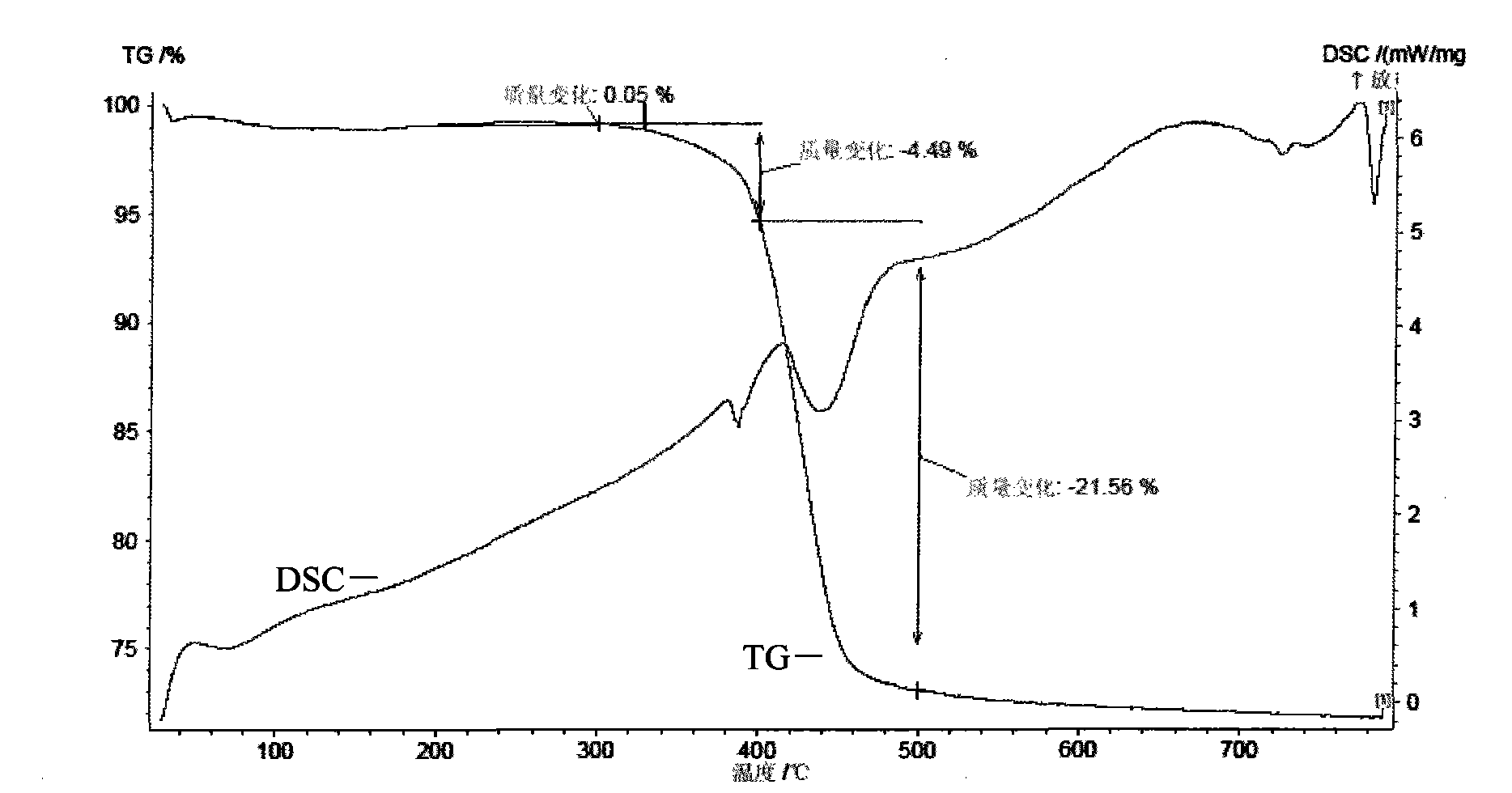
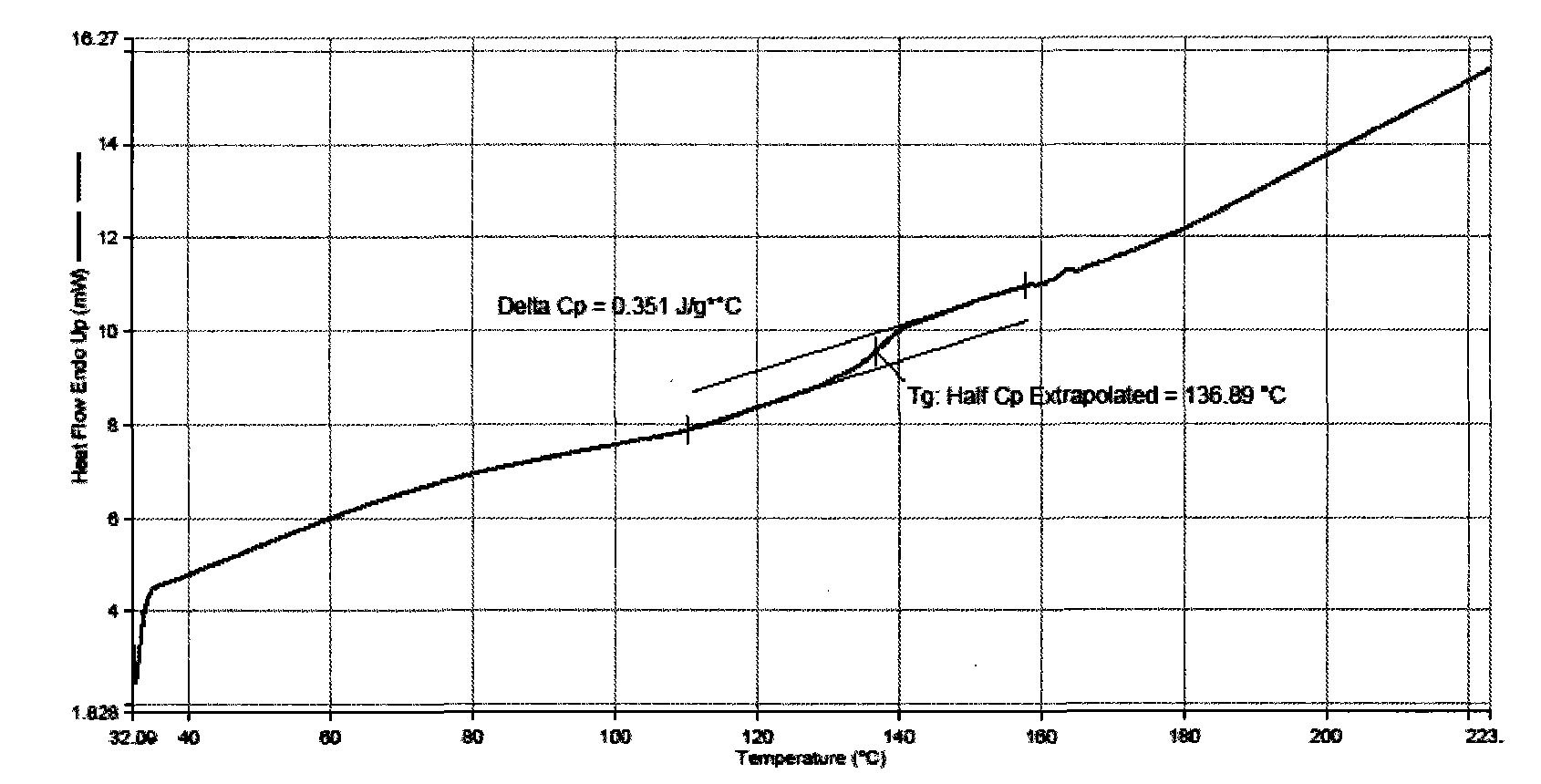
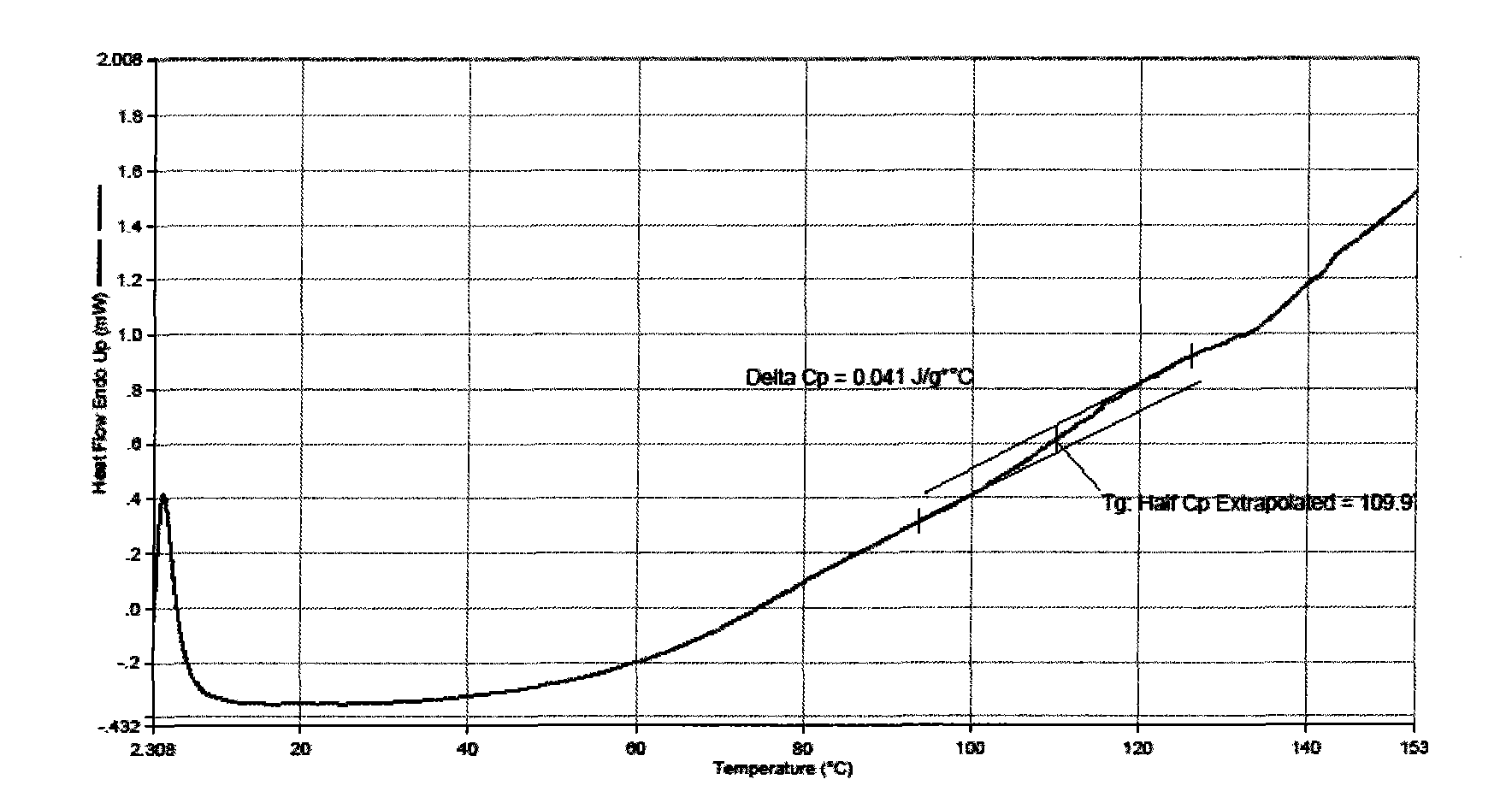
Isotropous conductive adhesive and preparation method thereof
An isotropic, conductive adhesive technology, applied in the preparation of carboxylic acid nitrile, conductive adhesives, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low heat resistance, high price of silver-containing conductive adhesive, etc., and achieve the reduction of silver content , Improve liquidity, reduce production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Step 1: Put a certain amount of phenol in the reaction flask, add hexamethylenediamine at a molar ratio of 1:2.0 to 2.5, raise the temperature to 40-50°C, start stirring, and add dropwise organic aldehyde with a molar ratio of 1:2 to phenol, Control the heating rate not to exceed 80°C, reflux reaction for 0.5-1h, raise the temperature to 110-120°C, dehydrate and reflux reaction for 2-4 hours, until no water flows out of the receiver, cool down to 60°C, dropwise add the same mole number of phenol Acrylonitrile, control the temperature not to exceed 80°C, when the temperature of the reactant no longer rises, cool down to 60°C by itself, filter, and obtain an amber low-viscosity liquid, which is a modified amine curing agent.
[0082] Step 2: Put a certain amount of maleopimaric acid anhydride in the reaction flask, add triethylenetetramine at a molar ratio of 1:3 to 4, start stirring, heat up to 120°C to 140°C, and reflux for 1 to 5 hours. Gradually raise the temperature ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Step 1: Put a certain amount of phenol in the reaction flask, add methylcyclopentyldiamine at a molar ratio of 1:2.0~2.5, raise the temperature to 40~50°C, start stirring, and dropwise add phenol with a molar ratio of 1:2 For organic aldehydes, control the heating rate not to exceed 80°C, reflux for 0.5-1 hour, heat up to 110-120°C, dehydrate and reflux for 2-4 hours until no water flows out of the receiver, cool down to 60°C, add dropwise with phenol For acrylonitrile with equivalent moles, control the temperature not to exceed 80°C. When the temperature of the reactant no longer rises, cool down to 60°C by itself, and filter to obtain an amber low-viscosity liquid, which is a modified amine curing agent.
[0087] Step 2: Put a certain amount of maleopimaric acid anhydride in a reaction flask, add diethylenetriamine in a molar ratio of 1:3 to 4, start stirring, heat up to 120°C to 140°C, and reflux for 1 to 5 hours. Gradually raise the temperature for dehydration until...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Step 1, put a certain amount of phenol in the reaction flask, add methylcyclohexanediamine in a molar ratio of 1:2.0~2.5, raise the temperature to 40~50°C, start stirring, and dropwise add phenol with a molar ratio of 1:2 For organic aldehydes, control the heating rate not to exceed 80°C, reflux for 0.5-1 hour, heat up to 110-120°C, dehydrate and reflux for 2-4 hours until no water flows out of the receiver, cool down to 60°C, add dropwise with phenol For acrylonitrile with equivalent moles, control the temperature not to exceed 80°C. When the temperature of the reactant no longer rises, cool down to 60°C by itself, and filter to obtain an amber low-viscosity liquid, which is a modified amine curing agent.
[0092] Step 2: Put a certain amount of maleopimaric acid anhydride in the reaction flask, add triethylenetetramine at a molar ratio of 1:3 to 4, start stirring, heat up to 120°C to 140°C, and reflux for 1 to 5 hours. Gradually raise the temperature for dehydration u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com