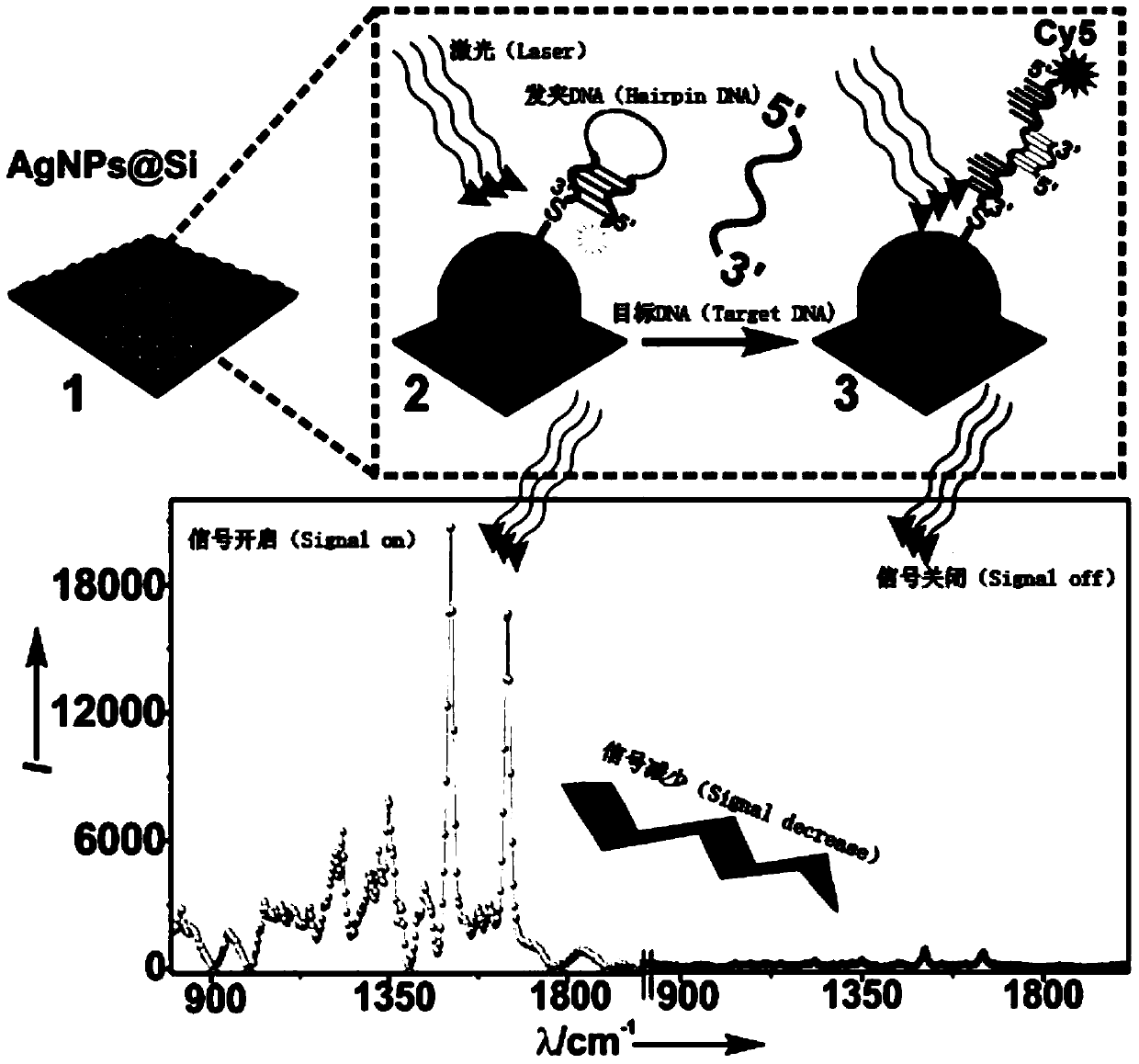
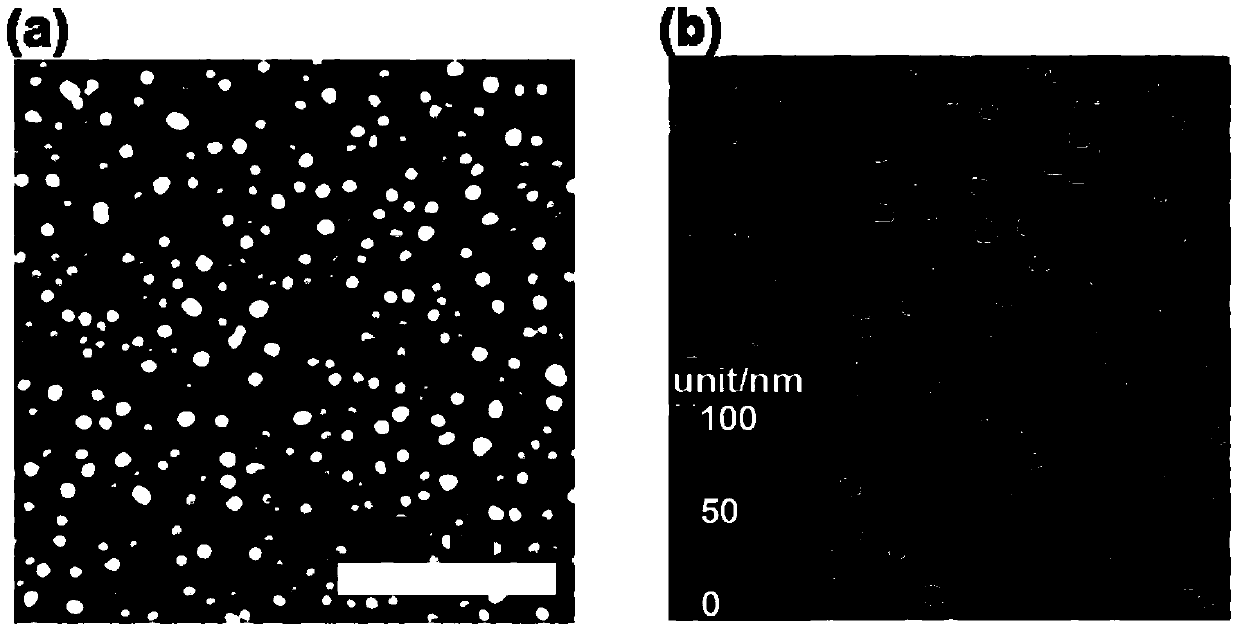
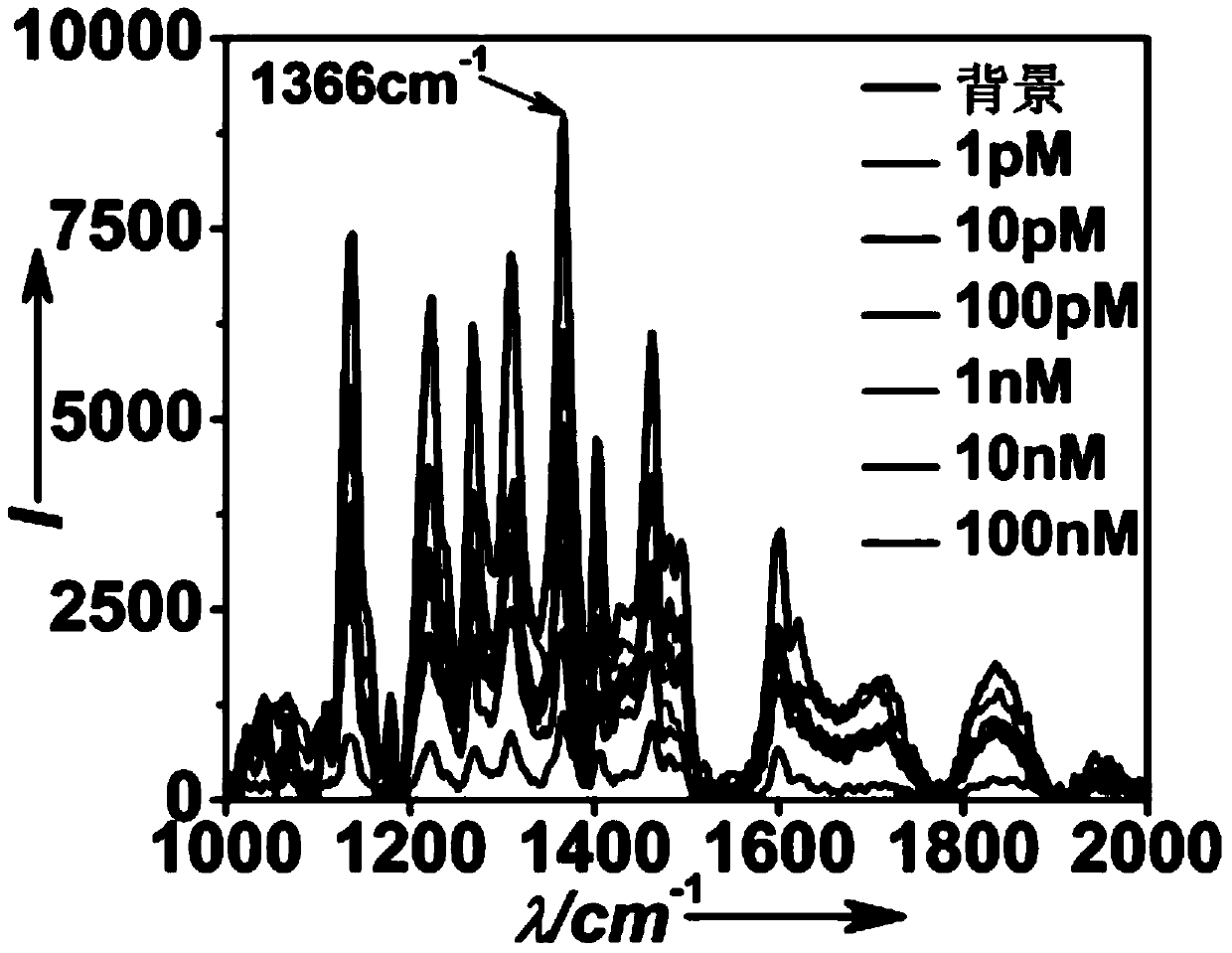
Method for detecting deafness genes based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A technology of surface-enhanced Raman and spectral detection, applied in the detection of deafness genes, based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in the field of detection of deafness genes, to achieve the effect of easy popularization and dissemination, overcoming poor reproducibility and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Pretreatment process of silicon wafer
[0037] Take 1cm 2 3~6 large and small single silicon wafers are placed in a clean beaker and ultrasonicated with deionized water, acetone, and deionized water for 15 minutes in sequence to obtain silicon wafers with no impurities and organic substances on the surface for later use. Take 40mL of a mixed solution of 98wt% sulfuric acid and 30wt% hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 3:1, and shake slowly while adding. Then put the silicon wafer into it and soak for 30 minutes to remove insoluble impurities, and then wash with deionized water for 3 to 5 times to remove the reaction solution for later use.
[0038] Soak the silicon wafer with 10wt% hydrofluoric acid for 20 minutes to remove the silicon dioxide oxide layer on the surface of the silicon wafer to form Si-H bonds on the surface of the silicon wafer. Quickly add 15mL of silver nitrate solution (2.5mM) with different pH values and react for 20 minutes. According to...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) Pretreatment process of silicon wafer
[0045] Take 1cm 2 3~6 large and small single silicon wafers are placed in a clean beaker and ultrasonicated with deionized water, acetone, and deionized water for 15 minutes in sequence to obtain silicon wafers with no impurities and organic substances on the surface for later use. Take 40mL of a mixed solution of 98wt% sulfuric acid and 30wt% hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 3:1, and shake slowly while adding. Then put the silicon wafer into it and soak for 30 minutes to remove insoluble impurities, and then wash with deionized water for 3 to 5 times to remove the reaction solution for later use.
[0046] Soak the silicon wafer with 15wt% hydrofluoric acid for 15 minutes to remove the silicon dioxide oxide layer on the surface of the silicon wafer to form Si-H bonds on the surface of the silicon wafer. Quickly add 20mL of silver nitrate solution (3mM) with different pH values and react for 18 minutes. According to t...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) Pretreatment process of silicon wafer
[0053] Take 1cm 2 3~6 large and small single silicon wafers are placed in a clean beaker and ultrasonicated with deionized water, acetone, and deionized water for 15 minutes in sequence to obtain silicon wafers with no impurities and organic substances on the surface for later use. Take 40mL of a mixed solution of 98wt% sulfuric acid and 30wt% hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 3:1, and shake slowly while adding. Then put the silicon wafer into it and soak for 30 minutes to remove insoluble impurities, and then wash with deionized water for 3 to 5 times to remove the reaction solution for later use.
[0054] Soak the silicon wafer with 10wt% hydrofluoric acid for 25 minutes to remove the silicon dioxide oxide layer on the surface of the silicon wafer, so that the Si-H bond is formed on the surface of the silicon wafer, and then spread the silicon wafer in a petri dish, with the shiny side facing up, facing it Quickly add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com