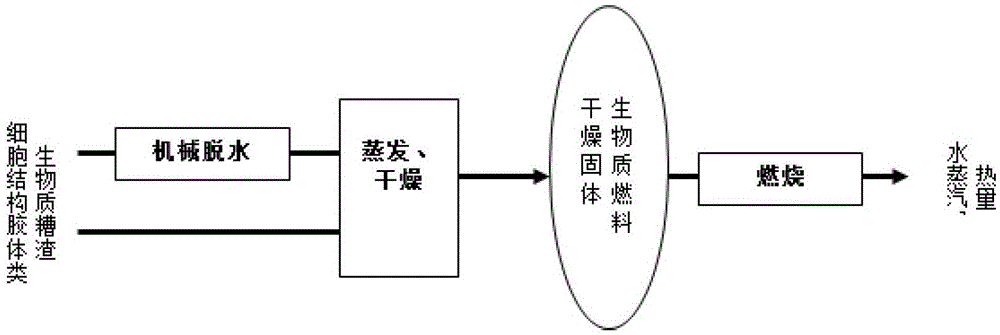
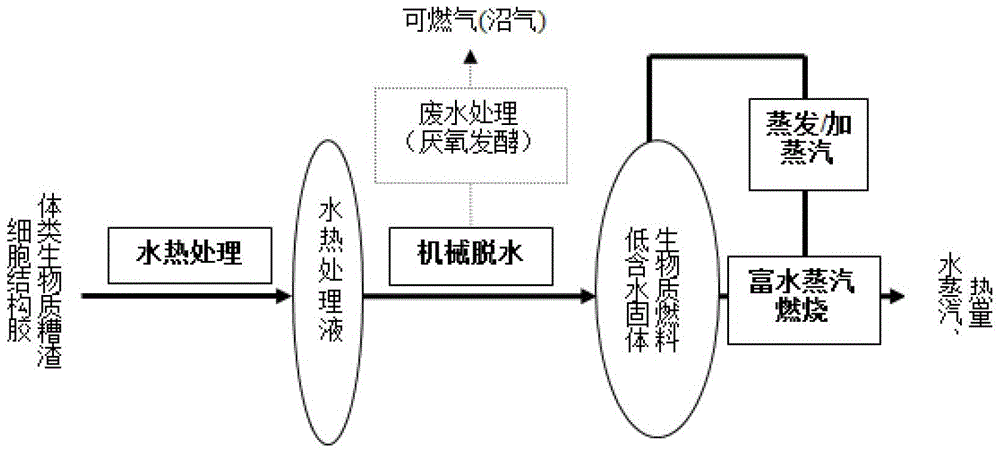
A method for energy conversion of colloidal biomass residue with cell structure
A cell structure and biomass technology, applied in combustion methods, incinerators, gas fuels, etc., can solve the problems of poor removal effect, ammonia leakage, high-efficiency catalyst operating costs, etc., and achieve quality improvement and biodegradability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Such as figure 2 Shown, a kind of method for energy conversion of colloidal biomass residue with cell structure, described method comprises the following steps:
[0031] 1) Use the dregs of the fermented antibiotic (cephalosporin C) as raw material, add 20% water to the raw material and put them into a hydrothermal reaction kettle together, stir and heat to 200°C, then treat at a constant temperature for 1.0h, then stop heating and Cool to below 100°C, open the hydrothermal reactor to release gas (including CO in addition to air components) 2 , CO and a small amount of C 1 -C 3 gaseous hydrocarbons), the hydrothermal treatment liquid continues to cool to room temperature;
[0032] 2) Pour the cooled hydrothermal treatment solution into a bag centrifuge (the bag aperture is 200 mesh) for dehydration, and process it for 5 minutes at a centrifugal factor of 600 to obtain a biomass solid fuel with a moisture content of 40%;
[0033] 3) Evaporation and drying adjusts th...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Such as figure 2 Shown, a kind of method for energy conversion of colloidal biomass residue with cell structure, described method comprises the following steps:
[0042] 1) Use the dregs of antibiotics (cephalosporin C) produced by fermentation as raw material, add 40% water to the raw material and put them into a hydrothermal reaction kettle together, stir and heat to 220°C, then treat at a constant temperature for 0.5h, then stop heating and Cool to below 100°C, open the hydrothermal reactor to release gas (including CO in addition to air components) 2 , CO and a small amount of C 1 -C 3 gaseous hydrocarbons), the hydrothermal treatment liquid continues to cool to room temperature;
[0043] 2) Pour the cooled hydrothermal treatment solution into a bag centrifuge (the bag aperture is 200 mesh) for dehydration, and process it for 5 minutes at a centrifugal factor of 600 to obtain a biomass solid fuel with a moisture content of 35%;
[0044] 3) Evaporate and dry to ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Such as figure 2 Shown, a kind of method for energy conversion of colloidal biomass residue with cell structure, described method comprises the following steps:
[0048] 1) Use the dregs of antibiotics (cephalosporin C) produced by fermentation as raw materials, directly put them into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, stir and heat to 160°C, then treat at a constant temperature for 1 hour, then stop heating and cool to below 100°C, and turn on the hydrothermal reaction Gas released from kettle (including CO in addition to air components 2 , CO and a small amount of C 1 -C 3 gaseous hydrocarbons), the hydrothermal treatment liquid continues to cool to room temperature;
[0049] 2) Pour the cooled hydrothermal treatment liquid into a bag centrifuge (the bag aperture is 200 mesh) for dehydration, and process it for 5 minutes at a centrifugal factor of 600 to obtain a biomass solid fuel with a moisture content of 50%;
[0050] 3) Evaporate and dry to adjust the water-to-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com