Method for detecting community structure and abundance of ammonia oxidizing bacteria in wastewater system
A technology of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and community structure, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms. , easy to popularize and apply, to ensure the effect of denitrification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Design of ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) specific primers
[0019] In order to ensure the accuracy of the amplification process and the single amplification product, the primer design method was selected on-line Primer-BLAST Primer design, where the login URL is http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / tools / primer-BLAST .
[0020] Select the FASTA file of the amoA gene template sequence, set the optimal primer design parameters, and perform BLAST analysis on each primer at the same time to make the primers specific. The designed primers were evaluated and screened using the software Oligo7.0, and the finally obtained specific primers, namely amoA1F with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.1 and amoA2R with the sequence number of SEQ ID No.2, are as follows:
[0021] Primer sequence wxya 5'-TCATGGACACCGTCTTGCTG-3' wxya 5'-CCAAAGGTTCGCAATGAGCC-3'
Embodiment 2
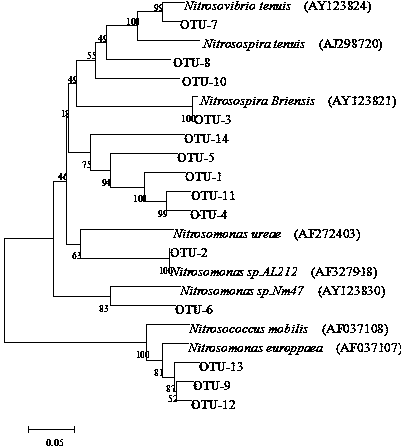
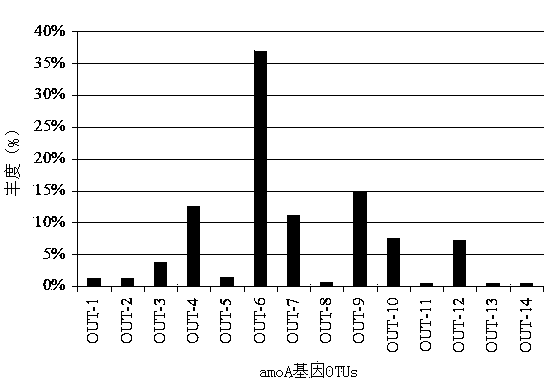
[0022] Example 2 Analysis of the community structure and species abundance of ammonia oxidizing bacteria in the activated sludge of an urban sewage treatment plant
[0023] 1. Extraction of total genomic DNA
[0024] The sample was taken from the activated sludge of an urban sewage treatment plant, and the total genomic DNA was extracted from the activated sludge sample using the FastDNA Soil Spin Extraction Kit produced by MP Biomedicals in the United States. Concentration and purity of total genomic DNA.
[0025] 2. PCR amplification of amoA gene
[0026] Configure the PCR reaction system to be 30 μL. First, calculate the content of each component according to the sample, and then add Taq enzyme, MgCl 2 , forward and reverse primers, deoxyribonucleotide dTNP and sterile double distilled water were added to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube in sequence, and centrifuged at low speed to mix them evenly. Divide the above reaction system into individual PCR reaction tubes, then add the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com