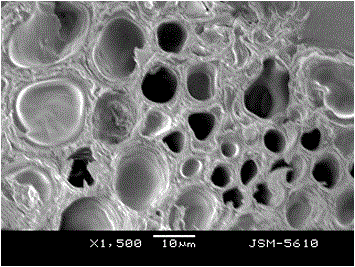
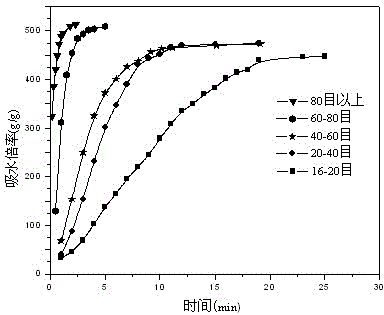
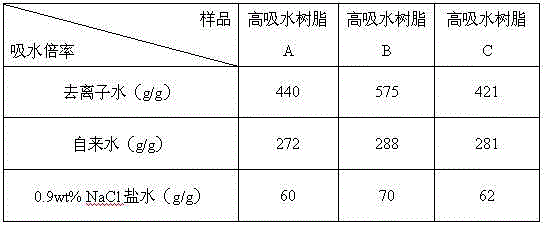
Method for preparing superabsorbent resin based on waste woody plant branches
A technology of superabsorbent resin and woody plants, which is applied in the field of superabsorbent resins based on waste woody plant branches, which can solve the problems of low utilization rate of waste woody plant branches, poor biodegradability, and low water absorption rate, and achieve excellent water absorption performance, The effect of low preparation cost and environmentally friendly source
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1) Wash and dry the discarded mulberry branches, then pulverize them with a plant grinder, and filter through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain mulberry branch powder with a particle size less than or equal to 0.15 mm;
[0022] 2) Put 1g of the mulberry branch powder obtained in step 1) into 25ml of deionized water;
[0023] 3) Heat the mixture of branch powder and deionized water, stir for 15 minutes, the heating temperature is 70°C, and nitrogen is introduced;
[0024] 4) Keep the heating temperature at 70°C and nitrogen gas, add 0.15g ammonium persulfate to the mixture of branch powder and deionized water for 10 min, then add 2.2g ammonium bicarbonate to 3.2g acrylic acid for neutralization, and then Add the neutralized acrylic acid and 0.8g of acrylamide for graft polymerization, then add 0.03g of N,N-methylenebisacrylamide and adjust the deionized water content of the whole reaction to 40 ml, and then react for 2 hours. A brownish-yellow gel is obtained;
[0025] 5) Tak...
Embodiment 2
[0027] 1) Wash and dry the discarded poplar branches, then pulverize them with a plant grinder, and filter through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain branch powder with a particle size less than or equal to 0.15mm;
[0028] 2) Put 1g of branch powder obtained in step 1) into 20ml of deionized water;
[0029] 3) Heat the mixture of branch powder and deionized water, stir for 30 minutes, the heating temperature is 60°C, and nitrogen is introduced;
[0030] 4) Keeping the heating temperature at 60°C and blowing nitrogen, add 0.2g ammonium persulfate to the mixture of branch powder and deionized water for 20 min, then add 3.3g ammonium bicarbonate to 4g acrylic acid for neutralization, and then add Acrylic acid and 2g of acrylamide obtained through neutralization were added for graft polymerization, then 0.05g of N,N-methylenebisacrylamide was added and the deionized water content of the whole reaction was adjusted to 30 ml, and then reacted for 2.5 hours to obtain a brown yellow gel;
...
Embodiment 3
[0033] 1) Wash and dry the discarded eucalyptus branches, then pulverize them with a plant grinder, and filter them through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain branch powder with a particle size less than or equal to 0.15mm;
[0034] 2) Put 1g of the branch powder obtained in step 1) into 30ml of deionized water;
[0035] 3) Heat the mixture of branch powder and deionized water, stir for 5 minutes, the heating temperature is 50 ° C, and pass nitrogen;
[0036] 4) Keep the heating temperature at 50°C and nitrogen gas, add 0.05g ammonium persulfate to the mixture of branch powder and deionized water for 5 minutes, then add 4.8g ammonium bicarbonate to 5g acrylic acid for neutralization, and then add Acrylic acid and 5 g of acrylamide obtained through neutralization were added for graft polymerization, then N, N-methylenebisacrylamide was added and the deionized water content of the entire reaction was adjusted to 35 ml, and then reacted for 3 hours to obtain a brown-yellow gel glue;
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com