Lipase CALB mutant and preparation method and application thereof
A mutant and lipase technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as enzyme instability, inferior color, substrate water insolubility, etc., achieve high expression activity and realize the effect of mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Construction of lipase CALB mutant library
[0027] 1. Amplify the gene calb encoding CALB by Klebsiella sp. that produces lipase;
[0028] 2. Connect the calb gene to the expression plasmid pPICZαA, and the restriction sites are EcoRI and XbaI to obtain the recombinant plasmid pPICZαA-calb;
[0029] 3. Using error-prone PCR technology, using the recombinant plasmid pPICZαA-calb as a template, design primers, and amplify the calb mutant gene;
[0030] 4. The error-prone PCR product obtained in step 3 and the expression plasmid pPICZαA were connected after double digestion with EcoRI and XbaI, and the ligated product was transferred into Pichia pastoris X33 competent cells and coated on bleomycin-resistant (Zec. + ) on the YPD plate, to obtain the constructed recombinant calb gene mutation library;
[0031] 5. The colonies grown on the YPD plate were transferred to methanol-containing tributyrin (Zec + ) plate, place the plate in a constant temperature incub...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Acquisition of lipase CALB mutant gene
[0033] Using 1 μg of the genomic DNA of the high lipase-producing strain of Example 1 as a PCR reaction template, the forward primer calb-F: 5′-AAAAAGAATTCAACAAACACGTCGCTGCTATGCTGACGATGCTTATTA-3′ and the reverse primer calb-R: 5′-AAAAATCTAGAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGTCTTTGAGATTTTGGTCTAAAAAA-3′ were designed, wherein The parts in italics are the restriction sites EcoRI and XbaI respectively. To ensure the correct reading frame, five additional bases are added to the 5' ends of the forward and reverse primers. The PCR reaction was carried out in a total volume of 50 μL. The reaction conditions were as follows: denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min and then start the cycle, then denaturation at 94 °C for 50 s, annealing at 58 °C for 1 min, and extension at 72 °C for 2 min for a total of 30 cycles, followed by extension at 72 °C for 10 min. Take 3 μL of PCR amplification products for verification by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the r...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Construction of expression vector pET-28b(+)-calb
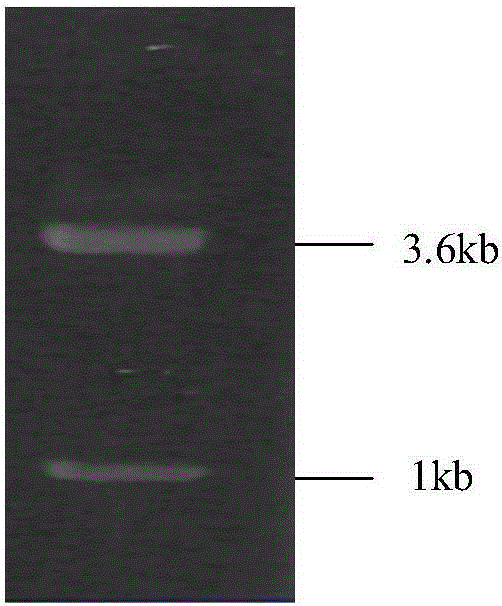
[0035] Gel recovery The PCR product of Example 2 and the pPICZαA vector were digested with EcoRI and XbaI, respectively, and recovered by a gel recovery kit, followed by ligation (16°C, 16h), transformed into DH5α competent cells, and positive clones were selected. After the plasmid was extracted, the enzyme digestion analysis was carried out to verify, and the results were as follows figure 2The nucleotide sequence encoding the CALB mutant of the lipase is shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and the amino acid sequence of the CALB mutant is shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The constructed expression plasmid was named pPICZαA-calb.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com