[0004] 1. The operation process method of pouring concrete first and then installing wall panels causes the bottom of the wall panels to be unable to be connected as a whole. The steel bars can only be connected through the connection method of steel sleeve grouting. The concrete structure cannot be connected as a whole, forming the overall horizontal joints of the structure, reducing
shock resistance;
[0005] 2. The manufacturing process and installation process of the laminated slab must be poured twice. The concrete integrity of the second pouring is poor and the joint part is prone to hollowing and
cracking quality problems. The second pouring causes the thickness of the floor to increase. The increase in thickness increases the weight and reduces the In order to improve the
earthquake resistance, labor and materials increase the cost;
[0006] 3.
Mortar leveling is necessary for the secondary pouring of the laminated slab, which increases the construction process, and the construction operation is difficult to operate. It is often affected by uncontrollable factors such as manual operation and climate environment, and the quality
controllability is poor;
[0007] 4. The height of a single building is limited, the weight of a
single component of a
solid structure is
overweight, and the
solid component (wall panel / column) cannot realize the integral connection between the upper and lower parts of multiple vertical components;
[0013] 1. Poor component integrity
[0014] 1.1. Wallboard: The outer protective layer of the insulation board is a 60mm thick concrete layer connected by horizontal connectors and structural
layers in point form. It is an independent component and non-integral structure. Earthquakes, etc.) have the potential safety
hazard of loosening and falling off;
[0015] 1.2. Composite
floor slab: The
prefabrication of the floor slab is not a one-time forming and non-integral structure. It needs to be installed on site for secondary pouring and molding. There is a quality risk of hollowing and
cracking, and the increase in weight reduces the
earthquake resistance;
[0016] 2. The integrity of component installation and connection is poor
[0018] 2.2.
Welding connection method: low connection strength, poor integrity and
shock resistance, high
safety risk factor, and gaps in component interfaces cannot be connected into an overall structure;
[0019] 2.3. Reinforcement sleeve grouting connection method: ① few connection points and low connection strength; ② easy
grout leakage affects the connection strength; ③ difficult quality inspection of concealed construction; ; ⑤ The connecting joints of the upper and lower wall panels cannot be effectively combined, and the
structural integrity and seismic performance are poor;
[0020] 2.4. Installation of prefabricated laminated slabs: ①Increased materials (the thickness of laminated slabs is generally greater than the thickness of cast-in-place slabs ≥ 20%), which increases the weight of the building itself and reduces the earthquake resistance; Combining poor integrity issues
[0021] 3. Low self-weight and low earthquake resistance: the secondary pouring of 60mm concrete slabs and floor laminated slabs for the external
thermal insulation protection layer of the wall panels increases the thickness of the floor slabs and is a
solid structure, resulting in a substantial increase in the building's self-weight and reducing the earthquake resistance;
[0023] 4.1. Wall panel connection: The steel sleeve grouting connection method is a concealed construction, which is highly professional, low in technical maturity, has quality hidden dangers such as
grout leakage and maintenance difficulties, and the quality inspection is difficult and uncontrollable, and quality problems occur. Remedial measures are difficult question;
[0025] 4.3. The
prefabrication rate is low, the site construction
workload is large, and there are many uncontrollable factors such as environment, climate, and manual operation;
[0027] 1. Poor integrity of components affects durability:
[0028] 1.1. Wallboard: The outer protective layer of the insulation board is a 60mm thick concrete layer connected by horizontal connectors and structural
layers in point form. It is an independent component and non-integral structure. Earthquakes, etc.) affect the safety
hazard of loosening and falling off, affecting durability;
[0029] 1.2. Floor: There is a quality risk of hollowing and
cracking in the secondary pouring molding, and the increase in weight reduces the shock resistance and affects durability;
[0030] 2. Poor structural connection integrity affects durability
[0031] 2.1.
Bolt connection method: high cost, difficult construction and low connection strength, poor integrity and shock resistance, high safety
risk factor, and gaps between component interfaces cannot be connected into an overall structure, which affects durability;
[0032] 2.2.
Welding connection method: high cost, difficult construction and low connection strength, poor integrity and shock resistance, high safety
risk factor, and gaps between component interfaces cannot be connected into an overall structure, which affects durability;
[0033] 2.3. Reinforcement sleeve grouting connection method: ① few connection points and low connection strength; ② easy
grout leakage affects the connection strength; ③ difficult quality inspection of concealed construction; ; ⑤ The connection joints of the upper and lower wall panels cannot be effectively combined, and the
structural integrity and seismic performance are poor, which affects durability;
[0034] 2.4. Installation of prefabricated laminated slabs: ①Increased materials (the thickness of laminated slabs is generally greater than the thickness of cast-in-place slabs ≥ 20%), which increases the weight of the building itself and reduces the earthquake resistance; Combined with the problem of poor integrity, it affects durability;
[0035] 3. Self-heavy earthquake resistance and low
impact on durability: the secondary pouring of 60mm concrete slabs and floor laminated slabs for the external
thermal insulation protection layer of wall panels increases the thickness of the floor slabs and is a
solid structure, resulting in a substantial increase in the building's own weight, which reduces earthquake resistance and affects durability;
[0037] 4.1. Wall panel connection: The steel sleeve grouting connection method is a concealed construction, which has quality hidden dangers such as grout leakage and maintenance, and the difficulty of quality inspection is high and uncontrollable. It is difficult to take remedial measures for quality problems, which affects durability;
[0038] 4.2. Floor laminated slabs: Secondary large-area pouring of concrete, affected by uncontrollable factors such as the environment, climate, and manual operations, there are quality risks of hollowing and cracking, which affects durability;
[0039] 4.3. The prefabrication rate is low, the site construction
workload is large, and there are many uncontrollable factors such as environment, climate, and manual operation;
[0041] 1. Large
primary energy consumption: 60mm concrete slabs and laminated slabs for the external
thermal insulation protection layer of wall panels need to be installed on site for secondary pouring construction, and the thickness increases and is a
solid structure, resulting in a substantial increase in the main raw materials of concrete and steel bars, resulting in
primary energy Large consumption; (①Increased materials (the thickness of the laminated slab is generally greater than the thickness of the cast-in-place slab ≥ 20%), which increases the weight of the building itself and reduces the earthquake resistance; ②The cost of labor and materials increases; ③The cost of hoisting and transportation increases;)
[0042] 2. The
air tightness of the structural connection is poor, and the effect of energy saving and heat preservation is poor; the thickness of the heat preservation is limited and it is difficult to meet the 75% energy saving standard, and the use cost is high;
[0043] 3. The demolition process of the building needs to be demolished by blasting, and it cannot be disassembled as a whole for secondary recycling. The use cost of the whole life cycle is high and the energy saving is low;
[0048] 4. The demolition process of the building needs to be demolished by blasting, and it cannot be dismantled as a whole for secondary recycling, which has a great impact on the environment;
[0049] Five, low efficiency:
[0050] 1. The wall panel is not equipped with a positioning device, and the installation efficiency is low due to the displacement of the
steel bar;
[0051] 2. The floor laminated slab needs to be poured twice in a large area, and it cannot be installed continuously and the construction efficiency is low;
[0053] 1. High primary
investment cost: 60mm concrete slabs and laminated slabs for the external thermal insulation protection layer of wall panels need to be installed on-site to increase the thickness of the secondary pouring construction and are solid structures, resulting in a substantial increase in the main raw materials of concrete and steel bars, and the amount of materials used The increase will lead to an increase in the cost of labor and materials and the increase in the cost of hoisting and transportation; the use cost of special accessories is high, resulting in a high cost of one-time input;
[0054] 2. Cost of use: poor
air tightness of structural connections, poor energy-saving and thermal insulation effects; 60mm-thick concrete slab for
external wall insulation and maintenance layer, self-weight 150kg / m 2 The thickness of the insulation board is limited (≤100mm) and the energy-saving standard is reduced (it can meet the energy-saving standard of 65%, but it is difficult to meet the energy-saving standard of 75% and above), and the cost of use is high;
[0055] 3. The cost of self-heavy transportation / hoisting is high;
[0056] 4. The small transportation
radius affects business expansion, and the operation and management costs are high;
[0057] 5. The laminated slab needs secondary pouring and cannot be installed continuously, the construction efficiency is low, the construction period is long, and the
time cost is high;
[0060] 1. There is no positioning device installed on the wallboard, and the installation efficiency is low due to the displacement of the
steel bar, which is difficult and difficult to construct;
[0061] 2. Laminated slabs require secondary large-area pouring operations, which are affected by many environmental factors (rain-
proof construction in rainy seasons, and anti-freezing measures in winter construction are difficult and costly), and the construction is poor;
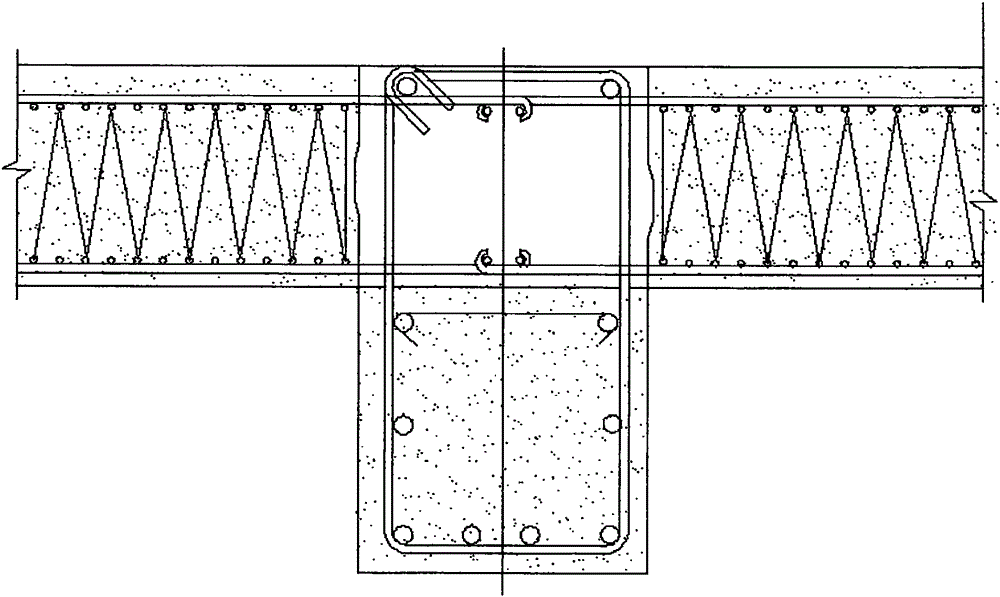
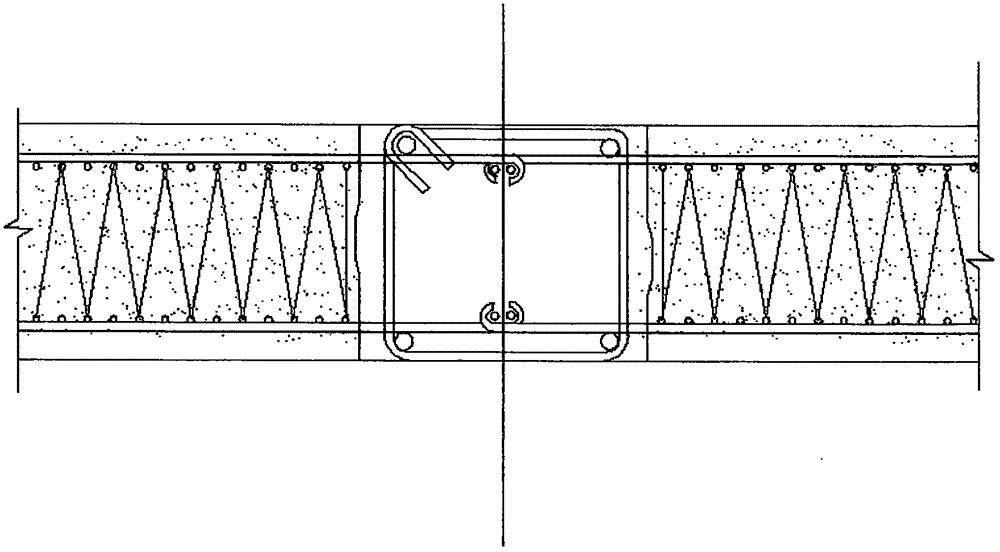
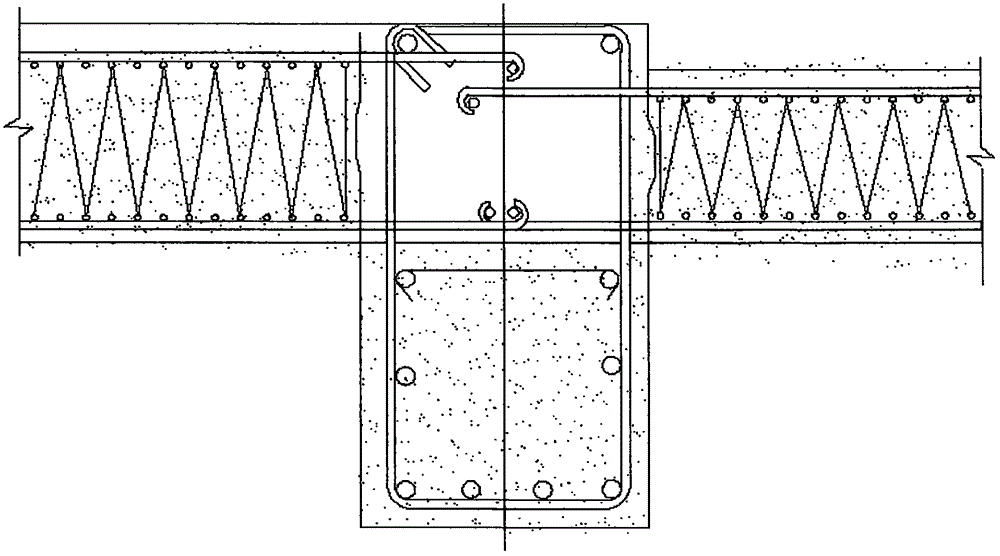
[0062] 3. The height of a single-story building is limited, and the wall panels / columns cannot be connected vertically in multiple pieces;
[0063] 8. Practicability: The increase of the thickness of the laminated board and the increase of its own weight will affect the span of the housing bay, affect the free separation of the use of space and the personalized
layout, and the practicability is poor;
[0064] 9. Promoting: Due to the above technical reasons, problems in safety, durability, energy saving,
environmental protection, economy, efficiency, construction, practicality and other aspects cannot be effectively solved. Now it can only be promoted and applied to the country by government subsidies and support policies. It is used in investment projects. Only state-owned enterprises invest in the investment enterprises. Because of the high investment and high construction costs of private enterprises and insufficient commercial development capacity, it is difficult to promote the application on a large scale, and the promotion is poor;
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More