Method for reducing background signal of electrochemical sensor and sensor utilizing method
A background signal and sensor technology, which is applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve the problems that the background signal cannot be effectively reduced, and achieve the effect of improving sensitivity, reducing background signal, and improving relative signal change
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment l
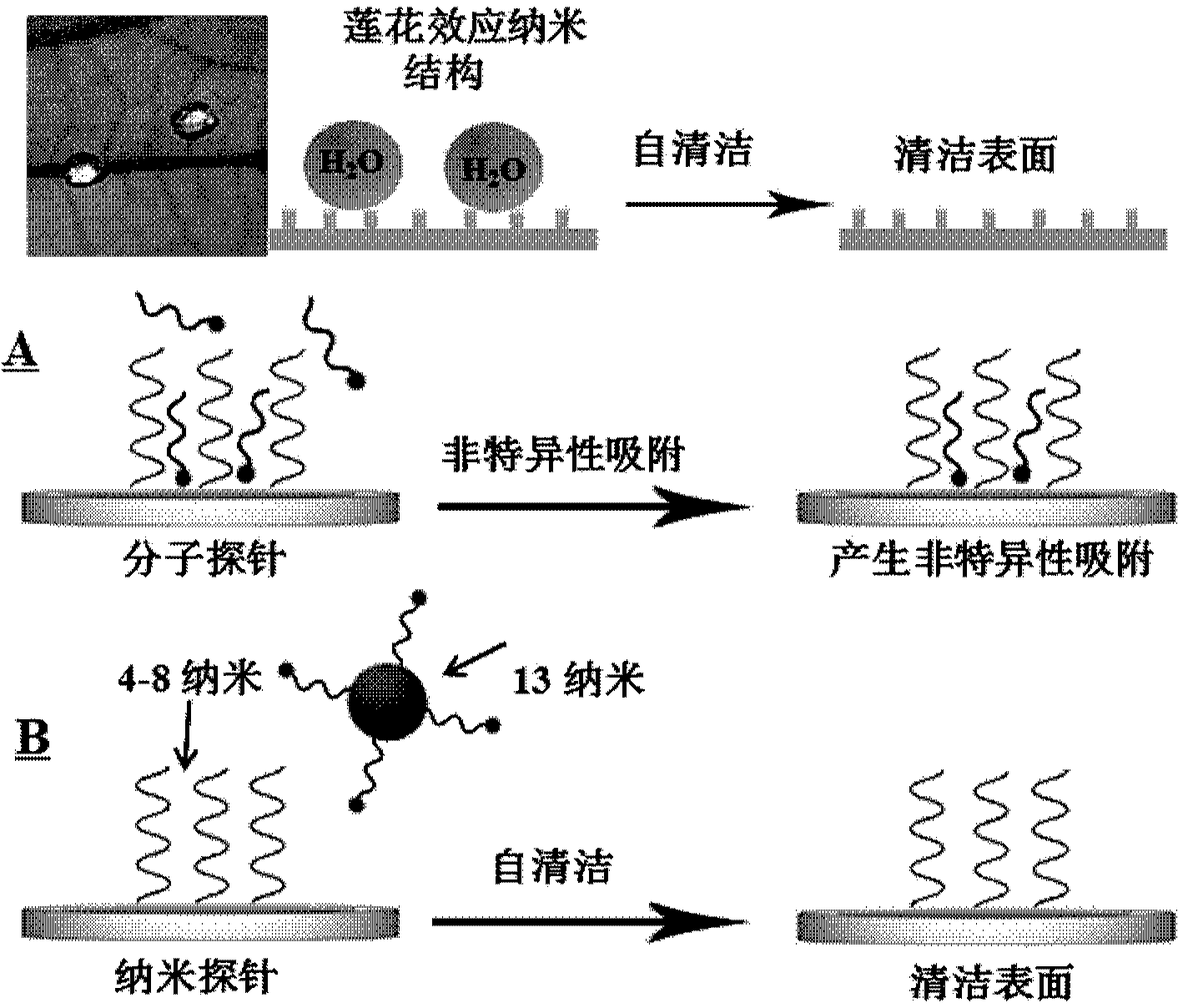
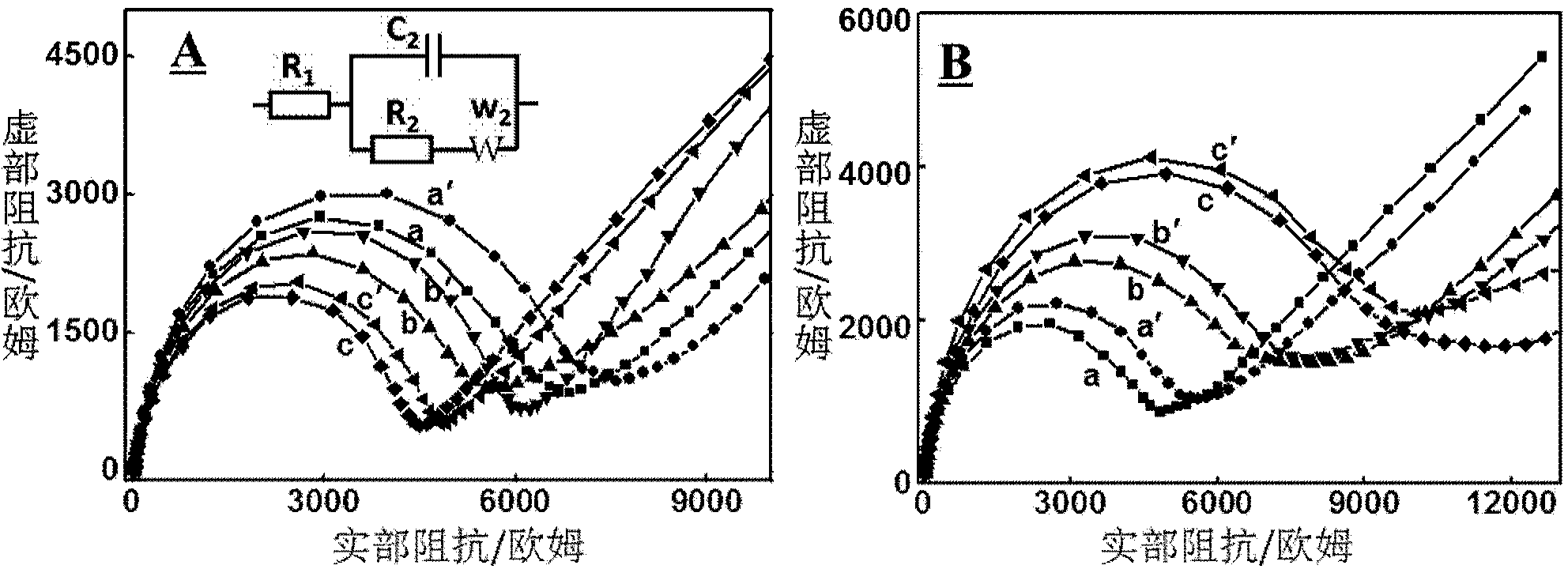
[0034] Example 1: Using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to confirm the non-specific adsorption of molecular probes on the surface of gold electrodes, and to study the relationship between the height and density of DNA self-assembled monolayers on the electrode surface and the strength of non-specific adsorption.
[0035] When preparing DNA self-assembly layers of different heights, respectively reduce 1 μM probes 1, 2 and 3 in 100 μM tris[2-carboxyethyl]phosphine (TCEP), 10 mM PB, 1.0 M NaCl, pH=7.0 at room temperature for 1 h , and then soak unmodified clean gold electrodes into it, and self-assemble overnight at room temperature. The assembled electrode was rinsed three times with ultrapure water, then placed in an aqueous solution containing 1mMMCH to seal for 30 minutes, and then rinsed three times with ultrapure water; when preparing self-assembled layers with different densities, 1 μM probe 1 Reduction in 100μM TCEP, 10mM PB, 0.2M NaCl, pH=7.0; 100μM TCEP, 10mM PB...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Immobilizing molecular signaling probes labeled with electrochemical redox groups to the surface of gold nanoparticles to synthesize nanoprobes.
[0039] The molecular signal probe labeled with the electrochemical redox group was dissolved in an aqueous solution of 50 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) and 2% triethylamine (TEA) by volume, and reacted at room temperature for 20 min. The NAP-5 column was used to purify the column twice, and the purified molecular signal probe was quantified by the UV-visible absorption value at 260nm to the reduced molecular signal probe. Then it was added to 9nM nano-gold solution with a particle size of 13nm, the molar ratio of molecular signal probes to nano-gold was 100:1, and aged at room temperature for 16 hours. After aging, add a solution of high salt concentration (10mM PB, 1M NaCl, pH7.4) several times under shaking in the molecular hybridization instrument to make the final concentration of NaCl in the system 0.2M. After shaki...
Embodiment 3
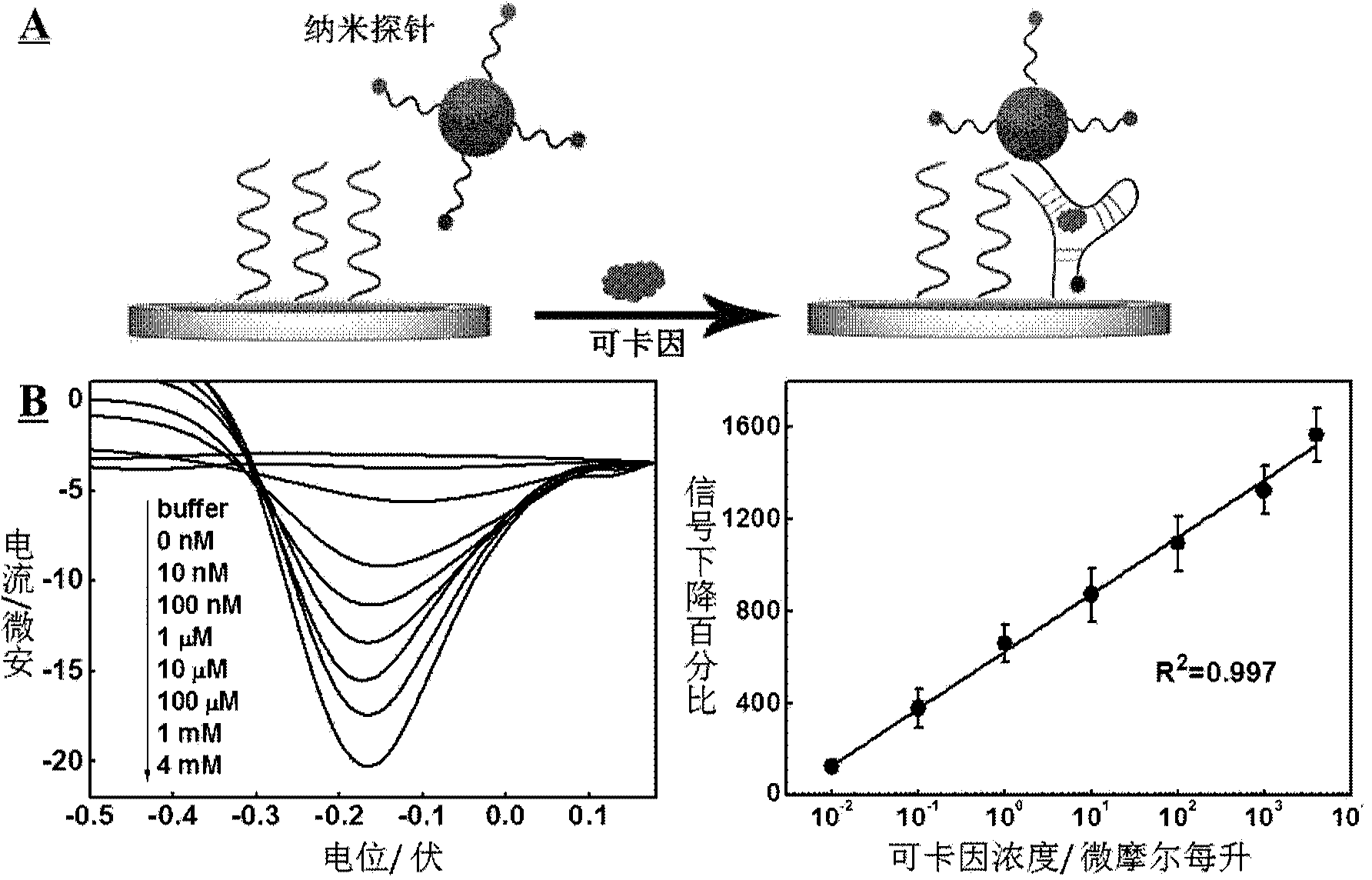
[0040] Example 3: Using nano-probes to remove non-specific adsorption on the surface of sensor electrodes to improve the sensitivity of the signal-increasing detection platform cocaine electrochemical sensor.
[0041] 1 μM probe 5 was reduced in 100 μM TCEP, 10 mM PB, 1.0 M NaCl, pH=7.0 at room temperature for 1 h, and then an unmodified clean gold electrode was soaked in it, and self-assembled overnight at room temperature. The assembled electrode was rinsed three times with ultrapure water, then placed in an aqueous solution containing 1 mM mercaptohexanol (MCH) to seal the electrode for 30 minutes, and then rinsed three times with ultrapure water. The needles were dissolved in a buffer solution (10 mM PB, 0.2 M NaCl, pH 7.0), and the final concentration of gold nanoparticles was 5 nM. A three-electrode system was composed of the above-mentioned gold electrode assembled with probe 5 as the working electrode, and a certain concentration of cocaine was added to the electrolyte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com