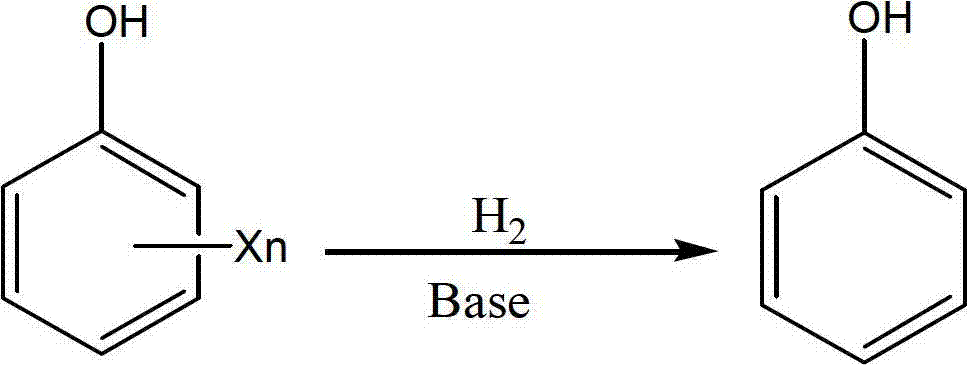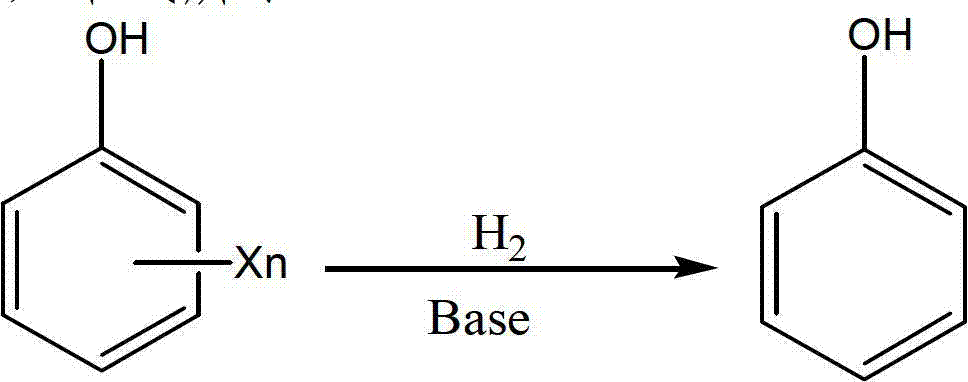Method for efficiently degrading chlorinated phenolic compound
A technology for chlorinated phenols and compounds, which is applied in the field of efficient degradation of chlorinated phenolic compounds, to achieve the effects of rapid and effective hydrodechlorination, rapid degradation, less catalyst consumption and high catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Preparation of Hydrodechlorination Catalyst
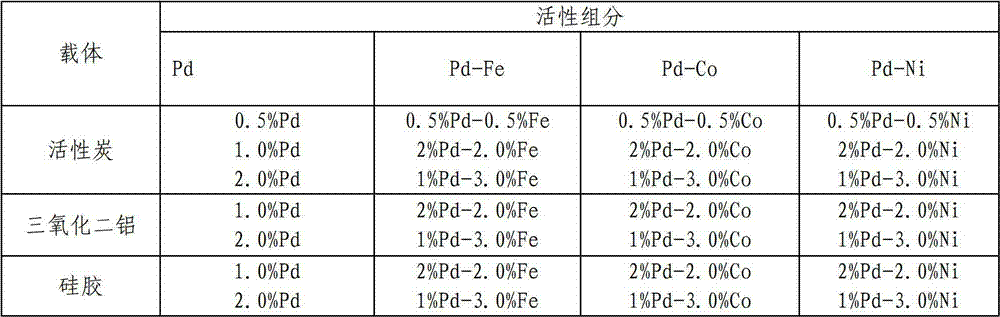
[0028] A certain amount of palladium chloride, ferric chloride, cobalt chloride and nickel chloride are dissolved in concentrated hydrochloric acid, diluted with water, and then impregnated into Activated carbon, placed at room temperature for 24h, then washed with ammonia and deionized water until free of Cl - So far, after being finally dried, it is reduced with sodium borohydride, and then sealed and stored to obtain palladium / carbon, palladium-iron / carbon, palladium-cobalt / carbon, palladium-nickel / carbon catalysts with different contents. The catalysts with different contents are listed in Table 1.
[0029] According to the preparation process of the catalyst described above, except that the carrier is different, the rest of the process is the same, and the bimetallic supported catalysts with different supports can be prepared, and the prepared catalysts are listed in Table 1.
[0030] Table 1 Catalysts with different ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The hydrodechlorination of different chlorinated phenolic compounds of embodiment 2
[0033] Weigh 25 mg of the catalyst prepared in Example 1, add it to a 100 ml three-necked flask, add 80 ml of an aqueous solution of 4-CP (wherein the concentrations of DCP, TCP and PCP are 1000 ppm) with a concentration of 5000 ppm, and stir the reactant with a magnetic stirrer. Adsorb for 15min; then pass N 2 , do this three times, and then pass H 2 , H 2 The flow rate is controlled within the range of 10-30ml / min, and the alkali used is sodium hydroxide. In order to ensure that the second-step oxidation reaction can be carried out relatively quickly, the ratio of the amount of alkali to the amount of chlorine in the reaction substrate is 1.1 : 1, the reaction temperature is controlled at 30°C, and the reaction pressure is normal pressure. According to the different dechlorination rates of different chlorinated phenolic compounds, the reaction time is also different. The specific d...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The influence of embodiment 3 different bases on 4-CP hydrodechlorination
[0038] Take by weighing the 1%Pd 3.0%NiPd-Ni / C catalyst that 25mg embodiment 1 prepares, join in the there-necked flask of 100ml, add the 4-CP aqueous solution 80ml that concentration is 5000ppm, make reactant be stirred under magnetic stirrer Adsorb for 15min; then pass N 2 , do this three times, and then pass H 2 , H 2 The flow rate is controlled within the range of 10-30ml / min, and the alkali used can be sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, triethylamine, sodium bicarbonate, pyridine, but in order to ensure that the second oxidation reaction can Relatively fast, the ratio of the amount of alkali to the amount of chlorine in the reaction substrate is 1.1:1, the reaction temperature is controlled at 30°C, the reaction pressure is normal pressure, and the reaction is carried out for 60 minutes. The specific dechlorination results are shown in Table 3 . ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com