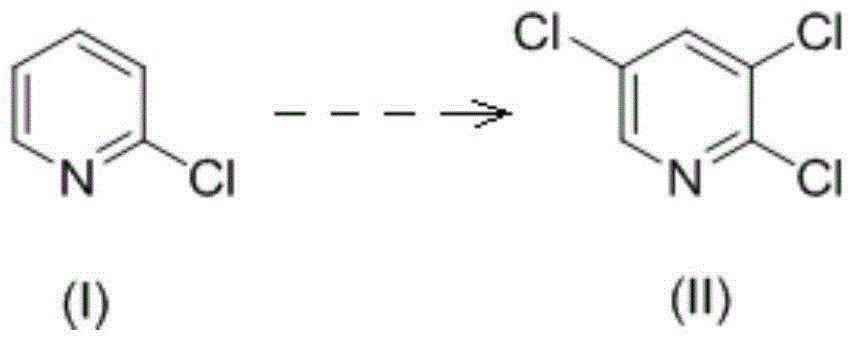
Synthetic method of 2, 3, 5-trichloropyridine
A triclopyridine and synthetic method technology, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve problems such as complex operation, large investment in reaction equipment, and many by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
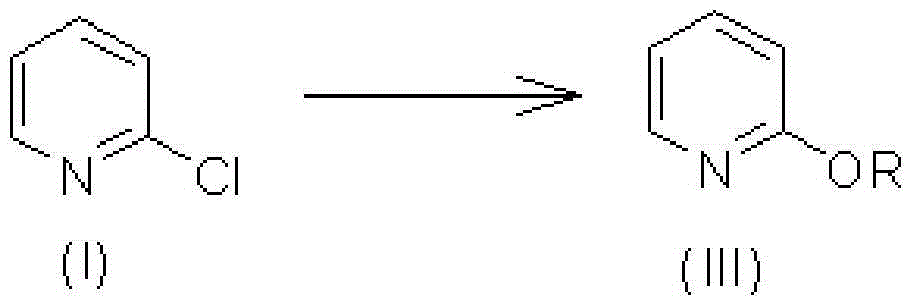
[0035] Embodiment 1: the hydrolysis reaction of 2-chloropyridine generates 2-alkoxypyridine
[0036] Hydrolysis (alcohol) reaction of 2-chloropyridine: under heating or reflux, raw material (I) reacts with water or alcohols under base catalysis to generate intermediate (III).
[0037]
[0038] Here, the R group can be H or methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl and other straight-chain or branched-chain alkyl groups with 5 to 8 carbons. The reaction temperature ranges from 60°C to the boiling point of various solvents, and generally does not exceed 100°C. Considering the suitable temperature of the alcoholysis reaction and the recovery of chlorinated alkanes produced by the subsequent reaction, the preferred alcohol is n-butanol or isopropanol, and the preferred molar ratio of alcohol to raw material is 3.0-10.0. General alkali metal and alkaline earth metal hydroxides can promote this reaction, the preferred base is NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH) 2Wait. The molar ratio of the...
Embodiment 2
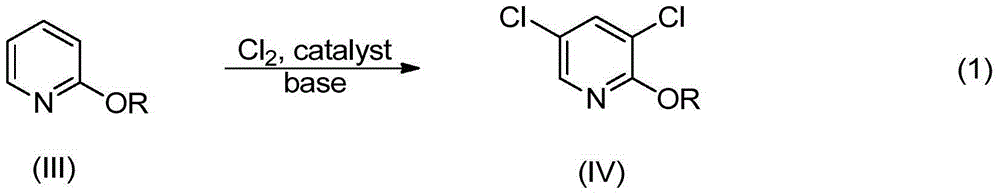
[0039] Example 2: Chlorination of 2-alkoxypyridine to obtain 3,5-dichloro-2-alkoxypyridine
[0040]
[0041] 2-Alkoxypyridine (III) can be reacted with various suitable chlorinating agents such as chlorine gas, alkali metal (such as sodium, potassium, etc.) hypochlorite or a mixture of hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide. The preferred chlorinating agent of the present invention is chlorine gas, and the molar ratio of chlorine gas to substrate (III) is 2.5-4. The catalyst used in the reaction of the present invention is simple substance iodine, and the consumption amount of the catalyst is 0.1 mol% to 2 mol% of the substrate. In the absence of a catalyst, the rate of the chlorination reaction was slightly reduced. The alkali used in the chlorination reaction can be alkali metal, alkaline earth metal oxide, hydroxide, carbonate and organic amine, such as MgO, CaO, NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH) 2 , Na 2 CO 3 , K2CO 3 , CaCO 3 , NaHCO 3 . The preferred base of the present inve...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: 3,5-Dichloro-2-alkoxypyridine Vielsmeyer-Haack Chlorination
[0044]
[0045] 3,5-Dichloro-2-alkoxypyridines were chlorinated by the well-known Vielsmeyer-Haack. Phosphorus oxychloride, thionyl chloride or oxalyl chloride is used as the chlorine source, and DMF is used as the catalyst. During the implementation of the present invention, it was found that phosphorus oxychloride would cause partial decomposition of the substrate during the reaction. However, using thionyl chloride and oxalyl chloride as the chlorination agent can make the reaction proceed under mild conditions, effectively avoiding the decomposition of the substrate, and significantly improving the yield. Generally, the molar ratio of the chlorinating agent to the substrate is 3-15, preferably 5-10, and the amount of catalyst dimethylformamide is 0.01-0.1 mol%. The reaction is carried out in the temperature range of 50-80°C, and the progress of the reaction is detected by GC. The complete ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com