bacterial cells, and the bacterial cells were washed twice with 0.6 times volume of sodium citrate buffer solution (1.0 mol / L). Then add 0.6 times the volume of wall-breaking enzyme mixed solution (0.5% wall-breaking enzyme, 0.1% cellulase and 0.01% lysozyme) to the thalline, at 28 ° C, 54 rpm shaker for 60 minutes; take out the treated bacteria solution, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0069] (1) The experimental procedure is the same as (1)-(2) of Example 1.
[0070] (2) Protoplast preparation: the cultured bacterial solution was collected by centrifugation, and the bacterial cells were washed twice with 1.0 times volume of sodium citrate buffer solution (0.8 mol / L). Then add 1.0 times the volume of wall-breaking enzyme mixture (0.6% wall-breaking enzyme, 0.05% cellulase and 0.005% lysozyme) to the thalline, at 30 ° C, place 40min in a 54rpm shaker; take out the treated bacteria solution, and the protoplasts were collected by centrifugation.
[0071] (4) The prepared protoplasts were washed twice with 1.0 times volume of sodium citrate buffer (0.8mol / L), and then adjusted to make its concentration approximately 10 with this sodium citrate buffer. 7 ~10 8 / mL.
[0072] (5) Add 1.0 times the volume of 20 μg / mL NTG to the treated protoplasts, and place in a shaker at 22°C and 54 rpm for 30 minutes;
[0073] (6) The liquid treated with NTG was taken out, th...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The astaxanthin production strain obtained in Example 1 was inserted into YM medium for shake flask culture, the liquid filling volume was 8% to 12%, the inoculum volume was 10%, 22°C constant temperature, 200rpm, cultured for 5 days, the result Such as Figure 9 shown. from Figure 9 It can be seen that the astaxanthin production strain is cultured in shake flasks on the YM medium, and the biomass reaches a maximum value of 7.083g / L at 46h. According to the chromatographic conditions provided in Example 1, it is recorded that astaxanthin reaches The highest is 25.57mg / L, at this time the biomass is 6.233g / L, that is, the astaxanthin content is 4743mg / kg (dry cell weight).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com