Method for selectively removing Fe<2+> and/or Fe<3+> from industrial waste water through electric adsorption technology
An industrial wastewater, electro-adsorption technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of no secondary pollution, low cost, and convenient and quick recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
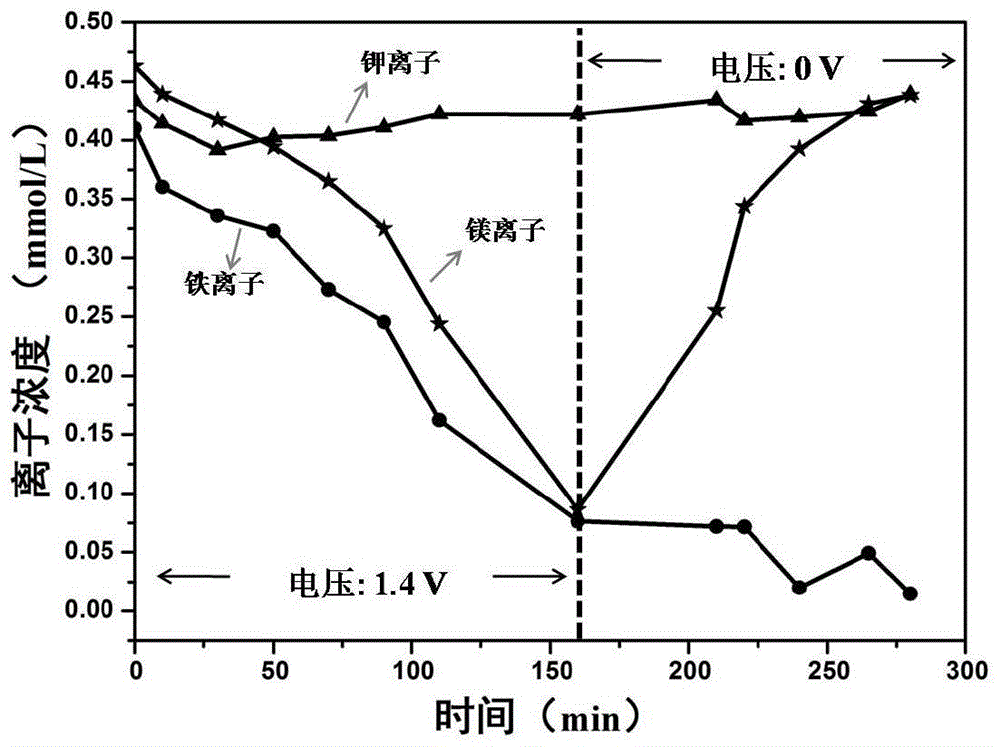
[0024] a. Configure a multi-cation mixed solution to simulate industrial wastewater: take 16mg of potassium chloride, 44mg of magnesium chloride hexahydrate and 58mg of ferric chloride hexahydrate and three metal chloride salts in a 500ml volumetric flask, add deionized water to balance to the scale Wire. The molar concentration of each metal ion is 0.4mmol / L-0.5mmol / L, and the measured electrical conductivity of the above-mentioned simulated wastewater is 200 microSiemens / cm-300 microSiemens / cm;
[0025] b. Take 100ml of the polycation mixed solution of step a into a beaker and set aside;
[0026] c. Mix the nitrogen-doped nano-microporous carbon material, conductive carbon black and binder in a ratio of 80:15:5 by mass, then dissolve in an equal mass of absolute ethanol and ultrasonically form a suspension, and suspend the The liquid is evenly dropped on the current collector as a working electrode, wherein the current collector can be graphite paper or titanium sheet, and ...
Embodiment 2
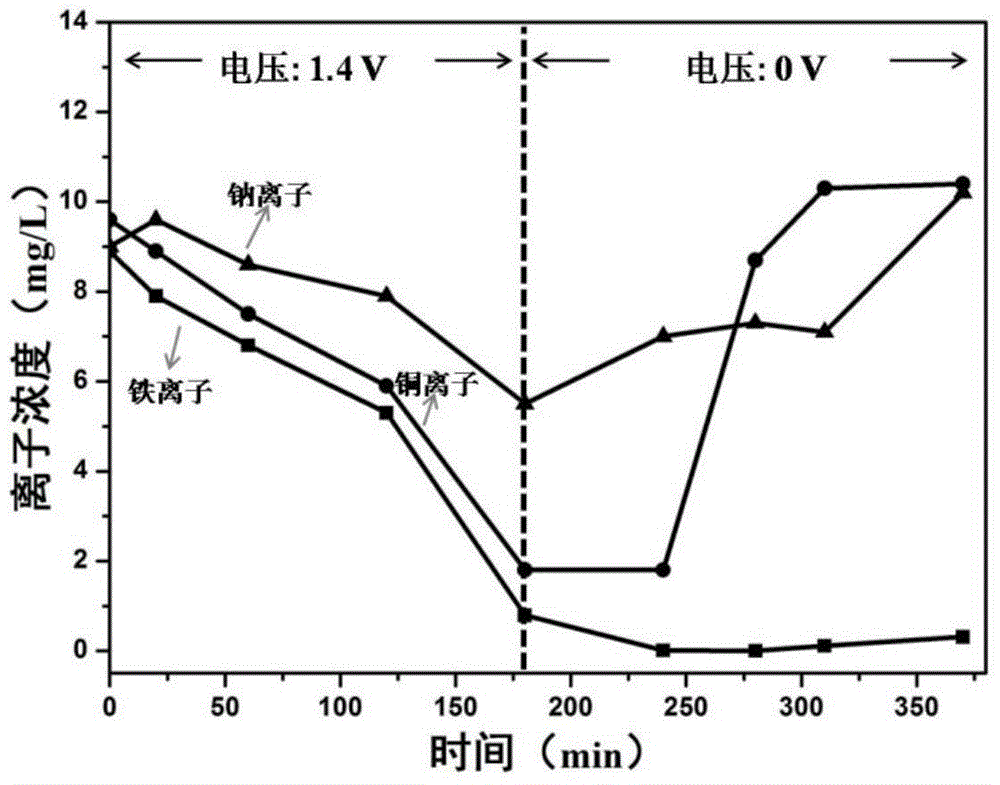
[0030]Referring to the method in Example 1, the substances in the multication mixed solution configured in Example 1 step a are changed to 63.5mg sodium chloride, 67.1mg copper chloride dihydrate, 72.6mg ferric chloride hexahydrate and 35.6mg tetrachloride Ferric dichloride hydrate Four metal chloride salts, Na + 、Cu 2+ And the mass concentration of total iron ions is 9mg / L-10mg / L. Obtain the curve graph of the concentration of various metal ions in the multi-cation mixed solution changing with time during the adsorption and desorption process, such as figure 2 shown.
[0031] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that in the adsorption stage, the adsorption rate of total iron ions is higher than that of Na + and Cu 2+ , while in the desorption stage, almost all of the Na adsorbed to the electrode material + and Cu 2+ All of them are desorbed and returned to the multi-cation mixed solution, while the total iron ions have not been desorbed and remain in the material, so as...
Embodiment 3
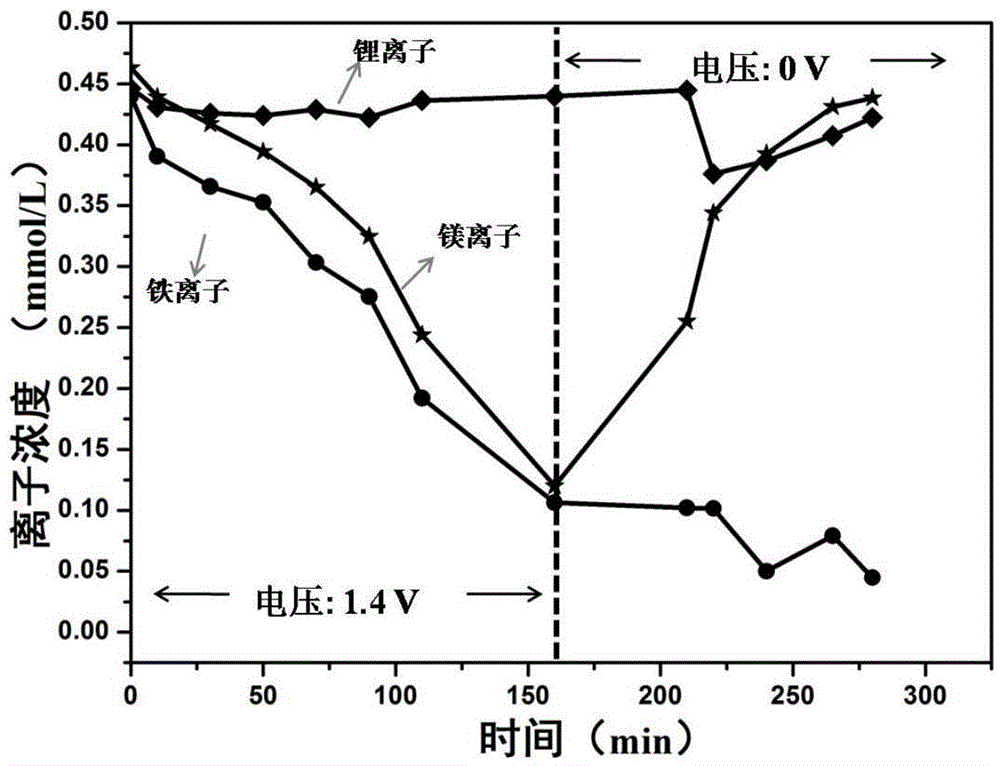
[0033] Referring to the method in Example 1, the material in the multication mixed solution configured in Example 1 step a is changed to three metal chloride salts of 9mg lithium chloride, 44mg magnesium chloride hexahydrate and 58mg iron trichloride hexahydrate, each metal The ion molar concentration is 0.4mmol / L-0.5mmol / L. Obtain the curve graph of the concentration of various metal ions in the multi-cation mixed solution changing with time during the adsorption and desorption process, such as image 3 shown.
[0034] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that during the adsorption stage, Fe 3+ The adsorption rate is higher than that of Li + and Mg 2+ , while in the desorption stage, almost all Li adsorbed into the electrode material + and Mg 2+ are desorbed back into the multi-cation mixed solution, while Fe 3+ has not been desorbed and remains in the material, thus reaching the Fe 3+ separation from other ions.
[0035] In the present invention, the nitrogen-doped nan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com