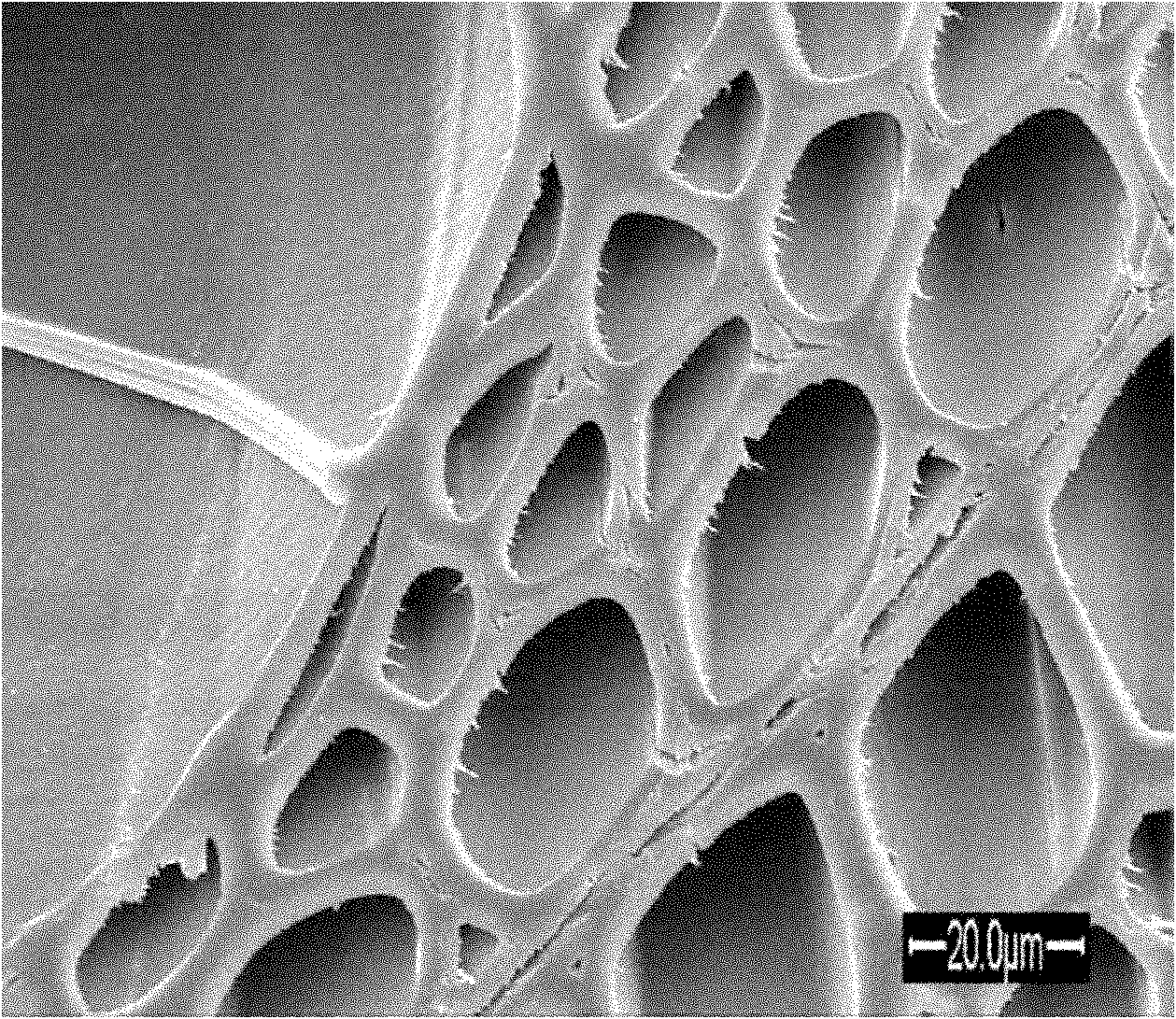
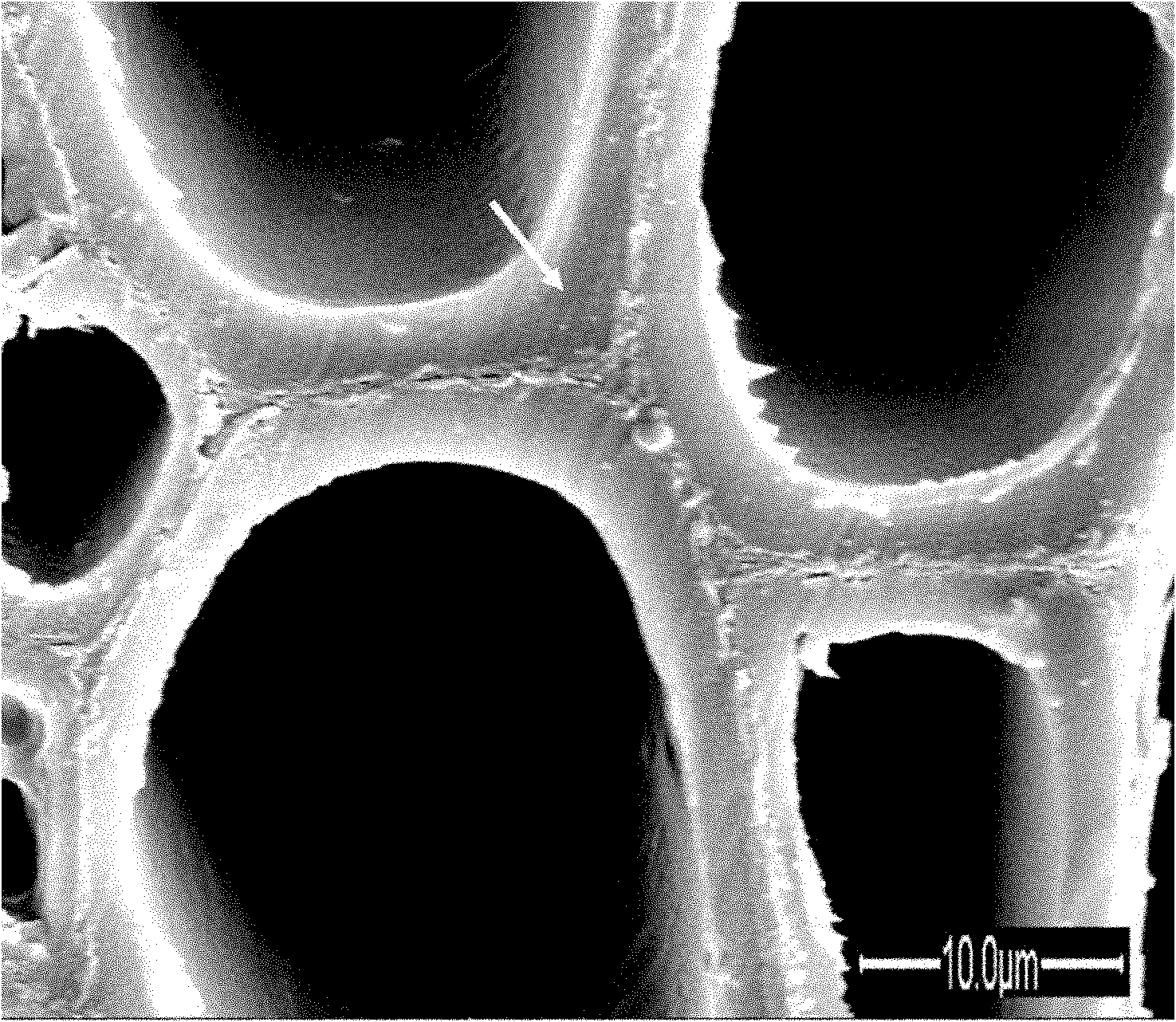
Method for modifying wood by filling grafted cell walls with organic monomers and polymerization-filling cell cavities
A polymeric filling and cell wall technology, applied in the direction of impregnated wood, wood impregnation, wood processing utensils, etc., can solve the problems that it is difficult to improve the mechanical properties and durability of wood at the same time, and achieve the improvement of two-phase interface compatibility, excellent durability, The effect of improving durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0011] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, the method of using organic monomers to inflate grafted cell walls and polymerize and fill cell lumens to jointly modify wood is as follows: 1. The configuration of the organic acid anhydride solution: dissolve the organic acid anhydride in acetone or tetrahydrofuran, and then Add 3 to 5 drops of pyridine to make an organic anhydride solution with an organic anhydride mass fraction of 10 to 30%; 2. Impregnation of wood with an organic anhydride solution: Immerse the wood in the organic anhydride solution at a vacuum of -0.08 Vacuum for 20 minutes under the condition of MPa, then pressurize for 20 minutes under the pressure of 0.8MPa, return to normal pressure, wrap the wood with aluminum foil and leave it for 12-24 hours at normal temperature and pressure; 3. The heating method realizes the organic acid anhydride swelling joint Branch wood cell wall: heat the wood covered with aluminum foil paper at 110°C-130°C for 2-4 hours, then remove...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the organic acid anhydride described in step 1 is a mixture of two or three of maleic anhydride, succinic anhydride and phthalic anhydride. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0018] In this embodiment, when the organic acid anhydride is a mixture, the ratios between the components are arbitrary.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019]Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the organic polymerizable monomer described in step four is methyl methacrylate, ethyl methacrylate, n-butyl methacrylate , isobutyl methacrylate, n-hexyl methacrylate, benzyl methacrylate, decyl methacrylate, lauryl methacrylate, stearyl methacrylate, alpha-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, methyl α-hydroxypropyl acrylate, dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, diethylaminoethyl methacrylate, 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate, 2,3-dimethacrylate Propyl Bromide, Cyclohexyl Methacrylate, Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, Diethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, Triethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, Tetraethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate, monopropylene glycol dimethacrylate, dipropylene glycol dimethacrylate, tripropylene glycol dimethacrylate, 1,3-butanediol dimethacrylate, 1,4 -Butanediol Dimethacrylate, Bisphenol A Dimethacrylate, 2,2-Bis[methacryloy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com