Nano-diamond surface boronation method
A technology of nano-diamond and boron source, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of low thermal stability and poor anti-oxidation ability, so as to improve anti-oxidation performance and synthesize The effect of simple process and simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
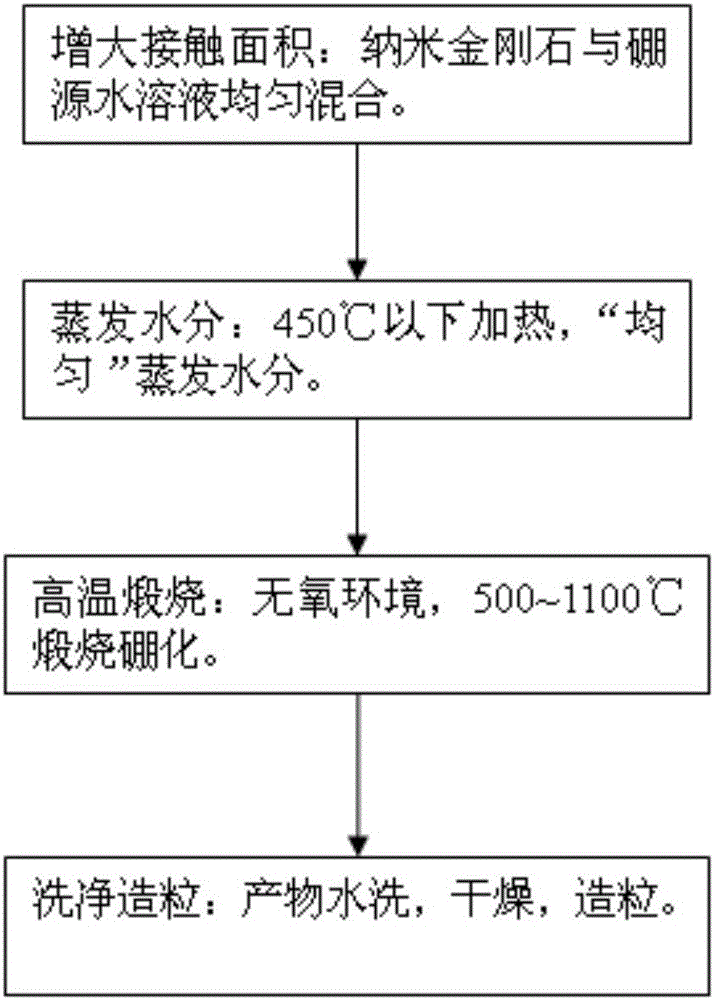
[0029] According to attached figure 1 Technological process. First, 5g of boron oxide (containing 1.57g of boron) was used to prepare an aqueous solution, and 5g of nano-diamonds was weighed and mixed with boric acid aqueous solution (mass ratio of boron to carbon B:C=31.4%). Then, it was slowly heated to 350°C in a muffle furnace to evaporate excess water. Then put the dry matter into a crucible, move to a vacuum furnace, heat to 1000°C, and keep it warm for 20 minutes. The product is taken out, washed with water, dried and granulated to obtain nano-diamond powder with surface boride. Finally, a series of tests and characterizations were carried out on the obtained boride nano-diamond powder.
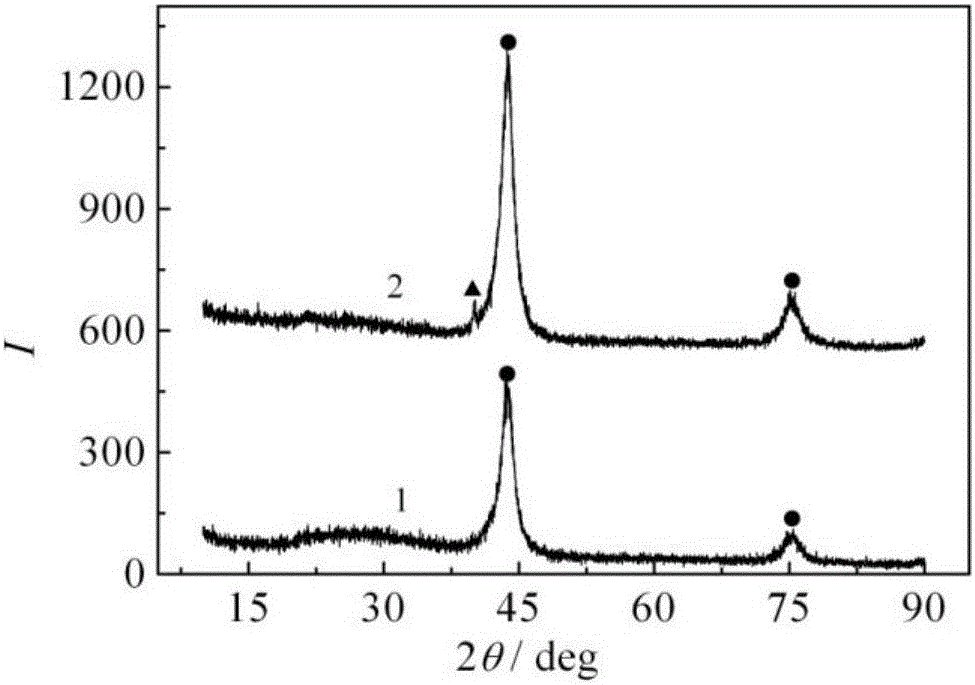
[0030] Such as figure 1 XRD patterns of nano-diamond raw material and boronized nano-diamond, respectively. It can be seen from the figure that the original nano-diamond crystal form is a single cubic diamond (as shown in curve 1), and the borided nano-diamond contains a small amo...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Take 5g of nano-diamond, press B:C=5~100%, and the mass is 2.381~47.625g Na 2 B 4 o 7 10H 2 O water and liquid are mixed evenly, dried at 450°C, moved to a high-temperature sintering furnace, heated to 880-1100°C in hydrogen, and kept at a constant temperature for 20-120min. The product is taken out, washed with water, dried, and granulated to obtain boron similar to Example 1. Nanodiamonds.
[0035] Some physical and chemical properties of borax decahydrate (sodium borate): lose eight molecular crystal water at 60°C, lose all crystal water at 320°C, melting point 741°C, boiling point 1575°C, melting into glass at 878°C, melt Contains acidic oxides (boron oxide).
Embodiment 3
[0037] Take 5g of nano-diamond, according to B:C=5~100%, mix it with 1.525~30.5g of boric acid aqueous solution evenly, evaporate excess water in a horse boiling furnace at 450°C, move it to a high-temperature sintering furnace, and heat it to 500~1100°C under nitrogen protection. The temperature was kept constant for 20-120 minutes, and the product was taken out, washed with water, dried, and granulated to obtain boride nano-diamond similar to Example 1.
[0038] Partial physical and chemical properties of boric acid: Heating to 70-100°C gradually dehydrates to generate metaboric acid, generates pyroboric acid at 150-160°C, generates boric anhydride (boron trioxide) at 300°C, and boric anhydride (boron oxide) is in a molten state at 450°C , 600°C is a very viscous liquid with a boiling point of 1500°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com