Enzymatic antibiotic for killing gram-positive bacteria and preparation and use of enzymatic antibiotic
A sequence and protein technology, applied in the field of microbial chemistry, can solve the problems of low enzyme activity and difficulty in mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
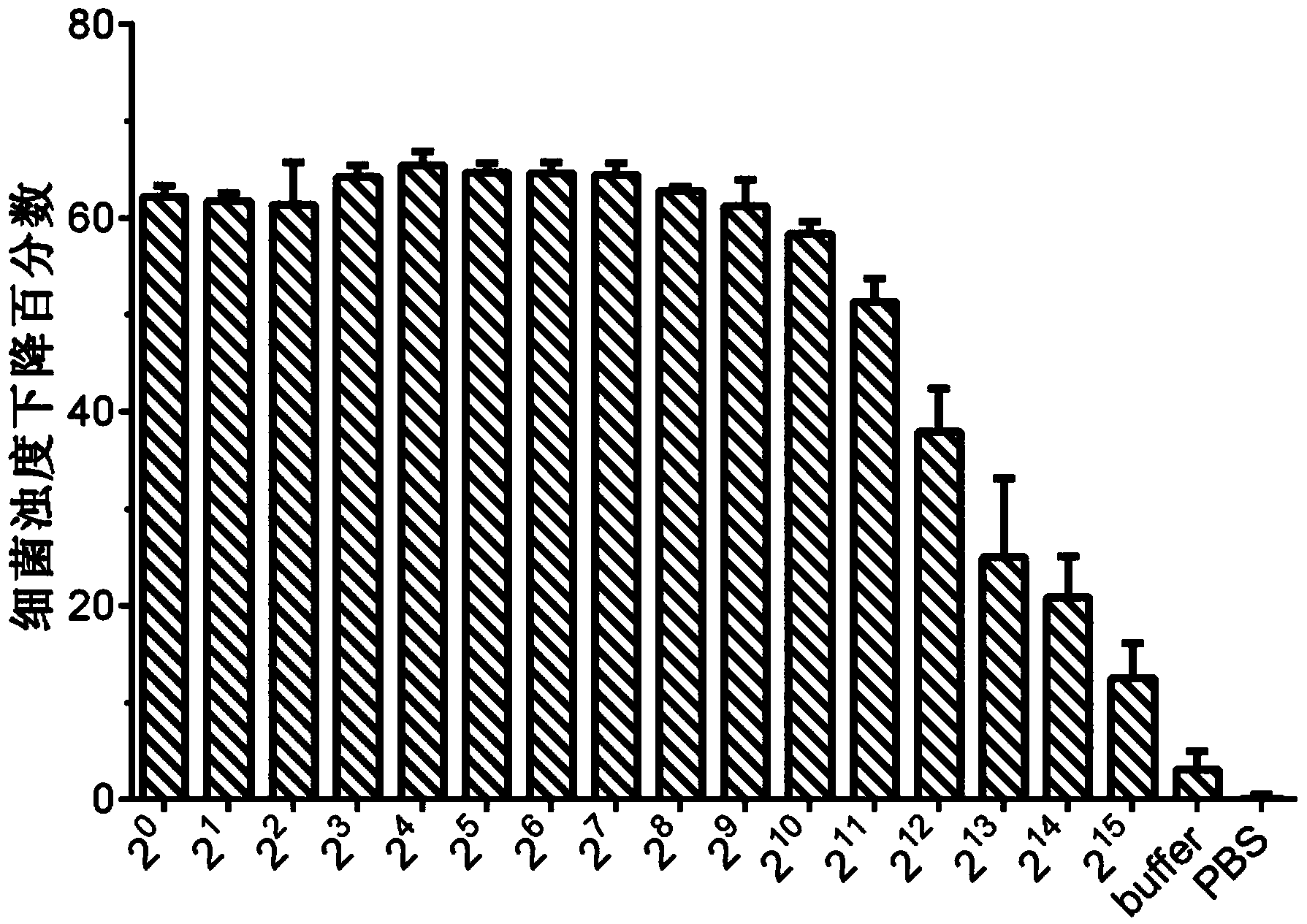
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1, design primer, PCR amplification target gene fragment
[0051] Refer to the gene sequence of Streptococcus suis strains in GenBank, design primers, use Streptococcus suis genomic DNA as a template, and use PCR technology to amplify the target gene. The size of the target gene is 738bp. The specific operation is as follows:
[0052] Primers were designed, the primer sequences are shown in Table 1, the target gene was amplified, and EcoR I and Hind III restriction sites were inserted at the 5' ends of the upstream and downstream primers, respectively. Using the genomic DNA of Streptococcus suis strain as a template, the target gene fragment was amplified according to conventional methods. After the PCR reaction, 10 μL of the product was taken for 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to check the size of the target band. The PCR product was recovered using a gel recovery kit.
[0053] Table 1 PCR primer sequence
[0054]
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, construction of recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-LySS7
[0056] Using the prokaryotic expression system pET-28a(+), construct a recombinant plasmid with the target gene obtained from the gel recovery kit in Example 1, perform sequence analysis and comparison, and determine the recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-LySS7 with the correct sequence; The operation is as follows:
[0057] The gel recovery product of Example 1 was connected to the vector pET-28a(+) for sequencing. The upstream and downstream of the designed primers respectively contain EcoR I restriction endonuclease cutting site and Hind III restriction endonuclease cutting site. The DNA and pET-28a(+) product digested by EcoR I and Hind III, at T 4 Under the action of DNA quick ligase (Fermentas company), the ligation was performed at 22° C. for 30 min. The ligated product was transferred into the cloning vector Escherichia coli DH5α, cultivated overnight at 37°C, and the plasmid was extracted. E...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3, prokaryotic expression of recombinant plasmid BL21 / pET-28a(+)-LySS7
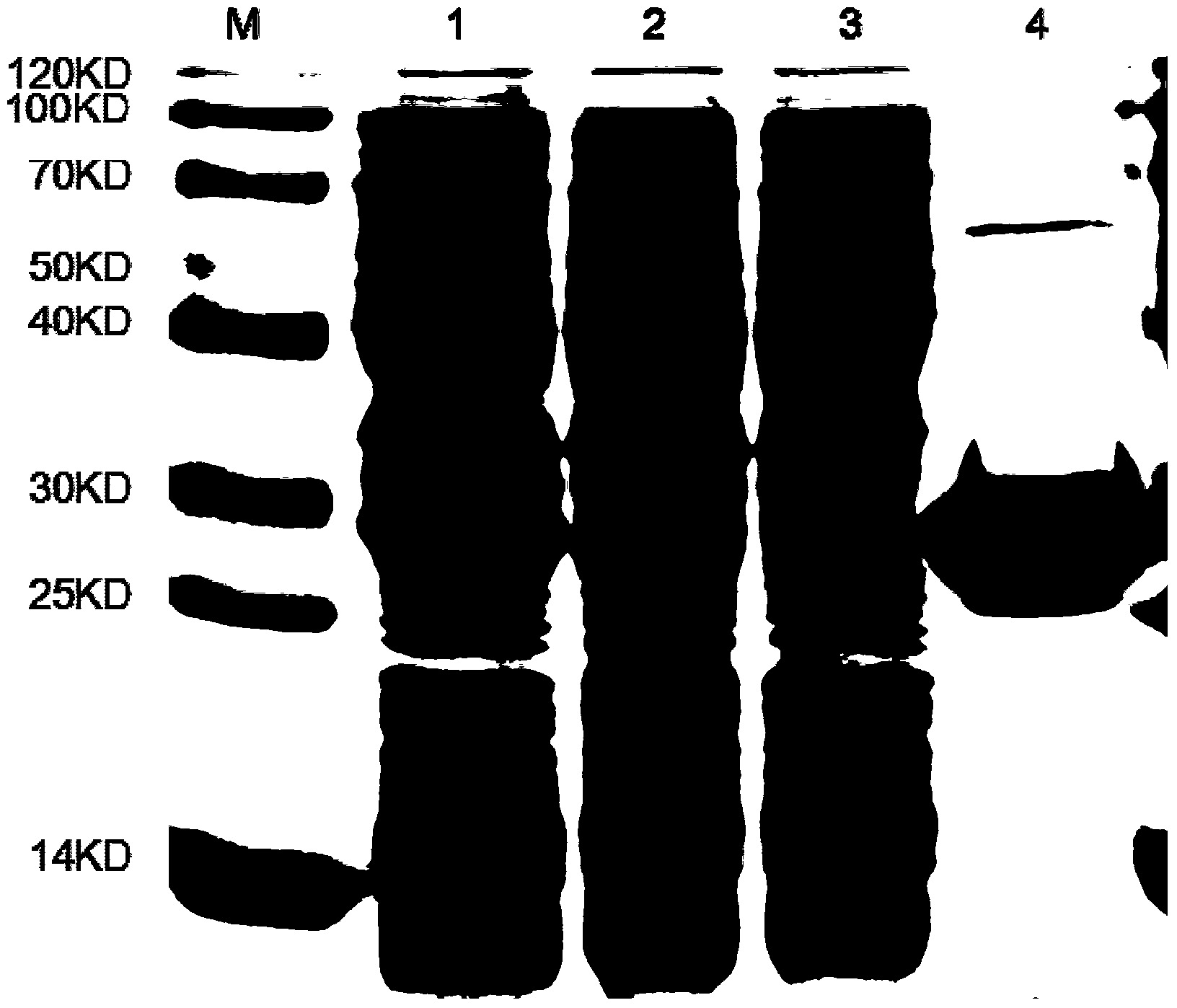
[0059] The recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-LySS7 in Example 2 was transformed into the expression vector Escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and the positive clone BL21 / pET-28a(+)-LySS7 was screened for inducible expression and identification of the protein to obtain recombinant Protein, the molecular weight of the recombinant protein is determined to be 29.8kDa; the specific operation is as follows:
[0060] The positive recombinant plasmid pET-28a(+)-LySS7 was transformed into the expression vector Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). The positive clone BL21 / pET-28a(+)-LySS7 was obtained, and a single colony was picked and inoculated into 5 ml of kanamycin-positive (1:1000) LB liquid medium for overnight culture. The overnight culture solution was transferred to 1L kanamycin-positive (1:1000) LB liquid medium at a ratio of 1:100, and cultured with shaking at 200 rpm at 37°C for 3-4 hours until OD 60...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com