Wild esterase B3 genetically engineered bacteria and building method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and construction methods, applied in the field of wild-type esterase B3 genetically engineered bacteria and its construction, can solve problems such as organic phosphorus pollution and achieve effective degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1) Extraction of the plasmid DNA of the Culex cDNA library resistant to organophosphate insecticides: the plasmid pUC-b3 (purchased from Queen's University, Canada) was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, and the single colony was inoculated in a medium containing Ampicillin / ml ampicillin in 5ml liquid LB medium, cultivate overnight on a shaker at 37°C, take 1.5ml of the culture and centrifuge to collect the bacteria. Extract plasmid DNA as a PCR reaction template (plasmid DNA extraction operation according to F. Osper, R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Compiled Molecular Biology Experiment Guide" New York John Wiley & Sons Publishing House, 2005 Fourth Edition P20).
[0022] 2) Design primers encoding the whole gene sequence b3 of wild-type esterase B3: design a pair of primers with NcoI and XhoI restriction sites and 5' end protection bases respectively as follows:
[0023] wB3-F: 5'-CCACCATGGATGAGTTTGGAAAGC-3'
[0024] wB3-R: 5'-AGGCTCGAGT...
Embodiment 2
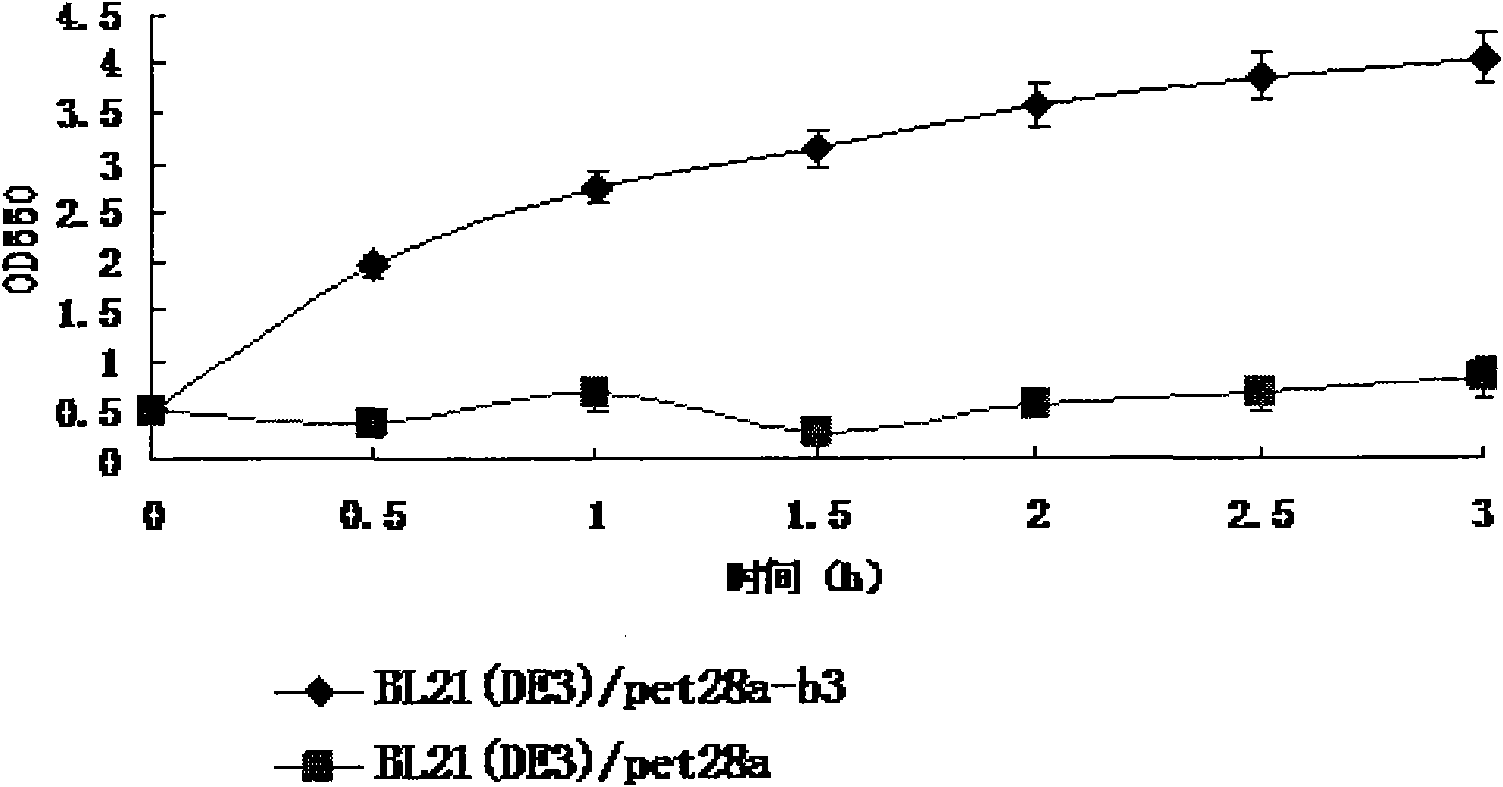
[0055] Determination of esterase activity in fermentation broth of wild-type esterase B3 genetically engineered bacteria:
[0056] 1) α-naphthyl acetate (α-NA) and β-naphthyl acetate (β-NA) are the specific substrates of esterase B1. Since the product amount of the enzymatic reaction is directly proportional to the OD value, if the esterase activity of the engineered bacteria is stronger, the OD value will be larger.
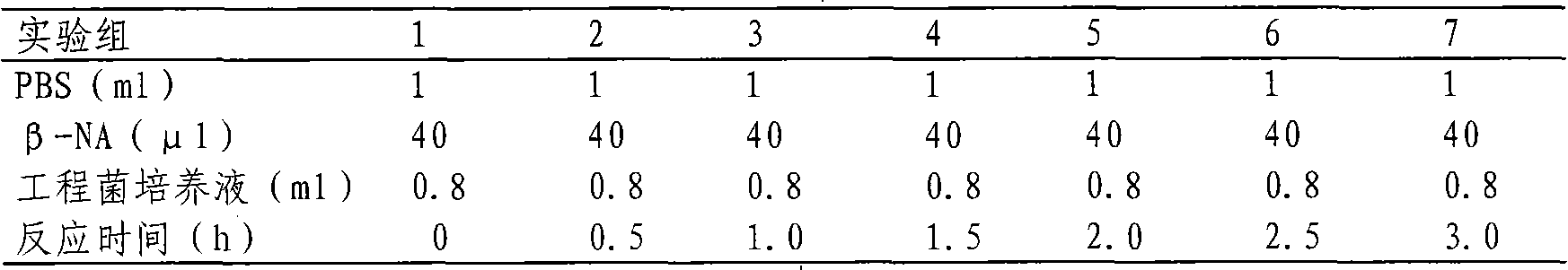
[0057] 2) heterologous expression of the wild-type esterase B3 protein in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE 3): the wild-type esterase B3 engineering bacterium single bacterium colony obtained in embodiment 1 is contained in 40ug / ml kanamycin In liquid LB medium, activate the culture overnight, transfer to the next stage with 1% inoculum, and culture on a shaker at 37°C until OD 600 was 0.6, added IPTG with a final concentration of 1.0 mmol / L, induced expression at 30°C for 6 hours, and collected the fermentation broth.
[0058] 3) Add the engineered bacteria solution...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Determination of the degradation activity of wild-type esterase B3 engineering bacteria broken protein solution on organophosphorus pesticides in vegetable leaves:
[0064] 1) heterologous expression of the wild-type esterase B3 protein in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE 3): the wild-type esterase B3 engineering bacteria single bacterium colony obtained in Example 1 was contained in 40ug / ml kanamycin In liquid LB medium, activate the culture overnight, transfer to the next stage with 1% inoculum, and culture on a shaker at 37°C until OD 600 was 0.6, added IPTG with a final concentration of 1.0 mmol / L, induced expression at 30°C for 6 hours, and collected the fermentation broth.
[0065] 2) Centrifuge the above-mentioned fermented bacterial liquid at 6,000g for 10 minutes at 4°C to collect the bacterial cells, resuspend the collected bacterial cells in 50 ml of PBS solution per 100 ml of fermentation liquid, and ultrasonically disrupt the bacterial cells at 4°C until the cells...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com