High temperature resistant silver coated substrates
A substrate, silver layer technology, applied in the direction of coating, metal material coating process, layered products, etc., can solve problems such as oxidation and adhesion problems that cannot be overcome, and achieve the effect of inhibiting adhesion failure and less adhesion failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
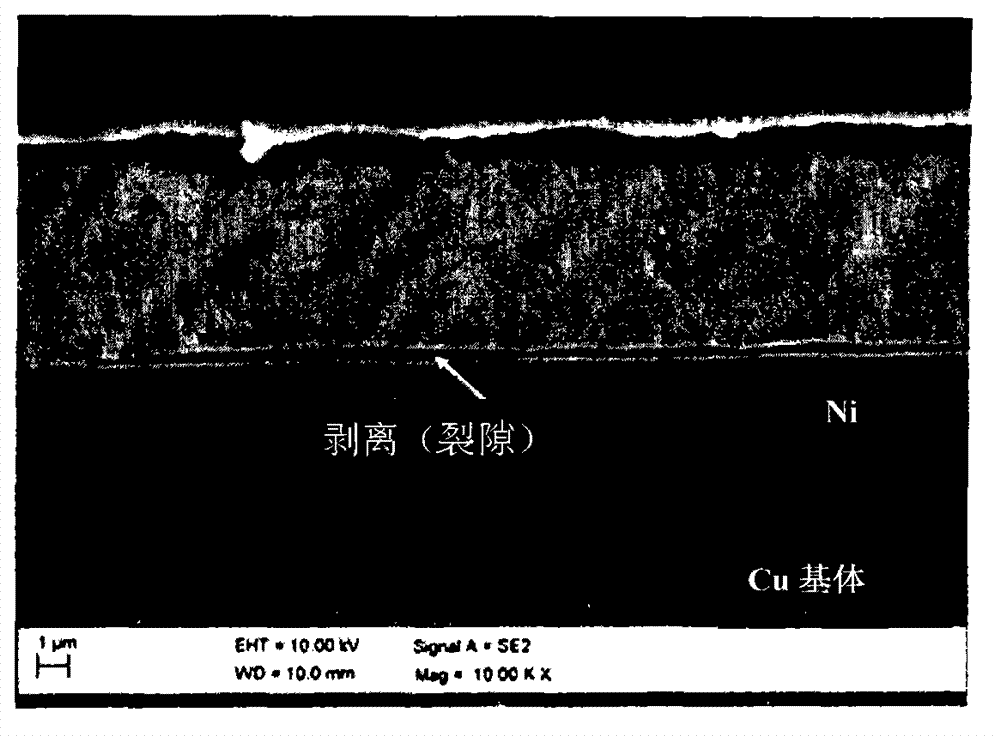
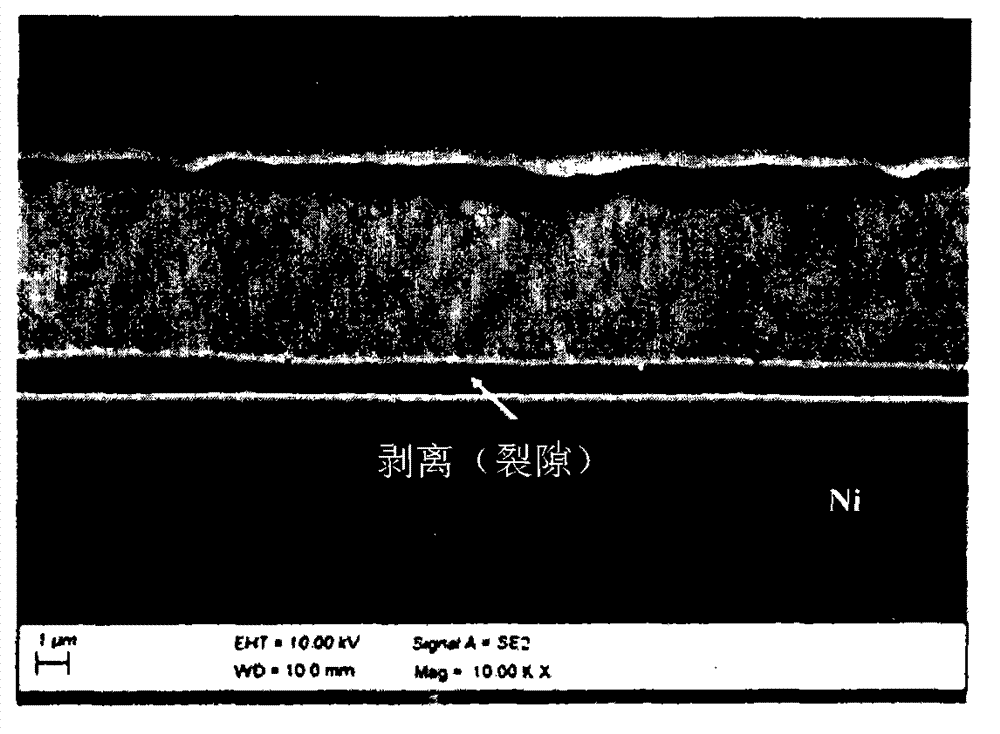
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1 (comparative example)
[0046] Three cleaned copper-based samples (copper or copper / zinc) of 2 cm x 5 cm were placed in a nickel electroplating solution having the formulation described in Table 1.
[0047] Table 1
[0048] components
content
Nickel sulfate hexahydrate providing nickel ions
60g / L
Nickel chloride hexahydrate providing nickel ions
10g / L
45g / L
0.5g / L
Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylate Sulfate
2ml / L
[0049] The sample was connected to a rectifier and the counter electrode was a platinized titanium electrode. During the nickel plating process, keep the temperature of the nickel bath at 30 degrees Celsius. The current density is 1ASD. Electroplating was stopped when a nickel layer with a thickness of 2 μm was deposited on the surface of each copper sample. The samples were removed from the bath and rinsed with deionized water at room temperature.
...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2 (comparative example)
[0059] Three copper-based samples were prepared as described in Example 1, except that the nickel layer was plated with a gold strike instead of a silver strike. The composition of the gold strike plating solution is shown in Table 3.
[0060] table 3
[0061] components
content
Potassium gold cyanide providing gold ions
2g / L
Cobalt carbonate providing cobalt ions
0.5g / L
50g / L
[0062] The gold strike bath was kept at 40°C, and the current density used was 0.2ASD. Gold plating was stopped when the gold layer deposited on the nickel layer reached 0.1 μm.
[0063] Each sample was then electroplated with a 5 μm thick layer of silver using the silver cyanide bath described in Table 2. The parameters used for silver plating were the same as in Example 1.
[0064] The silver-plated samples were taken out from the silver-plating solution, rinsed with deionized wa...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3 (comparative example)
[0068] Three copper-based samples were prepared as described in Example 1, except that the nickel layer was plated with a palladium-nickel alloy strike instead of a silver strike. The formulation of the palladium-nickel alloy strike plating solution is shown in Table 4.
[0069] Table 4
[0070] components
content
20g / L
nickel sulfate
8g / L
50g / L
[0071] The palladium-nickel alloy plating solution is kept at 60° C., and the current density is 0.2ASD. Stop electroplating when the thickness of the palladium-nickel alloy reaches 0.1 μm.
[0072] Each sample was then electroplated with a 5 μm thick layer of silver using the silver cyanide bath described in Table 2. The parameters used for silver plating were the same as in Example 1.
[0073] The silver-plated samples were removed from the silver-plating bath, rinsed with deionized ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com