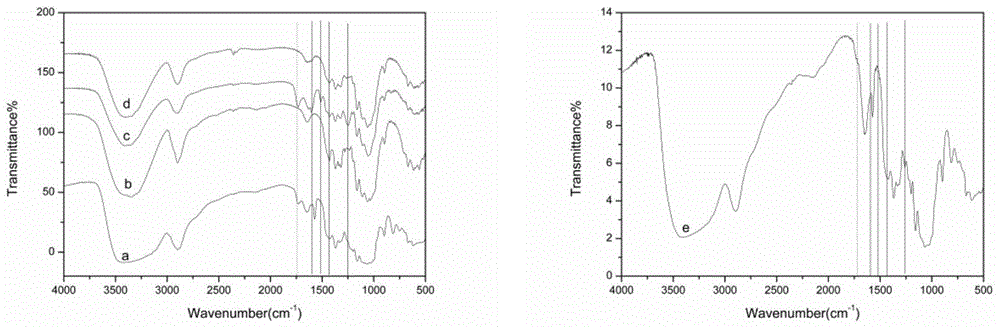
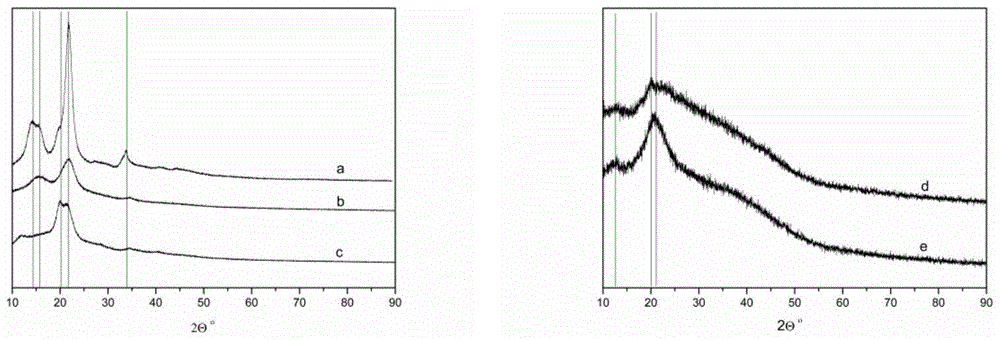
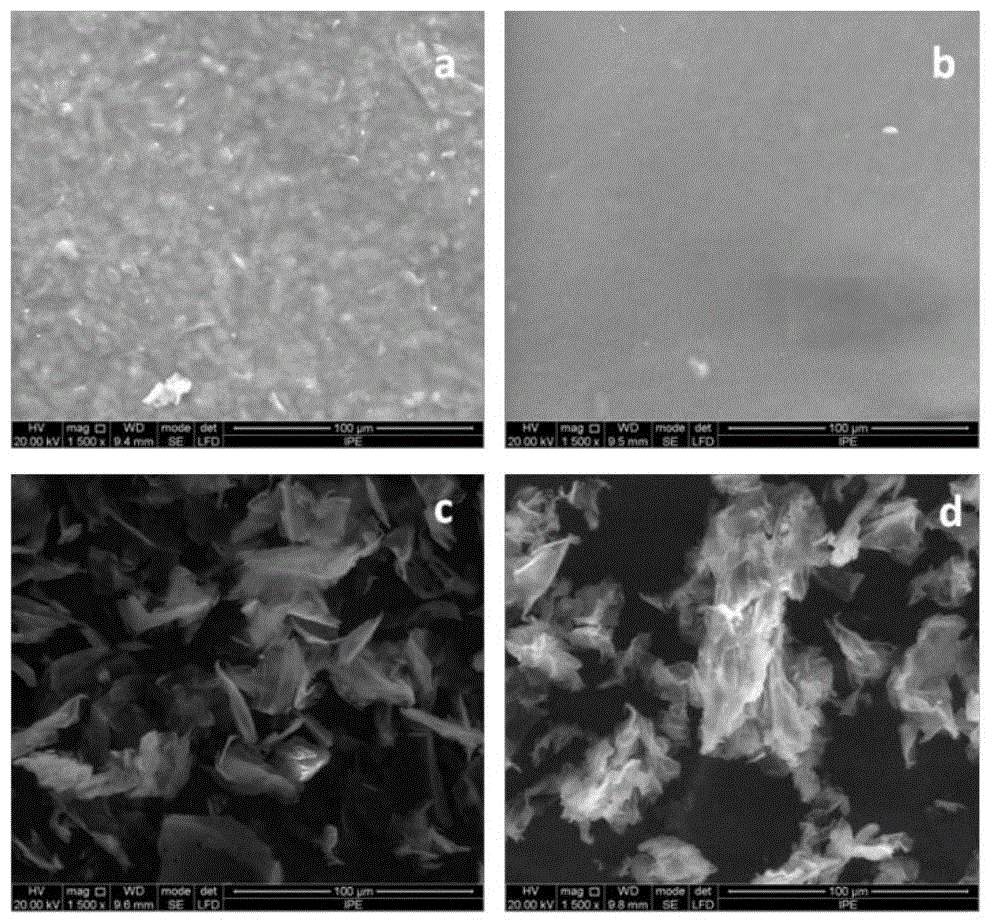
A two-step method for obtaining cellulose-rich materials from straw using ionic liquids
An ionic liquid and cellulose technology, applied in fiber raw material processing, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of high reaction pressure, long time, and reduce the crystallinity of cellulose, and achieve mild reaction conditions, low production cost, and high crystallinity. reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Weigh about 1.0964g of straw powder after washing with neutral detergent, add it into 20mL 50wt% choline hydroxide (ChOH) aqueous solution, stir at room temperature for 3h, centrifuge the residue and supernatant, and then use the residue 60 mL of distilled water was washed three times, filtered and dried to obtain a residue of 0.5218 g, and the dissolution rate of the straw in the solution reached 47.59%. The content of hemicellulose in the analysis residue component was 31.22%, the content of cellulose was 56.71%, that is, the content of cellulose was 87.93%, and the content of lignin was 12.07%.
[0021] Weigh about 0.5000g of the above residue, add it to 10.0028g 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole dimethyl phosphate ([Emim][DMP]) ionic liquid, heat to 130°C and magnetically stir for 5-10min to complete the reaction Dissolve, no residue remains, and the dissolution rate reaches 100%. After stopping the reaction, cool to normal temperature, add 10mL DMSO to dilute the reaction...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Weigh about 1.0964g of straw powder after washing with neutral detergent, add it into 20mL 50wt% choline hydroxide (ChOH) aqueous solution, stir at room temperature for 3h, centrifuge the residue and supernatant, and then use the residue 60 mL of distilled water was washed three times, filtered and dried to obtain a residue of 0.5218 g, and the dissolution rate of the straw in the solution reached 47.59%. The content of hemicellulose in the analysis residue component was 31.22%, the content of cellulose was 56.71%, that is, the content of cellulose was 87.93%, and the content of lignin was 12.07%.
[0024] Weigh about 0.5022g of the above residue, add it to 10.0244g of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetic acid ([Emim][OAc]) ionic liquid, heat to 130°C and magnetically stir for 30min to dissolve completely, and no residue remains , the dissolution rate reaches 100%. After the reaction was stopped, it was cooled to room temperature, and 10 mL of DMSO was added to dilute the ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Weigh about 1.0964g of straw powder after washing with neutral detergent, add it into 20mL 50wt% choline hydroxide (ChOH) aqueous solution, stir at room temperature for 3h, centrifuge the residue and supernatant, and then use the residue 60 mL of distilled water was washed three times, filtered and dried to obtain a residue of 0.5218 g, and the dissolution rate of the straw in the solution reached 47.59%. The content of hemicellulose in the analysis residue component was 31.22%, the content of cellulose was 56.71%, that is, the content of cellulose was 87.93%, and the content of lignin was 12.07%.
[0027] Weigh about 0.5000 g of the above residue, add it into 9.8572 g of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt ([Emim]Cl) ionic liquid, heat to 130°C and magnetically stir for 50 minutes to completely dissolve and no residue remains. The dissolution rate reaches 100%. After the reaction was stopped, it was cooled to room temperature, and 10 mL of DMSO was added to dilu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com