A genetically engineered bacterium that weakens the accumulation of acetic acid in the fermentation process to enhance the production of l-tryptophan and its construction method
A fermentation process, tryptophan technology, applied in the fields of metabolic engineering and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increasing costs, difficult to achieve dissolved oxygen conditions, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing specific activity, shortening transformation time, and increasing production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Cloning of wild-type phosphate acetyltransferase gene and construction of recombinant strains
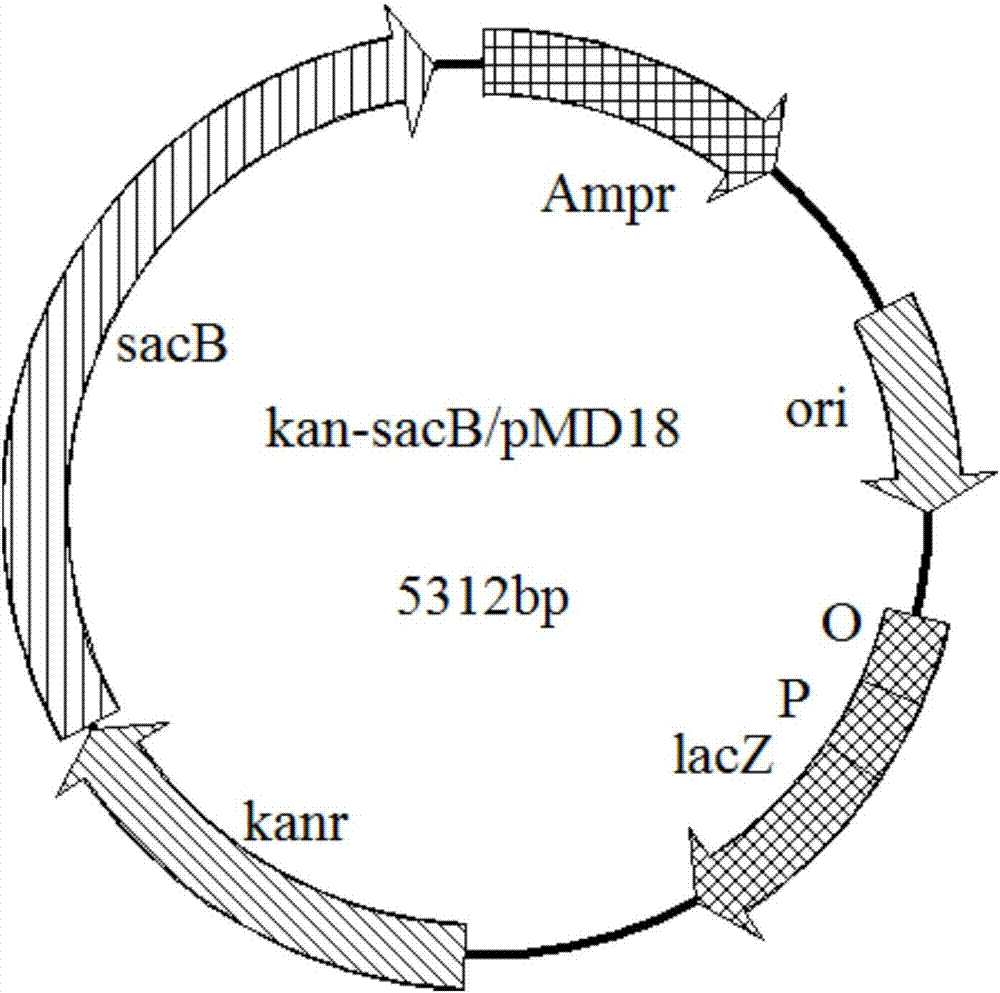
[0023] Using the gene sequence encoding phosphate acetyltransferase (Genbank accession number NC_000913.3: 2414747-2416891) as a template, the amplification primers P1 and P2 were designed to amplify the phosphoacetyltransferase gene pta by PCR and cloned into the pMD18 vector ( commercial tool vector), the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109, and the transformation product was coated on an LB plate containing 100 mg / L ampicillin. After culturing overnight at 37°C, colonies were selected and inserted into LB liquid medium. After 8-10 hours, the plasmid was extracted and named pta / pMD18, and the plasmid was sequenced. The results showed that the inserted fragment was a 2145bp DNA fragment encoding a protein containing 704 amino acids. The pET24a(+) plasmid and the T vector containing the pta gene were subjected to double enzyme digestion wi...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: the preparation of mutant
[0029] 1) Construction of mutants
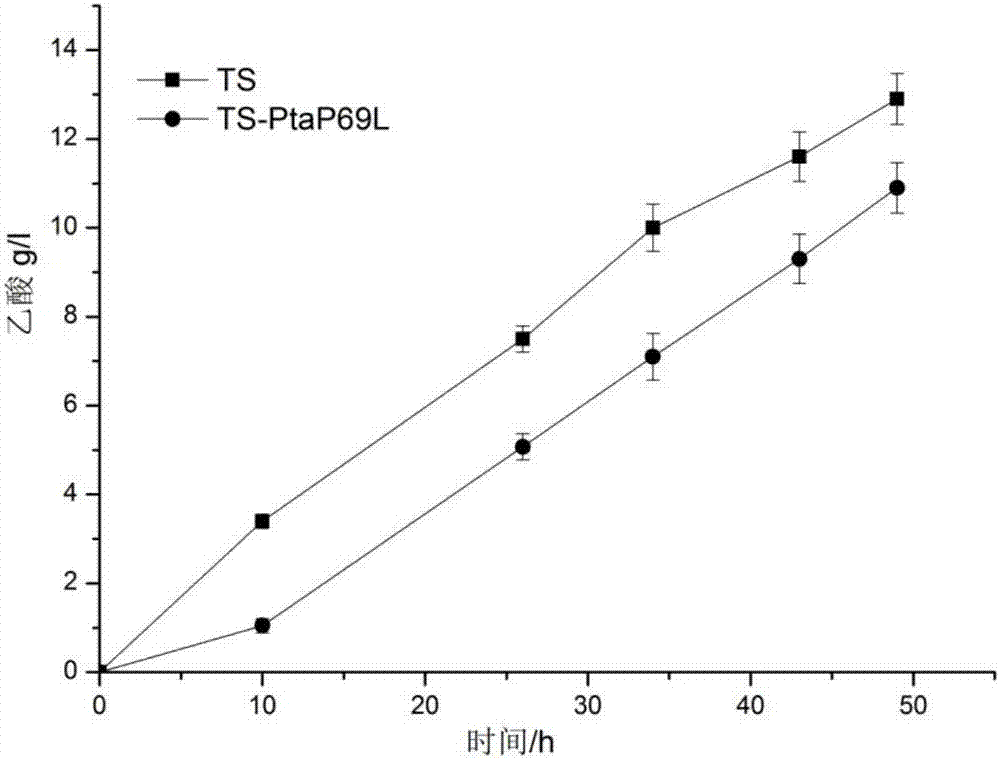
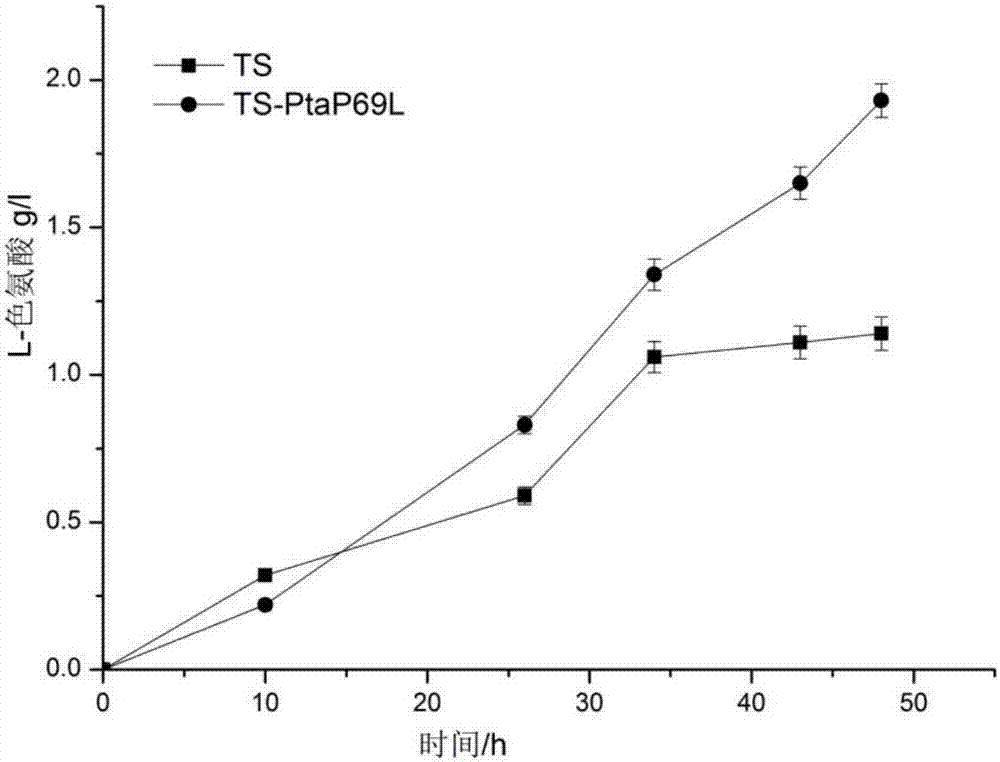
[0030]Simulated the protein structure of phosphate acetyltransferase derived from the L-tryptophan producing strain (recombinant E. An amino acid site Pro69 in the acetyltransferase molecule has a potential effect on the stability of the hexamer of the enzyme. The 69th proline (Pro) in the phosphoacetyltransferase was mutated into leucine (Leu), named P69L. According to the gene sequence encoding phosphate acetyltransferase (Genbank accession number NC_000913.3: 2414747-2416891), primers R1 and R2 introducing the P69L mutation were designed and synthesized, and the plasmid pta / pET24a(+) was used as a template to transfer phosphoacetyl Site-directed mutagenesis of the enzyme gene. The PCR product was digested with Dpn I (Fermentas Company), and transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells. After the competent cells were cultured overnight in LB solid medium (containing 30 μg / mL ka...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: DTNB chromogenic method measures the enzyme activity of phosphoacetyltransferase
[0039] 1) Enzyme activity assay method
[0040] The enzyme activity of phosphate acetyltransferase was determined by 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) colorimetric method. At 25°C, phosphoacetyltransferase catalyzes the substrate acetyl coenzyme A to produce coenzyme A, and coenzyme A reacts with DTNB to produce a yellow substance with an absorbance value at a wavelength of 412nm. The amount of coenzyme A is directly proportional, so colorimetry can be performed at a wavelength of 412nm to calculate the enzyme activity. Definition of enzyme activity unit: under the above conditions, the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the production of 1 μmol of coenzyme A per minute is regarded as an activity unit.
[0041] Enzyme activity assay steps: at 25°C, add 850ml 0.1mol / L pH=7.4 phosphate buffer, 50ml 1.6mmol / L DTNB, 50ml 4mmol / L acetyl-CoA (DTNB solution) to 1ml cuvette ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com