Ceramic 3D printing method
A 3D printing and ceramic technology, applied in the direction of ceramic molding machines, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of expensive equipment, high requirements for ceramic substrates, ceramic performance impact, etc., to reduce the research and development cycle and cost, low equipment cost, relative density high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
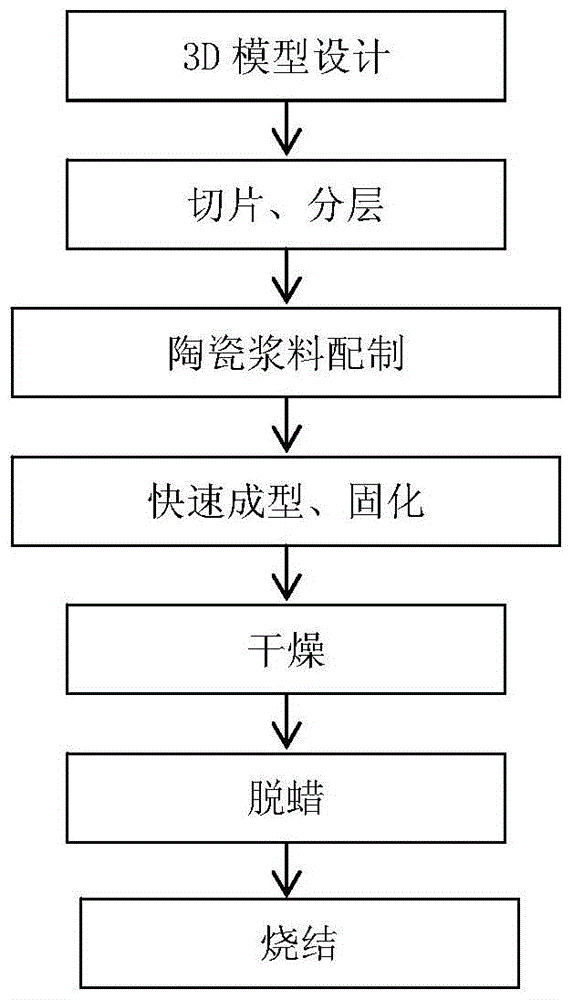
[0029] Such as figure 1 Shown, processing step of the present invention comprises:
[0030] 1) Establishment of 3D model. According to actual needs, use Pro / E or AutoCAD software to construct the 3D model of the part, and convert the 3D model data into an STL format file;
[0031] 2) Use the layering software of the rapid prototyping machine to layer the 3D model, and import the layered data into the manufacturing program;
[0032] 3) Take 250g of reaction-bonded silicon carbide raw material powder (mixed carbon powder and α-SiC at a mass ratio of 1:4-99), 0.306g of ammonia water, 40g of deionized water and stir for 30min, then add 1.8g of tributyl phosphate, 1.5 g gelatin, milled in a high-speed ball mill for 2 hours;
[0033] 4) Defoam the ball-milled slurry for 10 minutes in a vacuum defoaming machine at -0.08MPa vacuum;
[0034] 5) Put the defoamed slurry in the barrel of a rapid prototyping machine (preferably a motor-driven micro-injection 3D printer), start heating ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the ceramic powder used in step 3) is alumina ceramic powder, the curing agent is agarose, and the sintering in step 8) is: heating from room temperature at a rate of 2°C / min to 500°C, then raise the temperature to 800°C at a rate of 10°C / min, and then raise the temperature to 1700°C at a rate of 8°C / min and hold for 2 hours. The obtained alumina ceramics have a sintered density of 3.85 g / cm 3 above.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the ceramic powder used in step 3) is zirconia ceramic powder, the curing agent is organic monomer acrylamide and crosslinking agent methylenebisacrylamide, and in step 8) Sintering: from room temperature to 500°C at a rate of 2°C / min, then to 800°C at a rate of 10°C / min, and then to 1460°C at a rate of 8°C / min for 3 hours to obtain a zirconia ceramic The sintered density is 5.55 g / cm 3 above.
[0042] The present invention is based on the 3D printing molding technology for preparing ceramic parts. By adding a curing agent to the water-based ceramic slurry, rapid prototyping is performed in a 3D printer, and ceramic materials of desired shape are obtained through drying, dewaxing and sintering. The basic principle of the present invention is to use the gel curing characteristics of water-soluble gel substances, add a certain amount of gel curing agent to the water-based ceramic slurry, and vacuum defoam after ba...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com