Technology for treating heavy metal waste water through macroalgae
A heavy metal and seaweed technology, applied in filtration treatment, water/sewage treatment, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of cyanobacteria unable to grow or even die, high treatment cost, affecting equipment operation, etc., to increase the effect of wastewater treatment, The effect of facilitating regular replacement and reducing the pollution load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
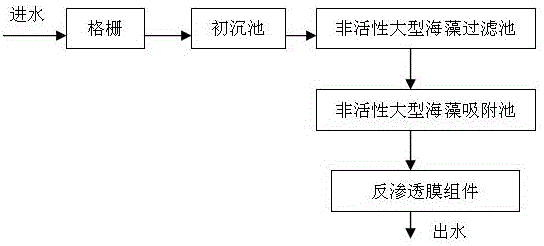
[0034] A process for treating heavy metal wastewater by using macroalgae, comprising the following steps: (1) wastewater pretreatment; (2) treatment in an inactive macroalgae filter pool; (3) treatment in an inactive macroalgae adsorption pool; (4) reverse osmosis membrane The component removes the remaining heavy metal ions (5) and discharges up to the standard.
[0035] The wastewater pretreatment includes grids and primary sedimentation tanks.
[0036] The preparation process for the macroalgae used in the non-active macroalgae filter tank and the non-active macroalgae adsorption pond may further comprise the steps:
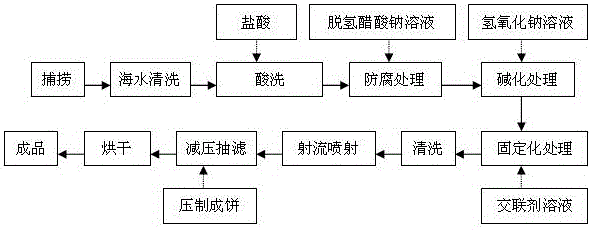
[0037] a. Preprocessing
[0038] Use fishing equipment to catch fresh large seaweed, and use seawater to clean it to remove impurities such as sediment;
[0039] b. pickling
[0040] Utilizing a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass fraction of 5% to soak the macroalgae treated in step a, remove metal ions such as calcium, magnesium, and sodium adsorbed on...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A process for treating heavy metal wastewater by using macroalgae, comprising the following steps: (1) wastewater pretreatment; (2) treatment in an inactive macroalgae filter pool; (3) treatment in an inactive macroalgae adsorption pool; (4) reverse osmosis membrane The component removes the remaining heavy metal ions (5) and discharges up to the standard.
[0052] The wastewater pretreatment includes grids and primary sedimentation tanks.
[0053] The preparation process for the macroalgae used in the non-active macroalgae filter tank and the non-active macroalgae adsorption pond may further comprise the steps:
[0054] a. Preprocessing
[0055] Use fishing equipment to catch fresh large seaweed, and use seawater to clean it to remove impurities such as sediment;
[0056] b. pickling
[0057] Utilizing a hydrochloric acid solution with a mass fraction of 10% to soak the macroalgae treated in step a, remove metal ions such as calcium, magnesium, and sodium adsorbed on ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com