A kind of method utilizing fixed-bed tubular reactor to produce isopropanolamine
A tubular reactor and isopropanolamine technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as difficult process control, low production efficiency, and many by-products, and achieve process stability , reduce production efficiency, and evenly distribute the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
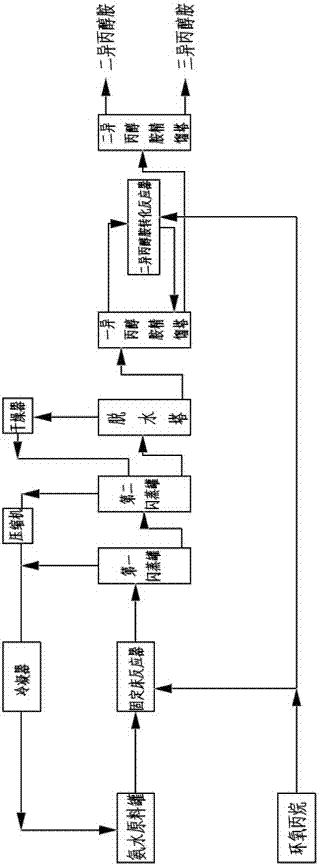
[0036] Such as figure 1 Shown is a method for producing isopropanolamine by using a fixed-bed tubular reactor, and its steps are:
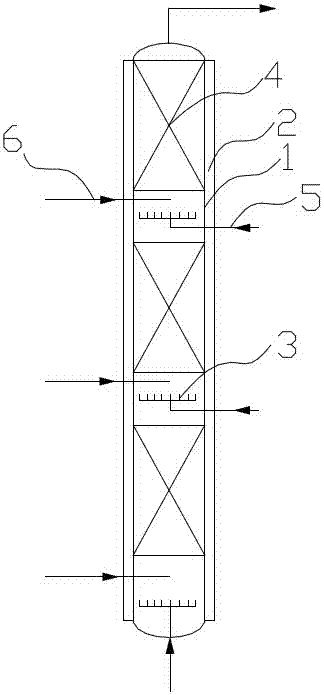
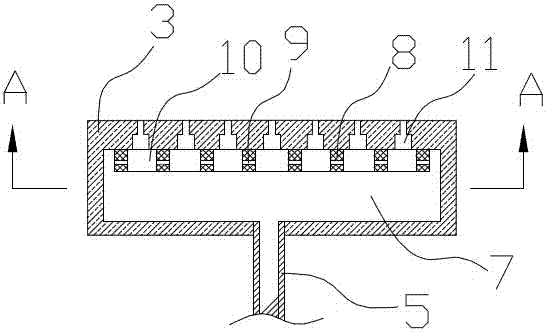
[0037] (A) Using water as a catalyst, mix ammonia and water to form a 90% concentration of ammonia and store it in the ammonia raw material tank. Put the ammonia and propylene oxide into the fixed-bed tubular reactor at the same time to react, the ammonia and propylene oxide The feeding molar ratio of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 3.5:1, the operating pressure of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 8MPa, and the operating temperature of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 160℃. The fixed-bed tubular reactor includes a reaction tube body 1. Jacket 2 (see figure 2 ), a number of propylene oxide feed liquid phase distribution discs 3 are arranged longitudinally in the reaction tube body. The propylene oxide feed liquid phase distribution disc divides the reaction tube body into several reaction zones, and the reaction zone is provided with a filling carrie...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The process flow of this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 1 figure 1 , Fixed bed tubular reactor structure and example 1 Figure 2~4 They are all the same, so I won’t repeat them here. The difference lies in the process parameters of each step:
[0044] (A) Using water as a catalyst, mix ammonia and water to form ammonia water with a concentration of 99.5% and store it in the ammonia water raw material tank. Put the ammonia water and propylene oxide into the fixed-bed tubular reactor at the same time to react, the ammonia water and propylene oxide The molar ratio of the feed is 15:1, the operating pressure of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 25MPa, and the operating temperature of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 220°C.
[0045] (B) The operating pressure of the first flash tank is 18 bar, and the operating pressure of the second flash tank is 1.0 bar.
[0046] (C) Pass the bottom output of the second flash tank into the dehydration tower, and separate water and p...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The process flow of this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 1 figure 1 , Fixed bed tubular reactor structure and example 1 Figure 2~4 They are all the same, so I won’t repeat them here. The difference lies in the process parameters of each step:
[0050] (A) Using water as the catalyst, mix ammonia and water to form 95% ammonia water and store it in the ammonia water raw material tank. Put the ammonia water and propylene oxide into the fixed-bed tubular reactor at the same time to react, the ammonia water and propylene oxide The molar ratio of the feed is 5:1, the operating pressure of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 10MPa, and the operating temperature of the fixed-bed tubular reactor is 180°C.
[0051] (B) The operating pressure of the first flash tank is 12 bar, and the operating pressure of the second flash tank is 0.5 bar.
[0052] (C) Pass the bottom output of the second flash tank into the dehydration tower, and separate water and part of monoisopropanolami...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com