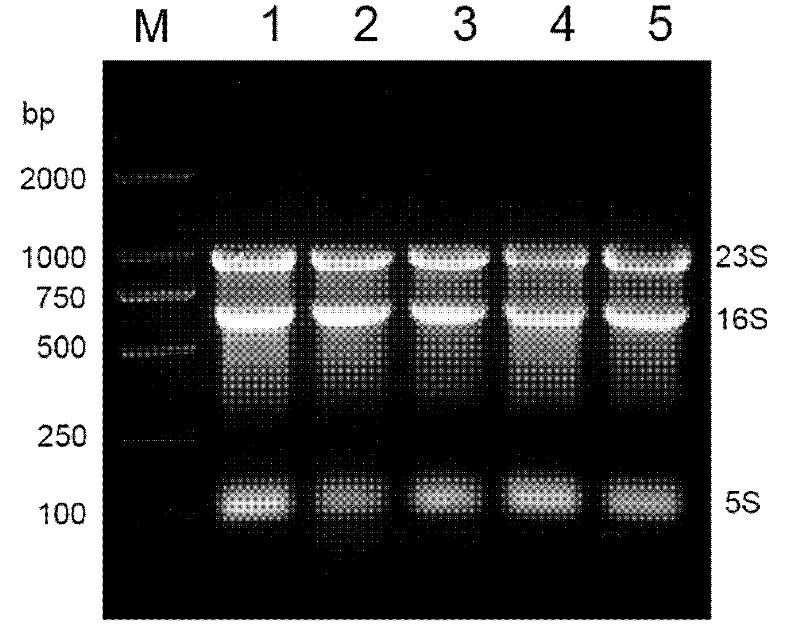
Total RNA preparation without genomic DNA
A genome and sodium dodecyl sulfate technology, applied in the field of total RNA, can solve the problems of RNA sample degradation, increase the time of RNA extraction, and result uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] a) Streak culture of single colonies of Escherichia coli strains AB1157, AB2463, AB2480, UNC1085 and DH5α on a flat plate, transfer to LB liquid medium, and culture with shaking overnight at 37. Bacteria were harvested by centrifugation. The bacterial cells obtained by centrifuging 1.5 mL of the bacterial liquid were resuspended with 100 μL of a mixed solution of 50 mmol / L glucose and 10 mmol / L sodium oxalate tetraacetate (EDTA).
[0028] b) Add 100 μL of 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate solution by weight, and lyse at room temperature for 3 minutes.
[0029] c) Add 2.5 μL of acidic potassium acetate solution. Mix evenly by inverting, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10 minutes to remove the precipitate, and take 200μL of supernatant.
[0030] d) Add 120 μL of acidic potassium acetate solution to the supernatant obtained in step c), and 160 μL of a 4.5 mol / L guanidinium thiocyanate stock solution. Add 480 μL of phenol extract, shake and mix. Centrifuge at 10,000rpm for 5 minutes...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Genomic DNA residue detection:
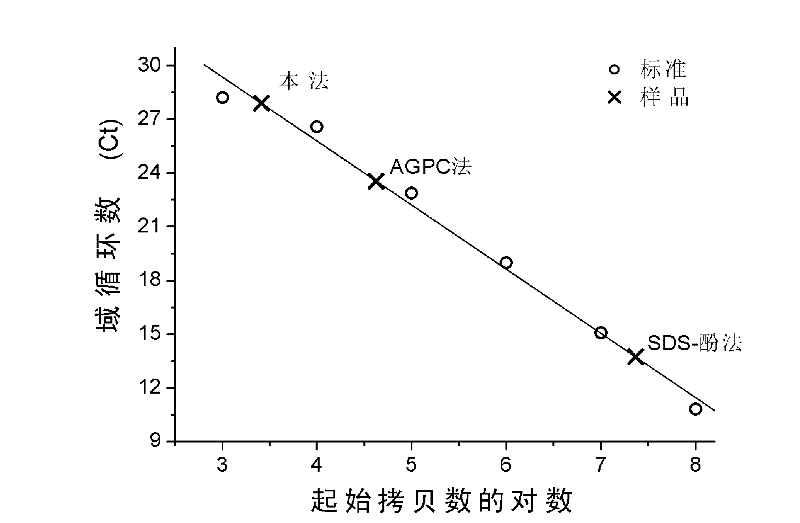
[0035]1 microgram of the total RNA sample obtained in step e), as well as the RNA samples obtained by the acid guanidine thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform (AGPC) method and the SDS-phenol method, were treated with RNase and then amplified with genome-specific primers. According to the comparison with the domain cycle number of the standard sample, it can be seen that the residual genomic DNA of the sample obtained by this method is the least, about 10 per microgram. 3 copies (about 4 pg). Residual genomic DNA in samples obtained by AGPC method and SDS-phenol method is about 10 per microgram respectively. 5 copy and 10 7 copy (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0037] Detection of RNA amplification ability:
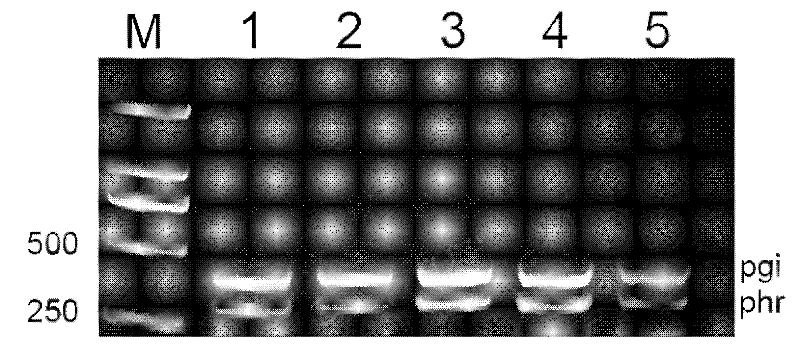
[0038] Take 1 microgram of the total RNA sample obtained in step e) as a template, and perform reverse transcription using AMV reverse transcriptase. The cDNA obtained by reverse transcription was used as template for semi-quantitative PCR reaction. The primers used are the specific primers of Escherichia coli phr and pgi genes. The pgi gene is a housekeeping gene of Escherichia coli, which encodes phosphoglucose isomerase; the phr gene encodes DNA photorepair enzyme of Escherichia coli. As a result, it can be seen that the phr gene expression level is all lower than the pgi gene in each bacterial strain, and is about about 40%-60% (see image 3 ), the expression levels of the two genes were significantly different, but there was no significant difference in the ratio of each strain. In the control experiment, the genomic DNA of each strain was amplified, which proved the differences in the expression of different genes, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com