Small brevibacterium strain capable of carrying out biological denitrification under high-salt condition and application of small brevibacterium strain to wastewater treatment
A technology of brevibacteria and high-salt wastewater, which is applied in the field of biological denitrification, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory biological denitrification effect, achieve the effects of saving infrastructure and operating costs, broad application prospects, and simplifying the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037]Example 1. Screening of Brachybacterium strains with high-salt heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification performance
[0038] Specific steps are as follows:
[0039] 1) Put 1mL of brine sample (collected from the sun-dried salt pool of Tianjin Hangu Salt Field) into 100mL of liquid medium (each L contains yeast extract: 5g, tryptone: 10g, NaCl: 3%-10%, pH: 7.0-7.5 , 121°C 20min steam sterilization) in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, 30°C 150r / min shaker culture for 5 days to enrich the bacteria;
[0040] 2) Dilute the enriched brine sample to 10 by the doubling dilution method -1 、10 -2 , ... 10 -6 For the bacterial suspension of each gradient, take the dilution as 10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 Each 0.1ml of the bacterial suspension was evenly spread on the pre-prepared high-salt solid medium (each L containing yeast extract: 5g, tryptone: 10g, NaCl: 3%-10%, agar: 16-18g, pH: 7.0-7.5, steam sterilization at 121°C for 20 minutes) on a 10ml solid plate;
[0041] 3) Place...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2. Bacterial strain is the denitrification experiment of 5% in salinity
[0047] Using glucose as the carbon source and ammonia nitrogen as the nitrogen source, the removal ability of the Brachybacterium strain described in Example 1 to ammonia nitrogen was determined. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
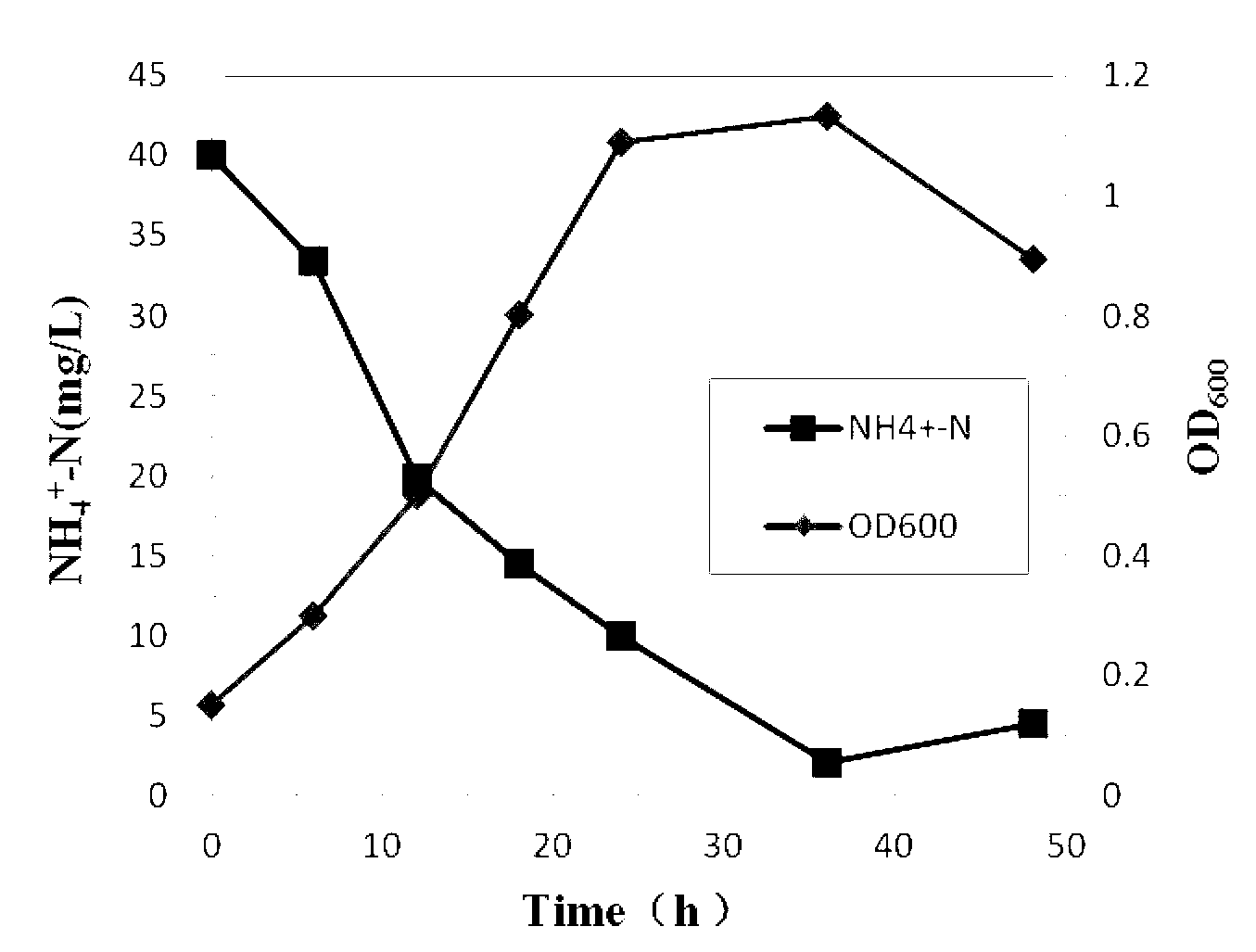
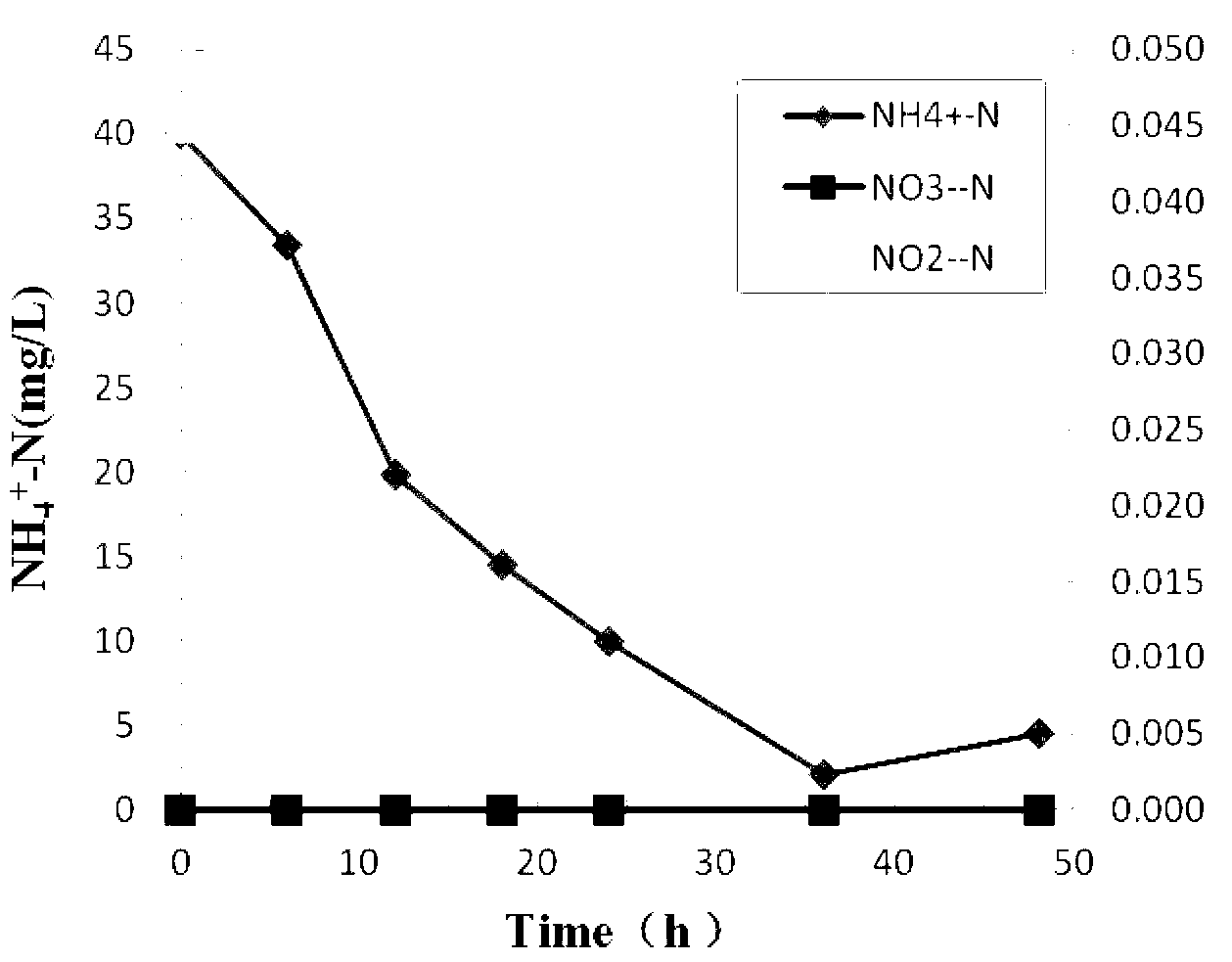
[0048] Inoculate the Brachybacterium strain in 100ml of inorganic salt medium with a salinity (calculated as NaCl) of 5% (containing 0.94g glucose and 0.153g NH per liter 4 Cl, 0.035g KH 2 PO 4 , 0.1gMgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.006g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, pH 7.0~7.5), cultured in a shaker at 30°C at 150 rpm. The culture medium that was not inoculated with the bacterial suspension was used as a blank control for experiments under the same conditions. A small amount of reaction solution was taken at 6h, 12h, 18h, 24h, 36h and 48h, a part of which was directly used to measure the optical density of the bacteria, and the rest was centrifuged at 8000rpm for...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3. Denitrification experiments of bacterial strains under different salinity conditions
[0051] Using glucose as the carbon source and ammonia nitrogen as the nitrogen source, the Brachybacterium strains described in the examples were tested for their ability to remove ammonia nitrogen at different salinities. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0052] Inoculate Brachybacterium strains in 100ml of inorganic salt medium with salinity (calculated as NaCl) of 1%, 3%, 5%, 8%, 10% and 13%, shake at 30°C at 150rpm pre-cultured in the bed. When the strain grows to the late logarithmic growth phase, take 10ml of the bacterial solution and insert it into 90ml of fresh inorganic salts with a salinity (calculated as NaCl) of 1%, 3%, 5%, 8%, 10% and 13% for culture Culture medium was shaken at 30°C and 150 rpm in a shaker. The culture medium that was not inoculated with the bacterial suspension was used as a blank control for experiments under the same c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com