Protogenic diamond fine particle for precisio machining and production method thereof
A technology for precision machining and production methods, applied in the field of primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining and its production, can solve the problems of poor sharpness of machining tools, broken and falling off abrasive particles, no crystal planes and edges and corners, etc., and achieves high machining efficiency. The effect of complete crystal form and long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
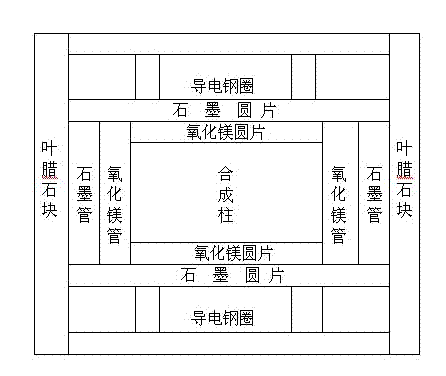
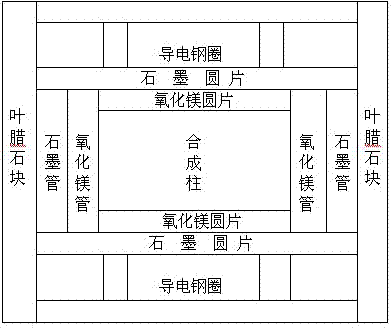
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: A kind of primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining and its production method
[0025] 1. A primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining, the particle size is 10-20 microns, the crystal shape is a complete octahedron, and the nitrogen content is 320ppm.
[0026] 2, the production method of above-mentioned native fine-grained diamond, comprises the following steps:
[0027] Weigh 50kg of high-purity natural graphite powder, 50kg of iron-nickel alloy powder (iron-nickel mass ratio 7:3), put it in a three-dimensional mixer with a volume of 100 liters, add 2kg of ammonium nitrate powder; the particle size of the graphite powder is less than 200 mesh , degree of graphitization > 95%, particle size of iron-nickel alloy powder is less than 200 mesh;
[0028] After sealing the feeding port tightly, turn on the mixer and mix for 10 hours to obtain a uniform mixture; put the mixture into a latex bag, let it stand for exhaust for 20 minutes, tie th...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: A kind of primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining and its production method
[0032] 1. A primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining, the particle size is 5-15 microns, the crystal shape is a complete hexahedron or hex-octahedron, and the nitrogen content is 450ppm.
[0033] Among them, the hexa-octahedral diamond crystal shape is a transitional crystal form of diamond between hexahedron and octahedron. This shape is due to the formation of diamonds under different pressures and temperatures during the production process. When the temperature is high, an octahedral diamond is formed, just like two pyramids buckled upside down. This diamond is composed of eight triangular crystal faces; when the temperature is low, a hexahedral diamond is formed, which is composed of six square crystal faces. When the temperature is moderate, diamond crystals composed of triangular and square crystal faces, or square and hexagonal crystal faces are fo...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: A kind of primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining and its production method
[0039] 1. A primary fine-grained diamond for precision machining: the particle size is 15-30 microns, the crystal shape is a complete octahedron or hexa-octahedron, and the nitrogen content is 270ppm.
[0040] 2, the production method of above-mentioned native fine-grained diamond, comprises the following steps:
[0041] Weigh 55 kg of 300-mesh high-purity natural graphite powder and 45 kg of iron-nickel alloy powder (the mass ratio of iron and nickel is 7:3), put them in a V-shaped mixer with a volume of 100 liters, add 1 kg of urea powder, and seal the feeding port After that, turn on the mixer and mix for 18 hours to form a uniform mixture; put the mixture into a latex bag and let it stand for exhaust for 20 minutes, tie the bag tightly and put it into a cold isostatic press, pressurize to 100Mpa, and keep Release the pressure after pressing for 20 minutes, and ta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com