Method for extracting and separating polypeptides
A separation method and target extraction technology, applied in the field of high-efficiency desorption polypeptide extraction and separation, can solve the problems of low desorption rate and low selectivity, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency desorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 (Adsorption and Release of Peptides)
[0027] polypeptide amino acid sequence pI molecular weight EE-6 EDAPA E 3.0 630.61 ED-9 ELRDD EAGD 3.4 1018.99 SP-20 SDEDS DGDRP QASPG LGPGP 3.4 1953.95 EL-25 EDDYE DHDGD DKDHD IDQKD DDDEL 3.5 3006.82 PP-6 PPGFS P 6.0 600.67 QF-9 QPLSS PPFF 6.0 1019.16 VE-18 VSEIQ LMHNL GKHLN SME 6.1 2080.42 PH-28 PSKPE DNPGA PAEDA RSALR HINLI TQH 6.1 3035.33 GI-6 GFLRR I 12.4 760.94
[0028] Porous silicon dioxide particles with an average size of 0.5 mm were put into 25 ml of hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, refluxed for 12 hours, filtered, washed with water, and dried. The dried sample was dispersed in 20 ml of toluene, slowly added trimethoxysilyl propyl glyceryl ether (5 ml dissolved in 5 ml of toluene) into the dispersion system under stirring, a few drops of triethylamine were added under nitrogen and refluxed 24 hours. Filter...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2 (polypeptide separation)
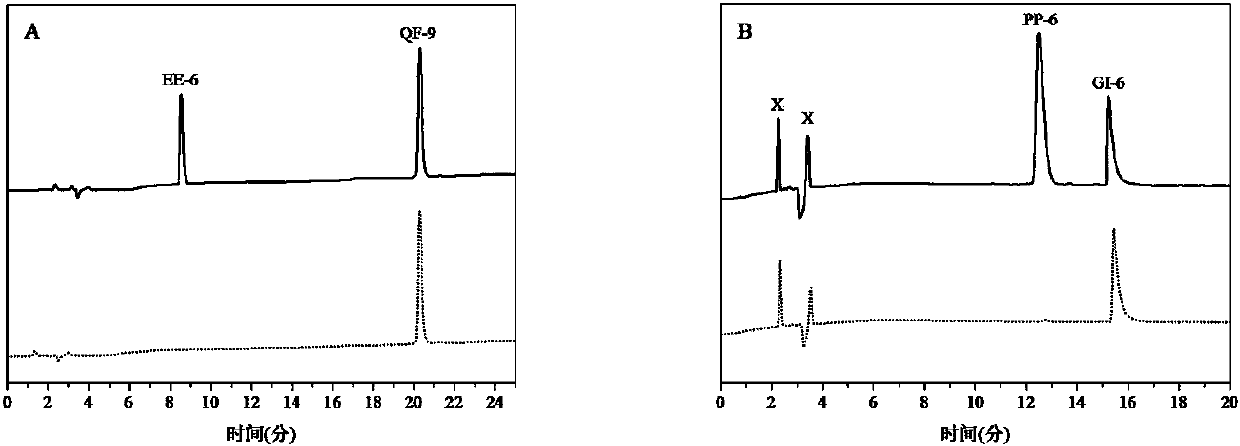
[0031] to peptides EE-6 (pI = 3.0) and QF-9 (pI = 6.0) (5.0 × 10 -5 M, 6 mL) in buffered aqueous solution (pH = 5, acetate buffer, 0.01 M) with the adsorbent SiO 2 PEI (30 mg) and allowed to stand for 20 hours. After separation of the solid adsorbent, the residual liquid was lyophilized (concentrated from 6 mL to 300 μL) and tested by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). HPLC test conditions: 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile and 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in water, the former rises from 18% to 100% within 25 minutes. The solution before adsorption was similarly concentrated and then subjected to control tests. The results are shown in Figure 1, indicating that the peptides with different isoelectric points can be completely separated after extraction.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3 (extraction and elution of trace polypeptide)
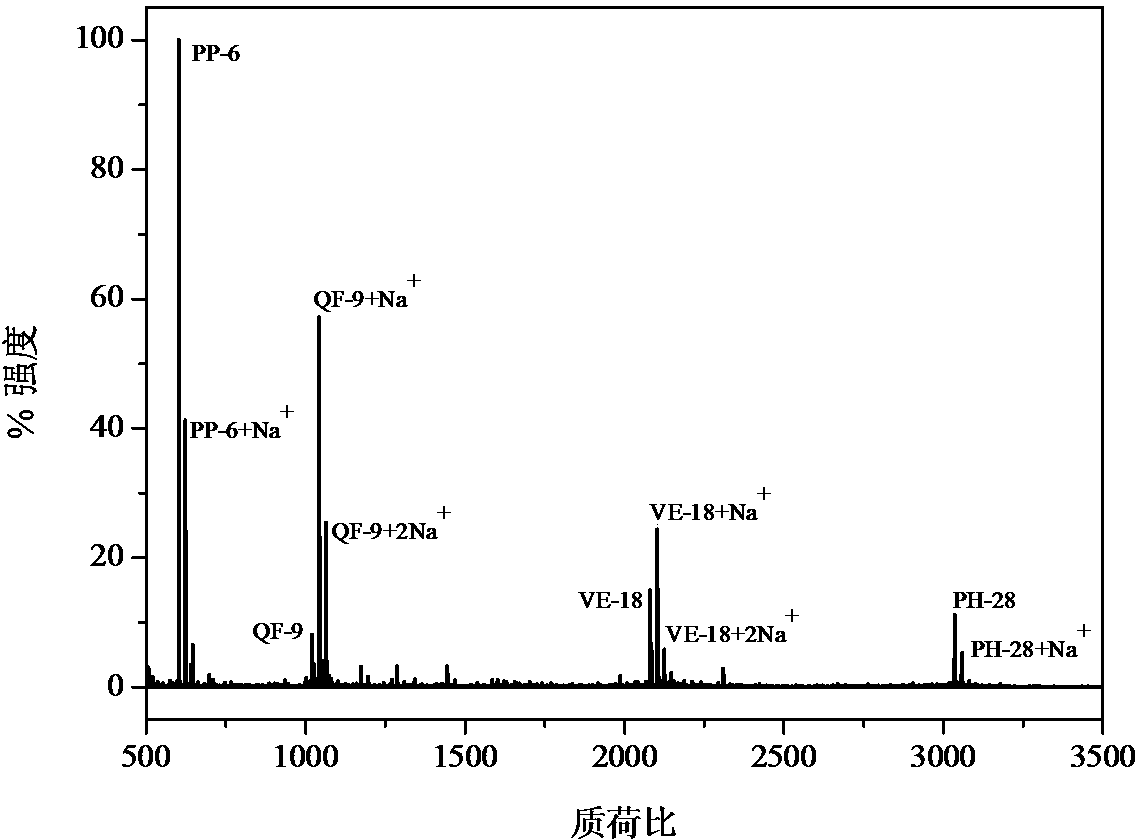
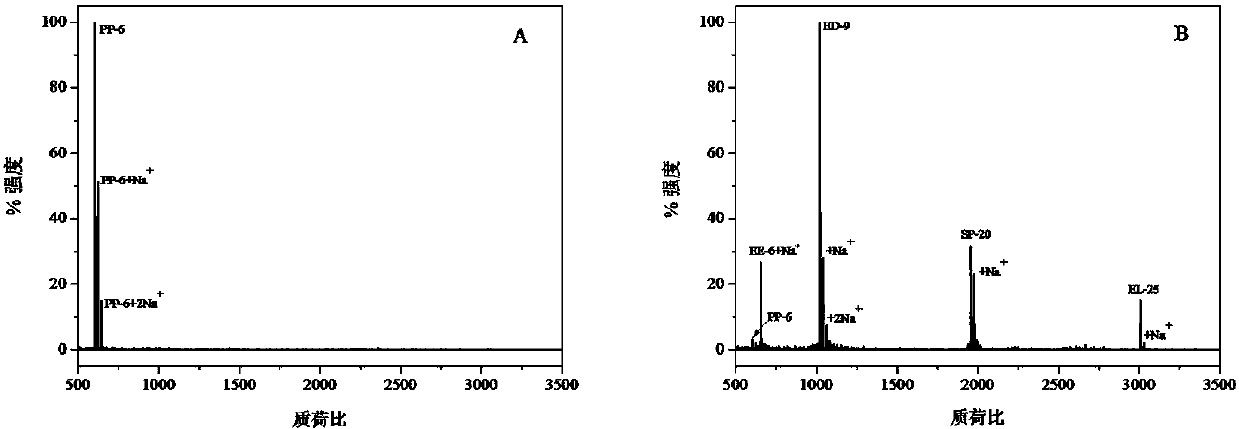
[0033] To a concentration of 1.0 × 10 -12 Add the adsorbent to PP-6, QF-9, VE-18 and PH-28 polypeptide aqueous solution (4 ml, pH 7.4 phosphate buffer) and let it stand for 20 hours. The solid adsorbent is adsorbed-separated-eluted (with pH 4 acetate buffer) followed by MALDI-TOF testing. The test uses the regular reflection mode. The results (Fig. 2) showed that all the signals of the four peptides appeared, indicating that all the peptides could be extracted. According to this result, it can be calculated that the adsorption constant reaches 10 12 m -1 , to further reduce the concentration of the peptide concentration to perform a similar test, showing that the extraction is still feasible, that is, the adsorption constant is higher than 10 12 m -1 , indicating that trace amounts of peptides can also be eluted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com