Application of GmbHLH transcription factor in promotion of synthesizing soy isoflavone
A technology of soybean isoflavones and transcription factors, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards of gene metabolites, and achieve the effect of increasing soybean isoflavone content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: Cloning and sequence analysis of GmbHHLH3a gene
[0034] Extraction of soybean RNA and synthesis of cDNA: RNAiso Plus (purchased from TaKaRa Company) was used to extract the total RNA of soybean Jilin 32 grain development for 30 days, and M-MLV reverse transcriptase (RNase H - ) (purchased from TaKaRa) for reverse transcription to synthesize the first cDNA.
[0035]Design and synthesis of primers: The sequences (completed by BGI) of immature embryo expression profiles of soybean variety Jilin 32 at three stages (20, 30 and 50 days) were input into phytozome10.1 for Blast comparison, and a sequence with The complete cDNA sequence of bHLH3-like with higher protein sequence homology of bHLH transcription factor in plants. According to the obtained cDNA sequence, its nucleotide sequence is as described in Sequence No.1, design synthetic primers, GmbHLH3a-RT-F: 5'-CGCCAAATCACAATACCC-3', GmbHLH3a-RT-R: 5'-GCCACTTAACCTACAAGACAGA-3 '. Using the above cDNA as a ...
Embodiment 2
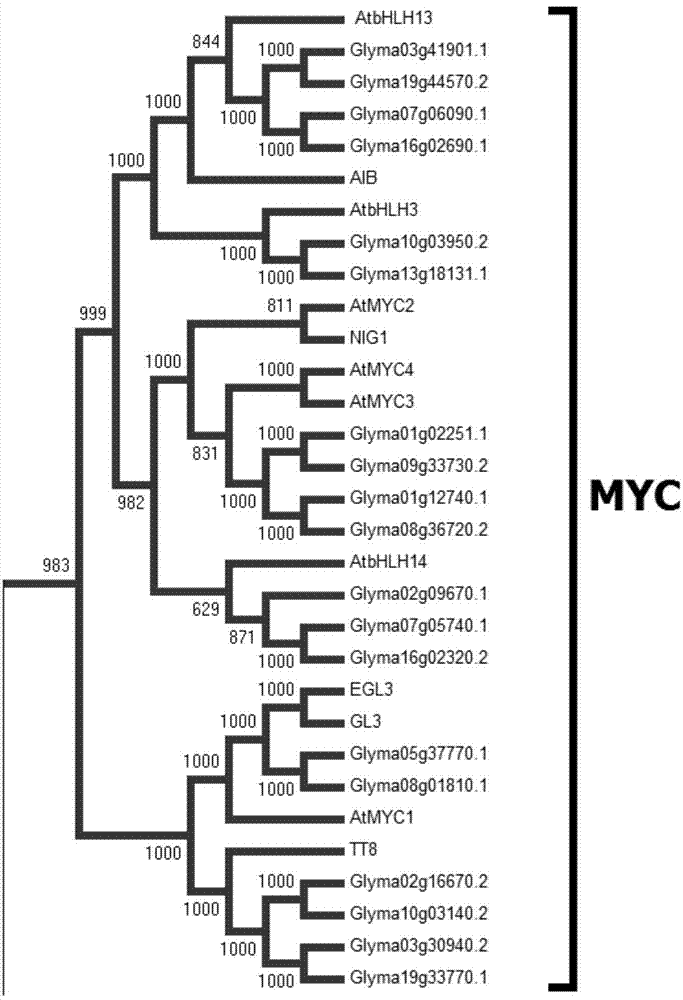
[0037] Embodiment 2: Phylogenetic tree analysis of GmbHHLH3a gene
[0038] According to the soybean bHLH transcription factor and Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factor data published in the plantTFDB online database, the two sets of data were synthesized using ClustalW2 software to generate an unrooted evolutionary tree, and MEGA 6.0 was used to classify and mark the subfamily of the evolutionary tree (the classification scheme refers to 2001 The taxonomic content of Ralf Stracke's article) derived soybean and Arabidopsis MYC-like transcription factor families. The obtained MYC transcription factors were blasted in the NCBI database to detect relevant research information. Change the names related to Arabidopsis or soybean transcription factors to published research names to better understand the homology and functional analysis of the GmMYC gene corresponding to the AtMYC transcription factor.
[0039] After analysis, 19 soybean MYC transcription factors (such as figure 2 ...
Embodiment 3
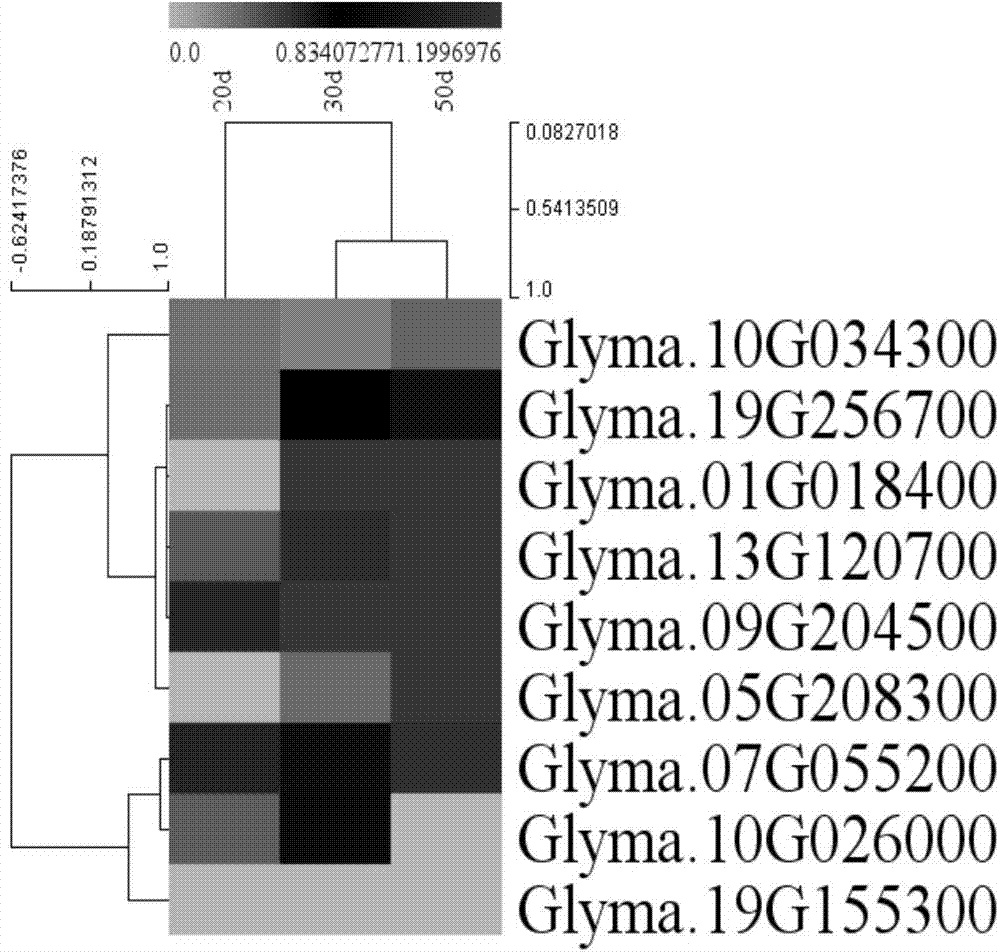
[0040] Embodiment 3: soybean bHLH-MYC class transcription factor gene grain development period expression pattern
[0041] The sequence obtained by sequencing the expression profile of immature embryos of soybean variety Jilin 32 at three stages (20, 30 and 50 days) was used to screen out the relevant MYC transcription factors using perl language. The cluster analysis of gene expression patterns using MeV found that 9 soybean MYC transcription factors were expressed, and the expression of MYC2 transcription factor that activated DFR gene expression decreased, while the transcription factors such as GmbHLH3 and GmbHLH13 that inhibited DFR gene expression were expressed during grain development significantly increased (e.g. image 3 ).
[0042] This result is highly consistent with the result that the accumulation rate of isoflavones in the soybean grain development period is greatly increased from 30 days to 50 days.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com