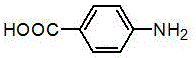
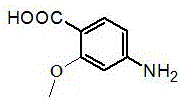
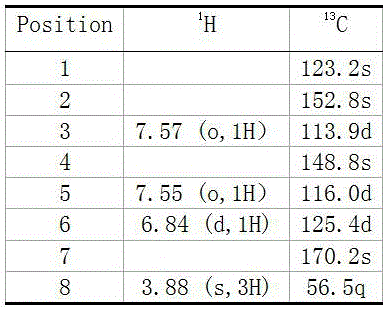
Preparation method of natural para aminobenzoic acid and derivative of natural para aminobenzoic acid
A technology of para-aminobenzoic acid and derivatives, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, and achieve the effects of being environmentally friendly, having a wide range of sources and being easy to industrialize production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0014] The preparation method of natural p-aminobenzoic acid and derivative thereof provided by the invention, its steps are:
[0015] 1) Liquid culture and fermentation product processing: the fungus Termitomyces albuminosus The slant strains were first inoculated in a Erlenmeyer flask containing 150mL potato liquid medium for activation. The activation conditions were 230 r / min, 28°C, and cultured for 7 days. Then, large-scale liquid fermentation was carried out. The medium formula was: : Each liter of water contains 200 g of potatoes, 20 g of glucose, natural pH, 0.1 Mpa, sterilized at 121 ℃ for 30 minutes, and cultured in a constant temperature shaker at 25-28 ℃ and 180-230 r / min. After 15 days of fermentation, the mycelium was separated from the fermentation broth by centrifugation. The fermented liquid was extracted with an equal volume of ethyl acetate, the obtained extract was dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then concentrated in vacuo with a rotary evapo...
Embodiment 1
[0019] Use potato glucose medium (containing 200g of potato per liter of water, 20g of glucose, natural pH, 0.1Mpa, sterilized at 121°C for 30min), and the activated strain Termitomyces albuminosus 37 L of liquid fermentation culture was cultured on a shaker at 28 °C for 15 days. After the bacterial cells were filtered, the fermentation broth was concentrated to 1 L, and the fermentation broth was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate part was dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate and then concentrated to obtain an organic crude extract (3.1 g).
[0020] The 3.1 g organic crude extract obtained in the previous step was fully dissolved in methanol, and subjected to reverse-phase silica gel (170 g) column chromatography, and eluted with 30% methanol water for 2 L at a flow rate of 15 mL / min. Collect 280 mL, concentrate in vacuo with a rotary evaporator, take samples separately for thin-layer chromatography analysis and combine (developing solvent is chloroform:metha...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Use potato glucose medium (containing 200g of potato per liter of water, 20g of glucose, natural pH, 0.1Mpa, sterilized at 121°C for 30min), and the activated strain Termitomyces albuminosus 37 L of liquid fermentation culture was cultured on a shaker at 28 °C for 15 days. After the bacterial cells were filtered, the fermentation broth was concentrated to 1 L, and the fermentation broth was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate part was dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate and then concentrated to obtain an organic crude extract (3.1 g).
[0028] Dissolve 3.1 g of the crude organic extract obtained in the previous step in methanol, perform reverse phase silica gel (170 g) column chromatography, and elute 2 L with 30% methanol water at a flow rate of 15 mL / min. Collect 280 mL, concentrate in vacuo with a rotary evaporator, take samples in separate tubes for thin-layer chromatography detection and combine (developing solvent is chloroform:methanol=10:1, chro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com