Method for preparing soluble glass by using waste residues with aluminum extracted by coal gangue
A technology of sodium silicate and coal gangue, applied in the direction of silicate, alkali metal silicate, solid waste removal, etc., can solve the problems of high equipment requirements and increased energy consumption, so as to reduce energy consumption and avoid strong The effect of corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
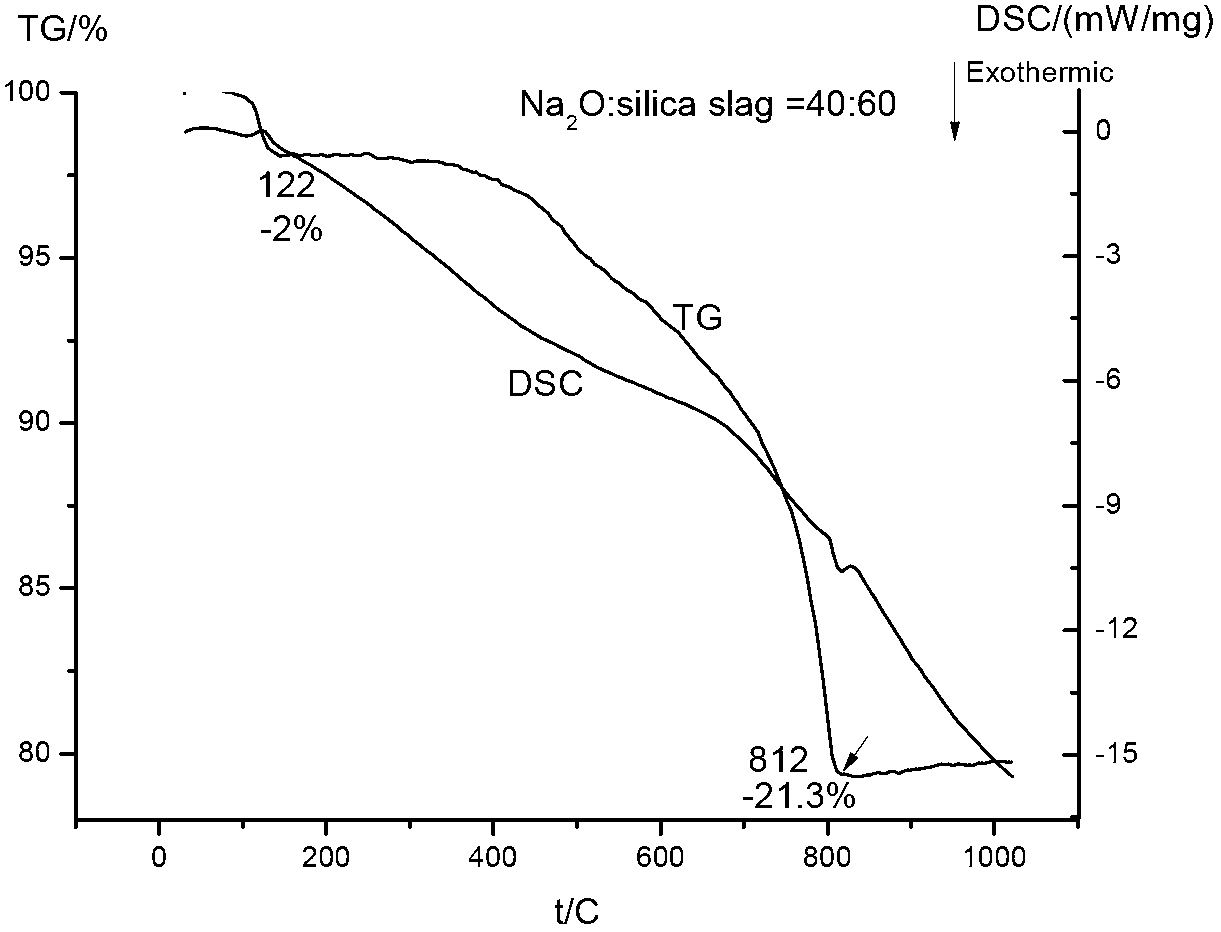
[0024] Weigh 100g of silicon slag and 110g of sodium carbonate, mix and grind them into particles of about 5 μm in a ball mill, and place them in a muffle furnace to program the temperature. The heating rate is 10°C / min between 0-500°C; °C / min; stop at 850 °C for 3 hours, then quickly place in boiling water for water quenching to obtain crude sodium silicate solid. Put the above crude sodium silicate solid in a 1-liter high-pressure reactor, add 500 ml of distilled water, raise the temperature to 150°C, stir and dissolve for 5 hours, then lower the temperature to room temperature, filter and separate to obtain colorless and transparent sodium silicate Solution and filter residue, the sodium silicate solution is evaporated and crystallized to obtain the sodium silicate product. ICP was used to determine the silicon content and impurity content of sodium silicate solution, filter residue and sodium silicate product (Table 2). The results of thermogravimetric differential therma...
Embodiment 2
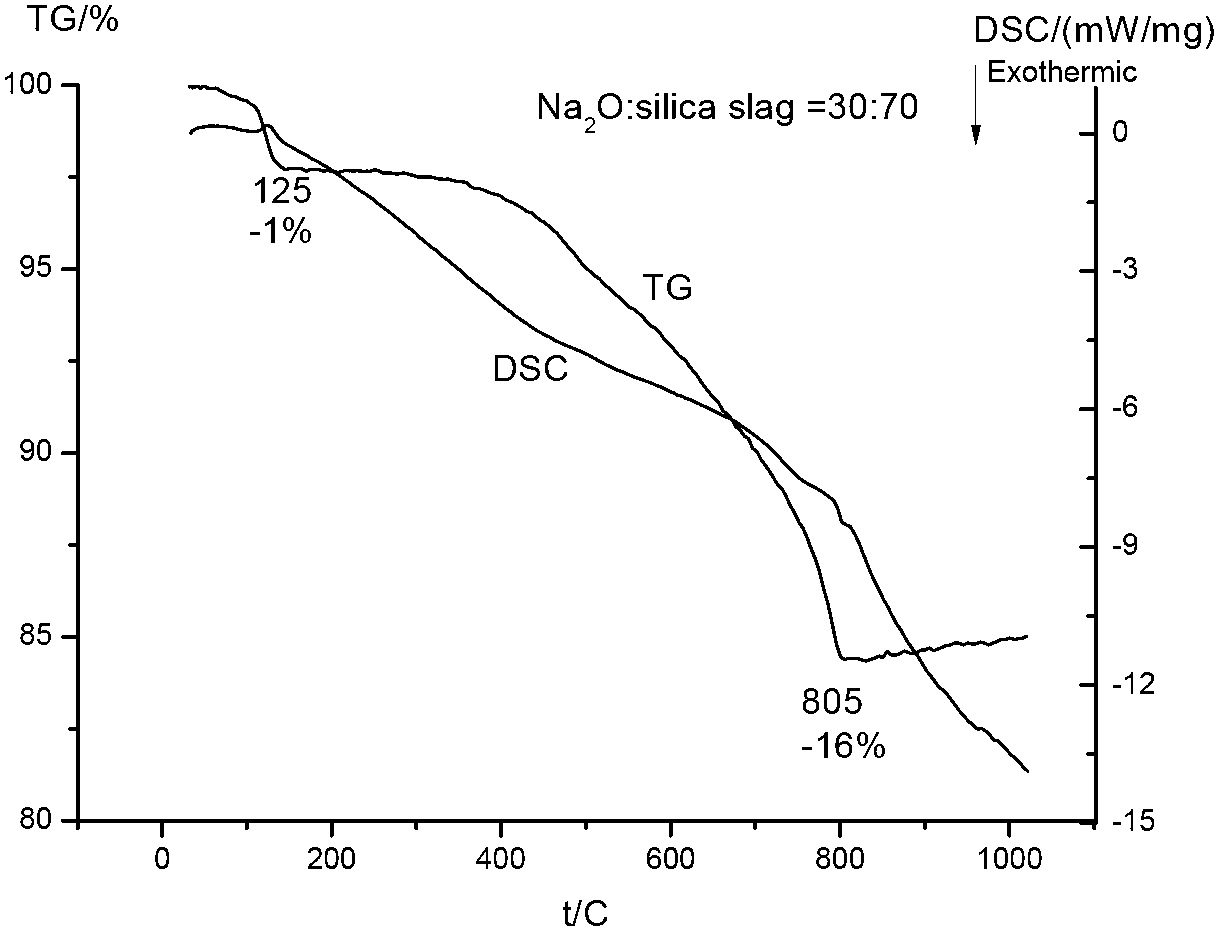
[0029] Weigh 100g of silicon slag and 70g of sodium carbonate and mix and grind. The rest of the conditions are the same as in Example 1. ICP is used to measure the silicon content and impurity content of the sodium silicate solution and filter residue (alkali dissolution method) respectively (Table 3). The results of thermogravimetric differential thermal analysis compared under the same process conditions are as follows: figure 2 , The dissolution rate of sodium silicate is 90.0%.
[0030] Table 3 Product composition analysis table
[0031]
[0032] It can be seen from differential thermal analysis (see figure 2 ), the thermogravimetric analysis results are the same as in Example 1, and the melting temperature can be obtained from the DSC curve at 805°C.
Embodiment 3
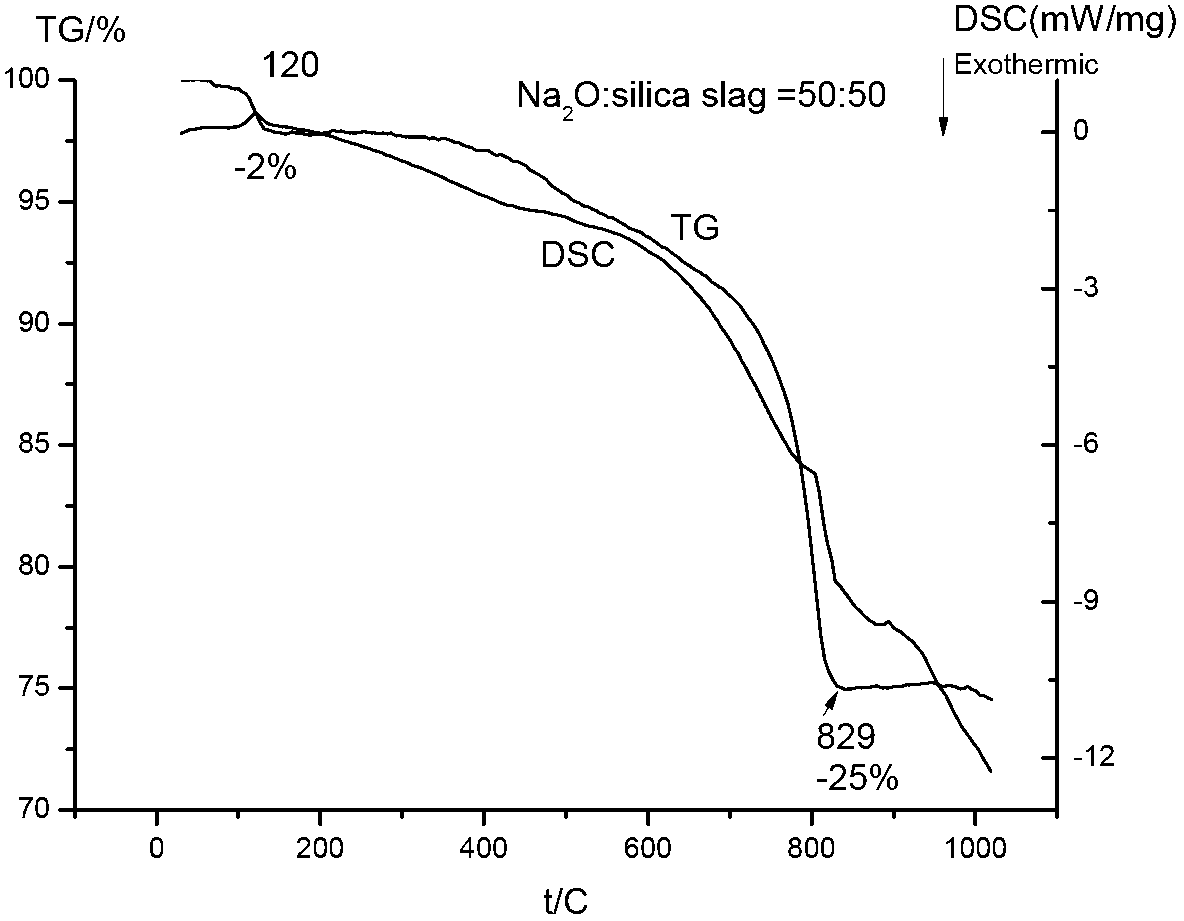
[0034] Take by weighing 100g of silicon slag and 164g of sodium carbonate and mix and grind, all the other conditions are the same as in Example 1. The silicon content and impurity content of sodium silicate solution and filter residue (alkali dissolution method) were determined by ICP (Table 3). The results of thermogravimetric differential thermal analysis compared under the same process conditions are as follows: image 3 , The dissolution rate of sodium silicate is 90.2%.
[0035] It can be seen from differential thermal analysis (see image 3 ), the thermogravimetric analysis results are the same as in Example 1, and the melting temperature can be obtained from the DSC curve at 829°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com