Raw starch expansion treatment and enzyme glycosylation method
A technology of swelling treatment and raw starch, which is applied in the fields of food processing and bioenergy, which can solve the problems of combination limitation and reduce the hydrolysis rate of granular starch, and achieve the effects of improving efficiency, reducing investment cost of process equipment, and reducing demand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 The method for characterizing each parameter
[0029] a Determination of expansion coefficient:
[0030] The expansion coefficient of starch was determined according to the tester and Morrison's blue dextran dye exclusion method. Add cornstarch (100mg, dry basis) into a 10ml special tube, and add 5mL of water, keep it at a certain temperature, keep it warm in a sealed tube, shake it in a water bath for 30min, then add 0.5mL of blue grape Polysaccharide solution (5mg / mL), mixed with the reaction solution and gently vortexed to mix. Centrifuge at 5000×g for 5 min, and measure the absorbance of the supernatant at 620 nm. The absorbance of the assay tube was measured without starch.
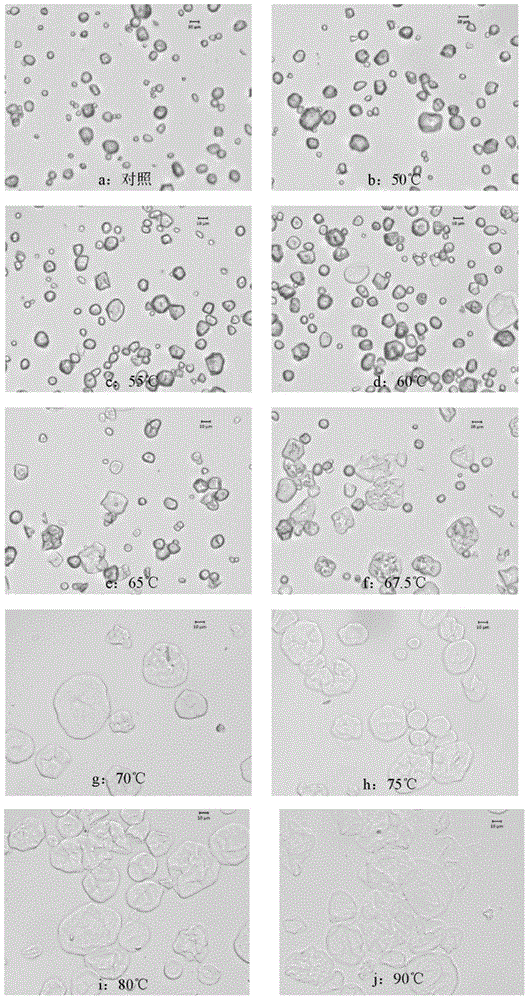
[0031] Light microscopy characterization of b-starch:
[0032] Starch is added to water to make starch slurry, heated in a water bath at a specific temperature for 30 minutes and shaken constantly. Starch slurry without heat treatment was used as a control. Starch samples we...
Embodiment 2
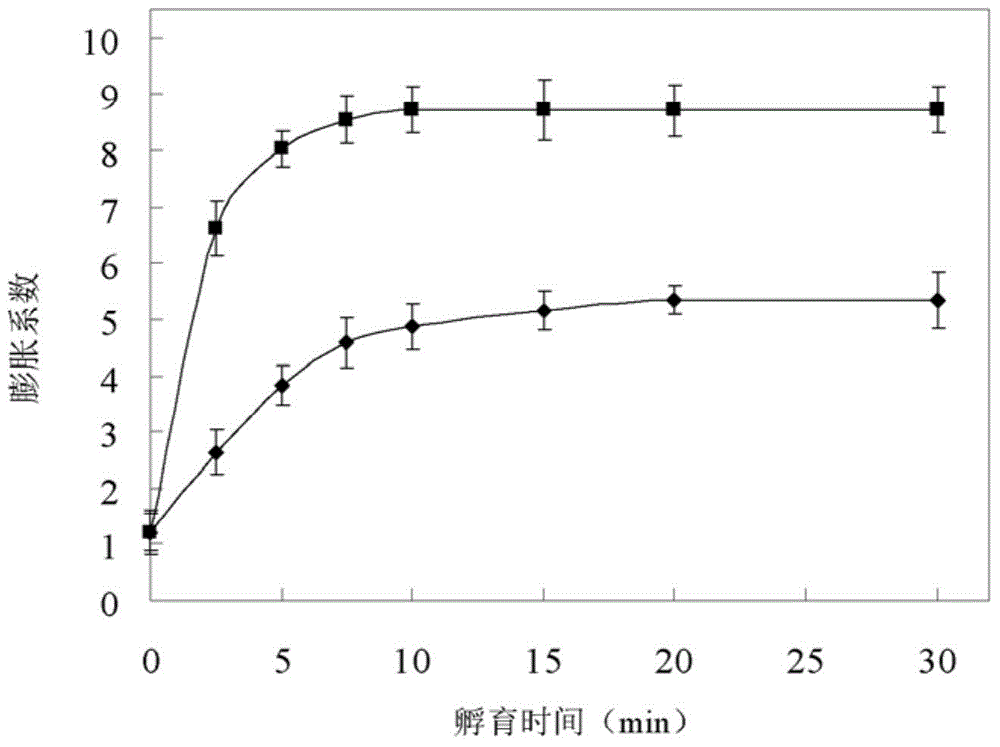
[0042] Example 2 Raw starch is analyzed by enzymatic kinetic parameters of enzymatic hydrolysis with raw amylase after heat treatment at different temperatures
[0043] In this example, cornstarch was purchased from National Starch Company (Bridgewater, NJ); raw amylase StarGen 001 was purchased from Genencor (Palo Alto, CA); blue dextran was obtained from Dextran Sugar (average molecular weight about 2×10 6 ) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO); other chemicals were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Santa Clara, CA).
[0044] Take 0.05-1g of the above-mentioned cornstarch, place them in 100g of 50mM citrate buffer solution (pH 4.2), configure and mix to obtain cornstarch slurry with a weight content of 0.05-1%, and prepare the cornstarch slurry at 50 , 55, 60, 65, 67.5, 70, 75, 80, 90°C and heated in a water bath for 30 minutes, and the starch slurry without heat treatment was used as a control, and was shaken constantly. Then, 0.05 mL of 100-fold diluted enzyme (Star...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The expansion coefficient of embodiment 3 raw starch after heat treatment at different temperatures
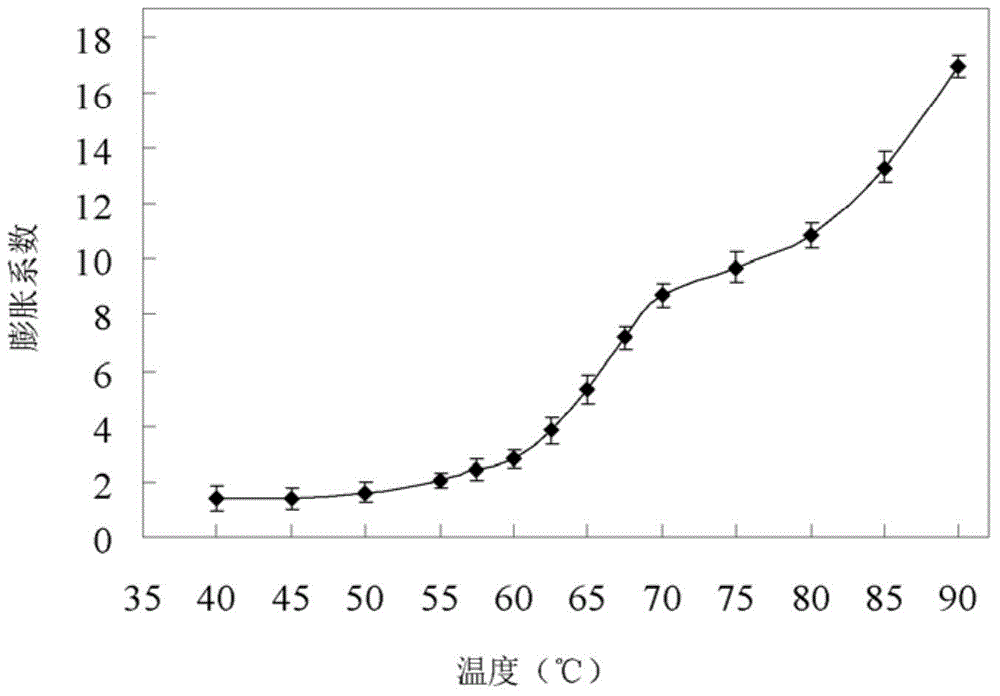
[0052] Select the cornstarch 100mg (dry basis) used in the embodiment 2 for use, add 5ml pure water. The starch slurry was heat-treated at 40, 50, 58, 60, 65, 67.5, 70, 75, 80, and 90°C for 30 minutes, and then the expansion coefficient was measured according to the method described in Example 1. Measurement results such as figure 1 shown.
[0053] In this example, the expansion coefficient of common corn starch granules is studied in the temperature range of 40-90°C. Such as figure 1 As shown, there is very little expansion at 40-50°C; the expansion coefficient is only slightly increased at 50-60°C, but when the temperature is higher than 60°C, the expansion coefficient increases significantly. It is well known that ordinary cornstarch begins to gelatinize at 58 °C, and above 58 °C, the granules swell significantly, resulting in the disappearance of crystallization...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com