Magnaporthe grisea MoPPF3 gene and function and application of coding protein of magnaporthe grisea MoPPF3 gene
A rice blast fungus and protein technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, application, etc., can solve the problems of gene cloning and few molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
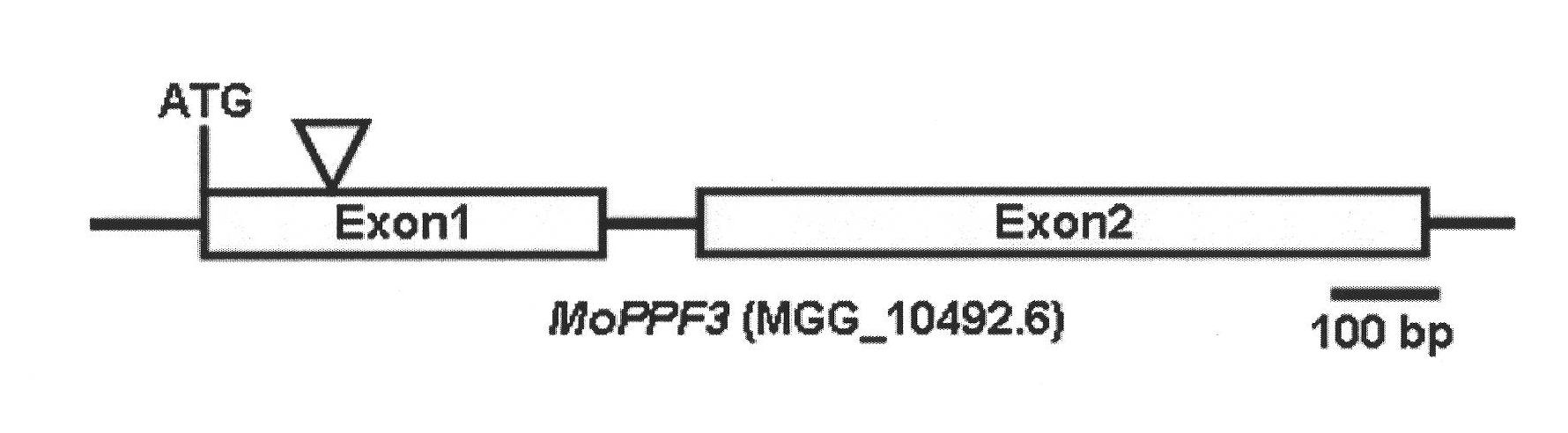
[0034] Embodiment 1, the isolation and identification of gene MoPPF3
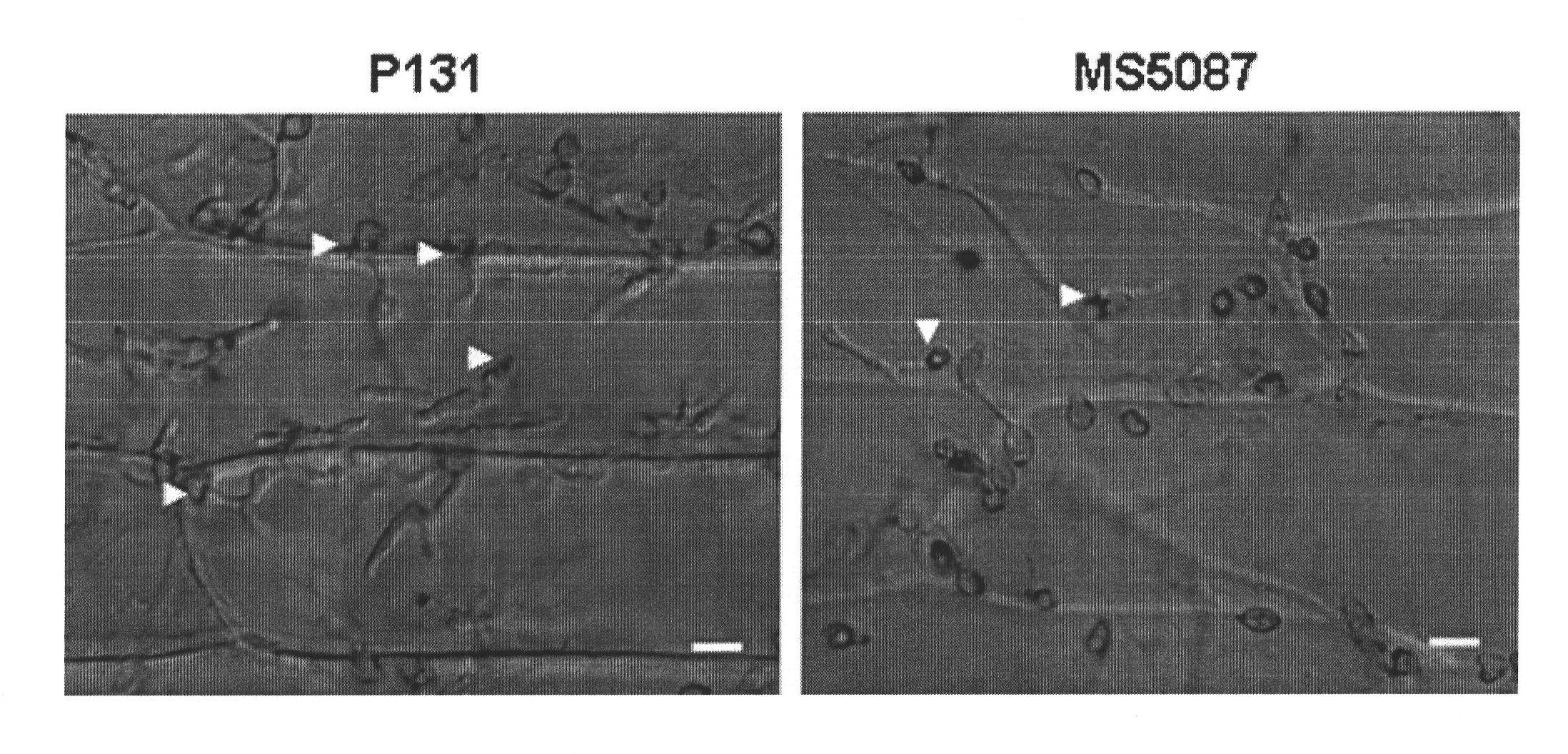
[0035] 1) Screening for mutants with reduced infection spike formation rate. The conidia (2 × 10 5 ) were respectively inoculated into onion epidermal cells, and after 24 hours of dark moisturizing at 25° C., observed and counted the formed infection nails under a microscope with a magnification of 10×40, and screened out a reduction in the formation rate of infection nails (about 27% ) mutant MS5087. See figure 1 .
[0036] 2) Genetic analysis of mutant MS5087. The mutant MS5087 was sexually crossed with the wild-type strain S1528, which has no hygromycin resistance and has the opposite mating type, and the ascospores of the hybrid offspring were selected for analysis of hygromycin resistance and infection spike formation rate. Among the 35 ascospores tested, 18 hygromycin-sensitive ascospores showed wild phenotypes, and 17 hygromycin-resistant ascospores showed mutant phenotypes (decreased infection ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2, the effect of gene MoPPF3 in the formation process of blast fungus infection spike
[0040] 1) MoPPF3 gene complementation mutant MS5087
[0041] a. Construction of complementary vector
[0042] The neomycin phosphotransferase gene was excised from plasmid pSM331 with XbaI, and ligated with pBlueScriptKS(+) digested with XbaI to obtain plasmid pKN. According to the nucleotide sequence of the gene MoPPF3, the forward primer hbup (5'-AGGTACCTGACAGCAGTCCGTG-3', KpnI) and the reverse primer hbdown (5'-ACTCGAGAGTTTGTGGCGTCTG-3', XhoI) were designed respectively. Using the genomic DNA of the wild-type strain P131 as a template, a 3118bp DNA fragment was amplified with fidelity LA-Taq enzyme, which contained the MoPPF3 gene and its upstream 1.5kb promoter sequence, and its sequence corresponds to SEQ in the sequence listing ID №: 1-3118bp in 1. After the fragment was digested with KpnI and XhoI, it was connected to the vector pKN digested with the same enzymes...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3, the effect of MoPPF3 gene in blast fungus pathogenicity
[0057] The conidia suspension (concentration of 5×10 4 per milliliter) evenly spray and inoculate on the front of rice leaves at the four-leaf and one-heart stage, or the front of barley leaves at the one-leaf and one-heart stage, or connect the mycelium blocks to the front of rice leaves at the four-leaf and one-heart stage, at 26°C and 100% relative humidity Incubate in the dark for 36 hours, and continue to moisturize and cultivate for 3 days after exposure to light, and observe the incidence. The results showed that the knockout CD5 of the MoPPF3 gene could not form diseased spots on the host plants rice and barley, and could not form diseased spots on the scratched rice leaves, while wild-type P131 could not form diseased spots on the rice and barley leaves can form typical rice blast lesions ( Figure 5 ). This indicated that, compared with wild-type P131, the pathogenicity of MoPPF3 knocko...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com