Graphene optical Q-switch and application
A kind of graphene optics, graphene technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of inconvenient production and application, complex production process, wavelength sensitivity, etc., achieve low cost, is conducive to industrialization, and is conducive to The effect of industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
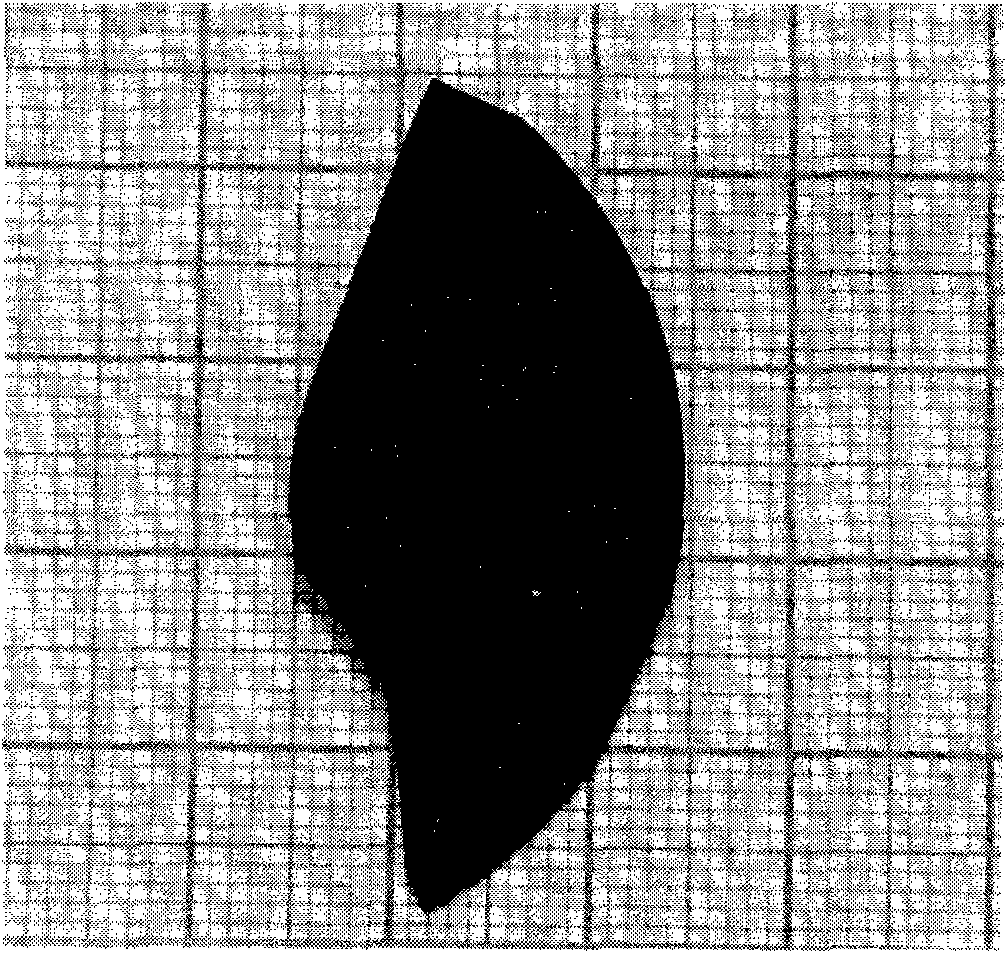
[0028] Photo of graphene grown on silicon carbide substrate as figure 1 As shown, the preparation method is to use 6H silicon carbide as the substrate and obtain it by epitaxial growth. The growth method is as described in University of Science and Technology of China, Doctoral Dissertation, Liu Zhongliang, page 102. The number of graphene layers is selected to be 10-30 layers, and the Q-switching switch can be cut into rectangles or circles according to the needs of the application. The schematic diagram of the rectangular graphene Q-switching switch is shown in figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 2
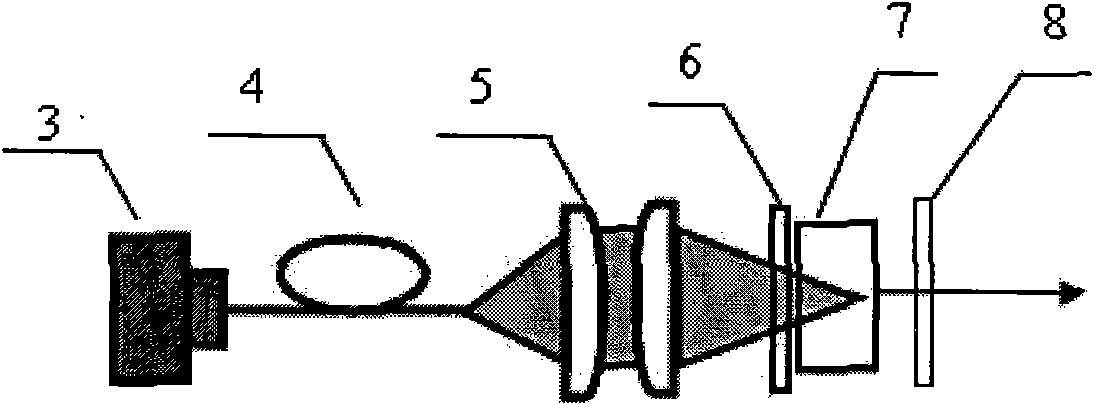
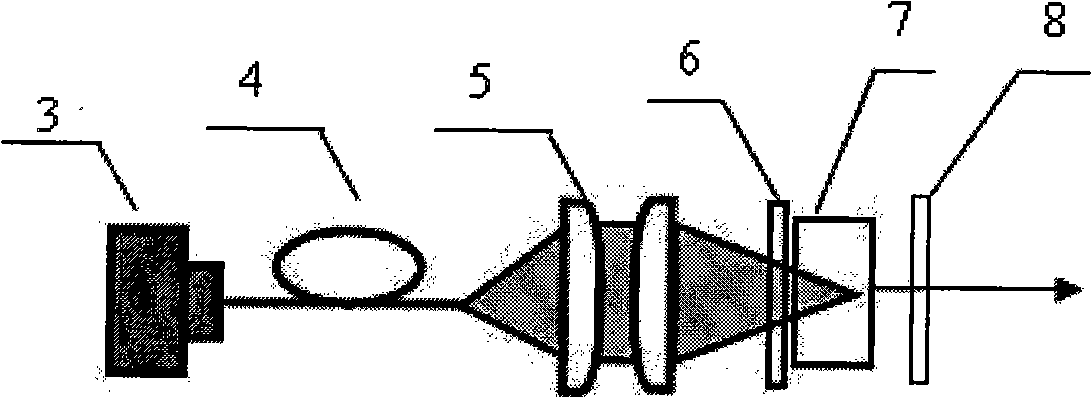
[0030] Using a laser with an emission wavelength of 808nm as the pump source and Nd:YAG crystal as the laser gain medium, adopt such as image 3 The cavity structure shown is fabricated into a pulsed laser. The laser comprises: a laser diode as a pumping source (3), a Nd:YAG crystal (6) as a laser gain medium, a coupling system (4, 5), a front cavity mirror (6) and a Q-switching element (8) of the present invention five parts. Wherein the Nd of the Nd:YAG crystal 3+ The ion concentration is 0.01-0.10 at. The pump light incident end of the Nd:YAG crystal is coated with a dielectric film that is highly transparent to 808nm and the 1.05-1.1μm band, and the output end is coated with a dielectric film that is highly transparent to the 1.05-1.1μm band. The front cavity mirror ( 6) It is a plano-concave mirror with a radius of 100-500mm, the plane is coated with 808 high-transparency, the concave surface is coated with a dielectric film with high reflection of 1.05-1.1μm, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] As described in Embodiment 2, the difference is that the surface of the graphene grown on the SiC substrate of the Q-switch switch of the present invention is not coated with a dielectric film to facilitate laser oscillation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com