Method for extracting selenium from mercury-selenium acid mud waste
A technology for selenium acid sludge and waste, which is applied in the field of selenium extraction, can solve the problems of difficult extraction, complex production process, low recovery rate, etc., and achieves the effect of easy operation and simple equipment requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
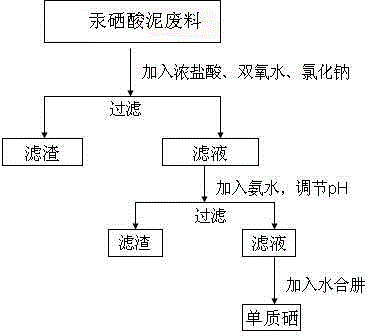
[0018] (1) Mix 20.03 g of the dried mercury-selenide mud waste with 3 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 50 ml of deionized water, 40 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide and 2 g of sodium chloride, and stir at room temperature for 3 h;
[0019] (2) Filtration and separation to remove insoluble impurity solids and collect the filtrate;
[0020] (3) Add 15 ml of ammonia water with a mass fraction of 30% to the filtrate, adjust the pH to about 8, and precipitate a white solid;
[0021] (4) After reacting at room temperature for 1 h, filter to remove the white solid impurities to obtain a light blue filtrate;
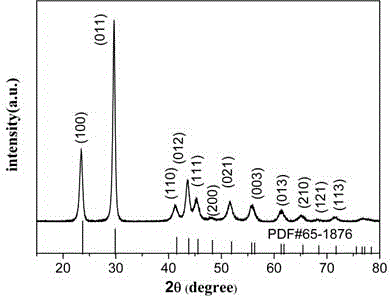
[0022] This white solid impurity is analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and is consistent with the standard card of product and aminomercuric chloride, Such as figure 2 shown.
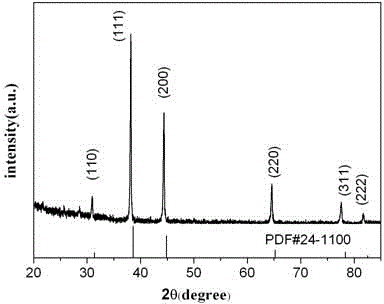
[0023] (5) The filtrate was reduced with 8 ml of hydrazine hydrate with a mass fraction of 80%, and selenium was precipitated from the solution, stirred at room temperature for 1 h, washed and ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Mix 20.09 g of the dried mercury-selenide mud waste with 5 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 50 ml of deionized water, 40 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide and 2.0 g of sodium chloride, and stir at room temperature for 3 h;
[0027] (2) Filtration and separation to remove insoluble impurity solids and collect the filtrate;
[0028] (3) Add 15 ml of ammonia water with a mass fraction of 30% to the filtrate to adjust the pH to about 8.5,
[0029] Precipitated white solid;
[0030] (4) After reacting at room temperature for 1 h, filter to remove the white solid impurities to obtain a light blue filtrate;
[0031] (5) The filtrate was reduced with 8 ml of hydrazine hydrate with a mass fraction of 80%, the simple selenium was precipitated from the solution, stirred at room temperature for 1 h, washed and dried to obtain 5.0 g of selenium;
[0032] The content of selenium waste was tested by plasma emission spectroscopy to obtain a selenium content of 26%, and the seleni...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Mix 20.42 g of dried mercury-selenide mud waste with 8 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 50 ml of deionized water, 50 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide and 2.0 g of sodium chloride, and stir at room temperature for 4 h;
[0035] (2) Filtration and separation to remove insoluble impurity solids and collect the filtrate;
[0036] (3) Add 20 ml of ammonia water with a mass fraction of 30% to the filtrate, adjust the pH to about 9, and precipitate a white solid;
[0037] (4) After reacting at room temperature for 1 h, filter to remove the white solid impurities to obtain a light blue filtrate;
[0038] (5) The filtrate was reduced with 8 ml of 80% hydrazine hydrate, the selenium element was precipitated from the solution, stirred at room temperature for 1 h, washed and dried to obtain 5.3 g of selenium;
[0039] The content of selenium waste was tested by plasma emission spectroscopy to obtain a selenium content of 27%, and the selenium element was tested by chemical tit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com